Cardiovascular Medicine ECG Interpretation Flashcards
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis?

Anterior STEMI
ST segment elevation with subsequent Q wave formation in precordial leads (V1-6) +/- high lateral leads. These changes are often preceded by hyperacute T waves
Reciprocal ST depression in inferior leads (mainly III and aVF)
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis?

Posterior STEMI
Posterior MI is suggested by the following changes in V1-3:
Horizontal ST depression
Tall, broad R waves (>30ms)
Upright T waves
Dominant R wave (R/S ratio > 1) in V2
Posterior infarction is confirmed by the presence of ST elevation and Q waves in the posterior leads (V7-9).
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis?

Inferior STEMI
Marked ST elevation in II, III and aVF with early Q-wave formation. Reciprocal changes in aVL. ST elevation in lead III > II with reciprocal change present in lead I and ST elevation in V1-2 suggests RCA occlusion with associated RV infarction: This patient should have right-sided leads to confirm this
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis?

Lateral STEMI
High lateral STEMI can present as ST-elevation involving lead I and aVL. Subtle ST elevation in V5, V6 and reciprocal changes in lead III and avF may be present.
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis

Mitral stenosis
- AF
- Bifid p wave/p mitrate
- R axis deviation/tall R waves in lead VI
- RVH
Review the following ECG and give a diagnosis, what would you expect an x-ray to show?

- Mitral reugurg
- ECG – show broad P wave (P mitrale – bifid; 2 peaks due to atrial hypertrophy)
- CXR (cardiomegaly, with enlarged LA and LV)
Review the following ECG and give a diagnosis

Aortic Stenosis
- ECG (LBBB due to calcification, L axis deviation,Next LVH)
Review the following ECG and give a diagnosis what would you expect an X-ray to show?

AORTIC REGURGITATION
- CXR – LV enlargement, enlarged cardiac silhouette and aortic root enlargement
- ECG – signs of LVH = tall R waves, deeply inverted T waves in L-sided chest leads and deep S waves in R-leads
Review the following ECG give a diagnosis, what would you expect an X-ray to show?

DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY (DCM)
-
ECG
- Sinus tachycardia
- T wave inversion + Q waves (even if no previous MI)
- ST-depression
- LBBB
-
CXR
- Cardiomegaly, signs of HF, pleural effusion
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis?

Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis?

Pericarditis
Classical ECG = saddle shaped ST elevation + PR depression
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis
Pericarditis
- ECG changes
- the changes in pericarditis are often global/widespread, as opposed to the ‘territories’ seen in ischaemic events
- ‘saddle-shaped’ ST elevation
- PR depression: most specific ECG marker for pericarditis
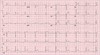
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis

ECG = electrical alternans (pathognomonic variation in R wave amplitude)
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis

AVNRT
ECG:
- Narrow QRS (<120s)
- No visible P waves (hidden by QRS or seen immediately before/after QRS)
- Tachycardia
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis

-
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome = best known type of AVRT
- In WPW there is an accessory pathway (Bundle of Kent) between atria and ventricle
- Resting ECG shows evidence of pathways existence if the path allows some of the atrial depolarisation to pass quickly to the ventricle before it gets through the AVN
- The early depolarisation part of the ventricle leads to shortened PR interval and a delta wave (slurred start to QRS)
- QRS is narrow
- These patients are prone to atrial and occasionally ventricular fibrillation
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis

WPW
Short PR interval (<0.12s)
Wide QRS complex (>0.12s)
Delta wave (slurred upstroke on QRS complex)
left axis deviation if right-sided accessory pathway* = Type Btype B = dominant R wave in V1
negative delta wave in V1 and V2
(majority of cases WPW associated with L axis deviation)
right axis deviation if left-sided accessory pathway* = type Atype A = no dominant R wave in V1
positive delta wave and QRS throughout
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis

AF
Absent p waves
Narrow QRS complex tachycardia
Irregularly irregular ventricular rhythm
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis

Atrial Flutter
Sawtooth appearance (in inferior leads: II, III, aVF)
Narrow QRS
Underlying atrial rate ~300/min (ventricular/HR is dependent on the degree of AV block e.g. if there is 2:1 block, ventricular rate will be 150/min)
Flutter waves may be visible following carotid sinus massage or adenosine
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis

Monomorphic VT
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis

Polymorphic VT
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis
Torsades de Pointes
Torsades de pointes is a specific form of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in patients with a long QT interval. It is characterized by rapid, irregular QRS complexes, which appear to be twisting around the electrocardiogram (ECG) baseline.
Describe the following ECG and give a diagnosis

Heart block
ECG findings in first-degree AV block include:
- Rhythm: regular
- P wave: every P wave is present and followed by a QRS complex
- PR interval: prolonged >0.2 seconds (5 small squares)
- QRS complex: normal morphology and duration (<0.12 seconds)
ECG findings in second-degree AV block (type 1) include:
- Rhythm: irregular
- P wave: every P wave is present, but not all are followed by a QRS complex
- PR interval: progressively lengthens before a QRS complex is dropped
- QRS complex: normal morphology and duration (<0.12 seconds), but are occasionally dropped
ECG findings in second-degree AV (type 2) include:
- Rhythm: irregular (may be regularly irregular in 3:1 or 4:1 block)
- P wave: present but there are more P waves than QRS complexes
- PR interval: consistent normal PR interval duration with intermittently dropped QRS complexes
- QRS complex: normal (<0.12 seconds) or broad (>0.12 seconds)
- The QRS complex will be broad if the conduction failure is located distal to the bundle of His 3
ECG findings in third-degree (complete) heart block include:
- Rhythm: variable
- P wave: present but not associated with QRS complexes
- PR interval: absent (as there is atrioventricular dissociation)
- QRS complex: narrow (<0.12 seconds) or broad (>0.12 seconds) depending on the site of the escape rhythm (see introduction)


