Carbohydrates Flashcards
what are the two simplest monosaccharides?
- glyceraldehyde (an aldostriose)
- dihydroxyacetone (a ketotriose)
what is the classification of monosaccharides based on?
number of carbons:
- triose (3)
- tetrose (4)
- pentose (5)
- hexose (6)
- heptose (7)
of the triose monosaccharides, which are aldoses and which are ketoses?
- aldoses: glycerose/glyceraldehyde
- ketoses: dihydroxyacetone
of the tetrose monosaccharides, which are aldoses and which are ketoses?
- aldoses: erythrose
- ketoses: erythrulose
of the pentose monosaccharides, which are aldoses and which are ketoses?
- aldoses: ribose, xylose, arabinose
- ketoses: ribulose, xylulose
of the hexose monosaccharides, which are aldoses and which are ketoses?
- aldoses: glucose, galactose, mannose
- ketoses: fructose
of the heptose monosaccharides, which are aldoses and which are ketoses?
- aldoses: glucoheptose, galactoheptose
- ketoses: pseudoheptulose
what is an isomer?
same molecular formula but different structures
what are constitutional isomers?
differ in the order of attachment of atoms
what are stereoisomers?
- atoms are connected in the same order but differ in spatial arrantment
- can be enantiomers or diastereoisomers
what are enantiomers?
a type of stereoisomer that has a nonsuperimposable mirror image
what are diastereoisomers?
a type of stereoisomer that are not mirror images
what are epimers?
a type of diastereoisomer that differs at one of several asymmetric carbon atoms
what are anomers?
a type of diastereoisomer that differs at a new asymmetric carbon formed on ring closure
what is this?
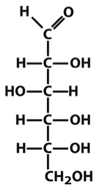
D-glucose, monosaccharide, an aldohexose

what is this?

D-fructose, monosaccharide, a ketohexose

are most CHOs in the D or L form?
D form
what are D-ribose and 2-deoxy-D-ribose?
- monosaccharides
- aldopentoses
name 3 projection models of molecules
- ball and stick models
- fischer projections
- haworth projections
name a D-aldotriose
- D-glyceraldehyde
- it is a monosaccharide
name a D-aldotetrose
- D-erythrose
- it is a monosaccharide
name three D-aldopentoses
-D-ribose -
D-arabinose
-D-xylose
-these are monosaccharides
name three D-aldohexoses
- D-glucose
- D-mannose
- D-galactose
- these are monosaccharides
what is this?

- D-galactose
- monosaccharide
- D-aldohexose
















