Cancers Flashcards
What are vulval cancers?
Uncommon
Over 80yrs old
Over 90% are squamous cell carcinoma
Also melanoma and Basal cell carcinoma
Present as: Lumps, ulcers, skin changes

What is VIN?
Vulval Intraepithelial Neoplasia
- In situ precursor of vulval squamous cell carcinoma
- -May or may not develop into SCC (squamous cell carcinoma)
- Atypical squamous cells
- Confined to epidermis
- No invasions of basement membrane
Are VIN and vulval SCC related to HPV?
Depends on case
30% cases - YES
- Usually HPV 16
- 60s -onset
- Risk factors same as cervical carcinoma
- Expose to HPV
- Ealry first pregnancy
- Multiple births
- Smoking
70% cases - NO
- Usually associated with longstanding inflammatory conditions (e.g. Lichen sclerosus)
- 80s -onset
How does vulval cancer spread?
Direct extension
- Anus
- Vagina
- Bladder
Lymph nodes
- Inguinal
- Iliac
- Para-aortic
Distant metastases
- Lungs
- Liver
What cells line the cervix and how does this change?
Transformation Zone:
Premenarchal: Endocervix (between internal and external os) is made from columnar epithelium and ectocervix is made from squamous epithelium.
Early reproductive age: Cervix everts under the influence of oestrogen (so the simple squamous becomes simple columnar). This means that the simple columnaris exposed to low vaginal pH. The low pH causes inflammation = ectropian.
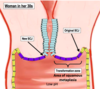
Women in her 30s: Simple columnar epithelium undergoes metaplasia into stratified squamous to adapt to low pH. This metaplasia means there is an increases risk of dysplasia.
What is HPV?
DNA virus that can be sexually transmitted.
Many subtypes
- HPV 6&11 = anogenital warts
- HPV 16&18 = high risk subtypes
- Infects trnasformation zone
- Produces viral proteins E6 and E7
- These inactivate tumour suppressor genes (P53 and Rb)
- Results in uncontrolled cell growth and proliferation
What is CIN?
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
- Dysplasia
- Confined to cervical epithelium (in situ)
- Caused by HPV infection (95%)
- Divided into CIN 1,2,3
- Increasing thickness of dysplasia
- Increasing risk of progression to invasive squamous cell carcinoma.

What are the risk factors for CIN and carcinoma?
- Increased risk of exposure to HPV
- Sexual partner with HPV
- Multiple partners
- Early age of first intercourse
- Early first pregnancy
- Multiple births
- Smoking
- Low socio-economic class
- Immunosuppression
How does the cervical cancer screeing program work?
Brush used to scrape cells from the transformation zone - send for cytological assessment.
Significant reduction in rates of cervical caner
- Aged 25-49 = every 3 years
- Aged 50-64 = eveyr 5 yeats
- 65+ - Only if recent abnormality
Discuss the HPV vaccine
Gardasil
- Vaccination against high risk HPV subtypes (6,11,16,18)
- Given aged 12-13
- Pretection from - cervical, vulval, oral and anal cancer
- Not given to men (controvercial)
- HPV> in penile, anal and oral cancers
- Men are carriers for HPV
- Screening has reduced rates of invasive cervical cancer
WHat is invasive cervical cancer and how do patients present?
- Most commonly invasive squamous cell carcinoma (Precursor = CIN)
- Also adenocarcinoma (arise from endocervical glandular mucosa)
- Presentation:
- Post-coital, inter-menstrual, post-monopausal bleeding
- Mass - exophytic and infiltrative
- Screening
How does cervical cancer spread?
..

How do you treat cervical cancer?
If advanced:
- Hysterectomy
- Lymph node dissection
- Chemoradiotherapy
What is Endometrial hyperplasia and what causes it?
Thickened endometrium - >11cm
Can be a precursor to endometrial cancer
Inter-menstrual / post-menopausal bleeding.
Caused by excessive oestrogen:
- Endogenous
- Obeisity
- Early Menarchy / late menopause
- Oestrogen secreting tumours (granulosa cell tumours)
- Exogenous
- Unopposed oestrogen - HRT
- Tamoxifen (partial agonist in endometrium)
- Irregular cycles
- PCOS
Hw does endometrial cancer present?
- Intermenstrual bleeding
- Postmenopausal bleeding
- Mass
What are the types of endometrial cancer?
- Endometrioid adenoarcinoma
- Mostcommon
- Resemble normal endometrial glands
- Commonly arises from endometrial hyperplasia
- Serous Carcinoma
- Less common
- More aggressive
- Poorly differentiated cells







