Cardio CB / Histo Flashcards
Which protein is responsible for the elasticity of striated muscle?
Titin. It binds the thick filament to the Z disk.
Mutations in titin can produce what type of disease?
Dilated cardiomyopathy. Titin defects result in overstretching of cardiac muscle during diastole, which in turn causes decreased overlap between actin and myosin, and impaired systolic function
Malignant hyperthermia can be brought on by what?
General anesthesia. Typically succinylcholine.
What is malignant hyperthermia?
Genetic condition. Susceptibility can occur due to at least six genetic mutations, with the most common one being of the RYR1 gene. In susceptible individuals, the medications induce the release of stored calcium ions within muscle cells. The resulting increase in calcium concentrations within the cells cause the muscle fibers to contract.[1] This generates excessive heat and results in metabolic acidosis.
Treatment for malignant hyperthermia?
Dantrolene sodium & rapid cooling.
What is SERCA and what regulates it?
ATP driven Ca pump found in the SR membrane Regulated by phospholamban
Is SR more abundant in skeletal muscle or cardiac muscle?
Skeletal
Dystrophin, dystroglycan, desmin, syntrophin, dystrobrevin…what do these all have in common?
All involved in molecular anchoring at the costamere
What is stained red in this picture?
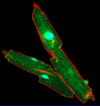
Dystrophin
A key component of the mechanical anchorage of successive cardiomyocytes in the intercalated disk is the?
fascia adherens
membrane anchorage is always via the plus end actin (thin) filaments, and not thick (myosin) filaments. In striated types of muscles, this means the terminal hemi I-band. The intercalated disk is where the next Z-line of the aligned myofibrils should be.
Where are connexins?
In gap junctions at intercalated disc.
What is stained green here?

connexin
Notice stepladder pattern. The majority of gap junctions are located at the lateral (longitudinal) component. Gap junctions function as electrical synapses.
What is pictured here?

Gap junction. It is a zipper-like structure where connexons embedded in the adjoining cell membranes are perfectly aligned to form tunnels connecting the cytosols. Connexons are composed of connexins.
All components of blood vessels are derived from?
mesenchyme
How does smooth muscle respond to hypercalcemia?
What about skeletal muscle? How does it respond to hypocalcemia?
Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle responds to hypercalcemia by increased and sustained contraction.
Skeletal muscle displays tetany in response to hypocalcemia (the increased excitability results in release of Ca2+ from the extensive sarcoplasmic reticulum).
Receptors linked with Ga,q stimulate PLC-b, thereby increasing IP3 and intracellular calcium. What are some examples?
All these receptors cause smooth muscle contraction.
Examples: a1-adrenergic, angiotensin II, V1 vasopressin (ADH), and oxytocin receptors. Think of vasoconstriction, uterine contraction.
Receptors linked with Ga,s stimulate adenylate cyclase, thereby increasing cAMP via PKA. What do these receptors cause? What are some examples?
All these cause smooth muscle relaxation. Examples: b2-adrenergic receptor.
Think of bronchodilation.
Increases in cGMP via PKG in penile arteries causes vasodilation and thus erection; cGMP is generated by soluble guanylyl cyclase stimulated by NO, and broken down by cyclic phosphodiesterase type 5.
How does Sildenafil (Viagra) work?
Sildenafil citrate (Viagra) preferentially inhibits cPDE type 5 (cGMP specific phosphodiesterase). cGMP is not broken down, so the erection is maintained.
Hyperthyroidism increases cardiac contractility and heart rate by?
- suppression of phospholamban gene expression
- increased expression of b1-adrenergic receptors
Phospholamban: ion-transport regulator in the
sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane (calcium).
When active (unphosphorylated), it inhibits SERCA (calcium pump).
Phospholamban is inactivated by PKA-mediated phosphorylation.
What is phospholemman?
Phospholemman: ion-transport regulator in the cell membrane (sodium/potassium)
When active (unphosphorylated), it inhibits the 3Na+/2K+ ATPase, mainly by reducing its affinity for intracellular Na+.
Phospholemman is inactivated by PKA- and PKC-mediated phosphorylation. Thus, activation of PKA and PKC disinhibits the 3Na+/2K+ ATPase.
What is ANP?
Atrial naturetic peptide.
ANP secretion commences when the patient’s volume is already expanded. ANP is responsible for the aldosterone escape phenomenon.
What are the three layers of the heart?
- endocardium —– tunica intima
- myocardium —— tunica media
- epicardium ——– tunica adventitia
What is the vasa vasorum?
The vasa vasorum (Latin, “the vessels of the vessels”) is a network of small blood vessels that supply the walls of large blood vessels, such as elastic arteries (aorta) and large veins (venae cavae).
What layer of the heart contains the Purkinje fibers?
The Purkinje fibers are located in the subendocardial layer (deep endocardium), and are thus more exposed to hypoxemia and tissue hypoxia.





