Cardiac Output and Blood Flow in Muscle Tissues Flashcards
(56 cards)
What is the definition of cardiac output?
Cardiac output is the volume of blood pumped by heart per minute.
What is the definition of cardiac index?
Cardiac index is cardiac output to surface area of being.
What is the cardiac index in a normal human being?
5 L/1.7 m2 = 3 L/min/m2
body surface area=1.7 m2
cardiac output= 5 L
What is the equation for cardiac index?
cardiac index= cardiac output/ body surface area
What is the primary controller of cardiac output?
venous return. Most believe that the heart is the controller of cardiac output but if the blood is not returned then the heart cannot possibly pump blood
Would an individual with a large body surface area or an individual with a smaller body surface area have the largest cardiac output?
The individual with a large body surface area would have the largest cardiac output because cardiac output has a direct relationship with body surface area.
What does the peak in this graph indicate?

The peak in this graph indicates an increase in cadiac index to meet the demands of growth and increased activity at this age level.
What does the slow drop off in this graph indicate?

The slow decrease in this graph indicates that after 10 years old there is a decrease of muscle mass and/or activity with age.
What is the oxygen fick principle?
The oxygen fick principle is a technique to measure cardiac output noninvasively.
The diagram shows that there was 200 mL/L blood leaving the heart a minute and 160mL/L of blood returning the heart a minute. This means that every liter of blood going through the lungs absorbs 40mL of oxygen.
200mL/ 40mL = 5 - 1 liter portions that must pass through the lungs every minute to absorb this amount of oxygen

What is the equation used in the Fick principle to calculate cardiac output?
cardiac output = O2 consumption/ [02]pul vein- [O2]pul art

What is the determining factor that controls how much blood the heart pumps out?
the venous return determines how much blood the heart pumps out.
True or false. All pressures in the systemic circuit are higher than the pulomonary circuit.
True
True or False. Cardiac output and rate of the systemic circuit is greater than the pulmonary circuit.
False. The systemic and pulmonary circuit have equal cardiac output and rate because they are connected in series.
Chemical composition of pulmonary venous blood is (different/similar) to that of systemic arterial blood.
Chemical composition of pulmonary venous blood is similar to that of systemic arterial blood.
Chemical composition of venous blood entering the right atrium is (different/similar) to the composition of pulmonary arterial blood.
Chemical composition of venous blood entering the right atrium is the same as the composition of pulmonary arterial blood.
What are 4 factors that directly affect cardiac output?
- basic level of body metabolism
- whether the person is exercising
- age
- size of body
What are normal values of cadiac output for:
young, health male:
women:
resting adult:
young, health male: 5.6 L/min
women: 4.9 L/min
resting adult: 5.0 L/min
What is the Frank-Starling Law?
The Frank Starling Law states that when there is an increase in blood pressure there is a stretch in the walls of heart chambers and as a reaction the heart muscles contract with increased force. Therefore, the blood that flows into the heart is automatically pumped without delay.
What is the bainbridge reflex?
Bainbridge reflex (atrial stretch reflex) is a response to increased stretch of receptors in the right atrium causing the heart to pump faster.
How does Beriberi effect cardiac output and peripheral resistance?
Lack of vitamine B1 causes diminished ability of the tissues to use some cellular nutrients, and the local tissue blood flow mechanisms in turn cause marked compensatory peripheral vasodilation and decreased peripheral resistance and increased cardiac output.

How do AV (atriovenous) shunts affect cardiac output?
Atriovenous shunt is an abnormal bypass from an artery to a vein and when done in a major vessel can markedly decrease the peripheral resistance. As a long-term response the body increases cardiac output.

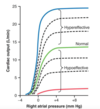
what effect does hyperthyroidism have on cardiac output?
Hyperthyroidism is an over production and secretion of T3 adn T4. T3 in particular works to increase basal metabolic rate and, thus, increases the body’s oxygen and energy consumption by dilating vessels. This creates decreased peripheral resistance and over time and increased cardiac output. Notice that hypothyroidism is on the other side of the graph and has the opposite effect.

What effect does anemia have on cardiac output?
Anemia is a deficiency of hemoglobin and as a result has a hard time delivering oxygen to tissue and the body will vasodilate to compensate. This vasodilation causes decreased peripheral resistance and over time increased cardiac output to keep the arterial pressure constant.

What effect does pulmonary disease have on cardiac output?
Pulmonary disease is any condition in which it is difficult to breathe, blocks airflow, an therefore decrease of oxygen loading. As a result the body will compensate by vasodilating, causing decreased peripheral resistance and over time increased cardiac output to keep the arterial pressure constant.