Cancer Cell Biology 2 - angiogenesis and metastasis Flashcards
(24 cards)
What percent of tumor cells go on to form metastases after they enter circulation?
0.01% survive to form metastases - but it only takes one cell
What are the rules for metastatic development?
- metastasis can occur on the basis of size- larger tumours have a higher chance of metastasis i.e) breast and colon cancer
- emtastasis can occur before the cancer has grown to a detectable size (soon after initiation)
- metastasis can be extremely infrequent or does not happen at all
*there are no rules - metastases can happen under any circumstance*
Where do breast tumors metastasize?
bone/brain
Where do prostate tumors metastasize?
Bone
Where do stomach tumors metastasize?
liver/ovary
Where do colon tumors metastasize?
liver, lungs
Where do melanoma tumors metastasize?
brain, liver and bowel
what is the ‘seed and soil theory’ for metastases?
cells are dispersed randomly but only grow in organs which provide the correct factors necessary for growth of that particular tumor (fertile soil)
What is the ‘mechanistic theory ‘ of metastases?
the first site to which a cancer emtastasises is the closest one in which there are small blood vessels
What are the key steps involved in metastasis?
- disruption of cell-cell and cell/matrix interactions and degradation of ECM
- invasion and migration through stroma
- intravasation into blood or lymph vessel
- survival in circulation
- extravasation out of blood or lymph vessel and micration into new tissue
- survival in new tissue
- once tumour reaches certai size, develops new blood vessels (angiogenesis)
*these cells need to survive in order to metastasis - if they do survive they are micrometastices which are undetectable - once they develop their own blood supply they are full blown metastatic tumours
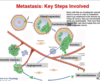
what are the steps of invasion of metastasis?
1) attachment - cell adhesion molecules/integrins
2) proteolysis - enzymes MMPs and uPA
3) migration- motility factors
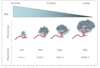
what is angiogensis ?
new blood vessel formation from pre-existing vasculature -
what is vasculogenesis?
new vessel synthesis from endothelial progenitor cells - from scratch
what are the steps in angiogenesis?
- secretion of angiogenic factors by tumour cells (VEGF)
- release of proteases from activated endothelial cells
- permeabilisation of blood vessel wall and release of vascular endothelial cells
- migration of the endothelial cells into the interstitial space and into the tumour
- endothelial cell proliferation
- lumen formation
- fustion of newly formed vessles
- initiation of blood flow
What are ‘Pro-Angiogenic’ factors?
VEGF
Epidermal growth factor (EGF)
platelet derived growth factor (PDGF)
transforming growth factor alpha (TGFalpha)
hypoxia
oncogene activation
loss of tumour suppressor genes p53 or VHL
how does hypoxia induce angiogensis and aggressive tumor proliferation?
hypoxia stimulates angiogensis to get more oxygen to the tissue- it impairs drug delivery and selects for more aggressive cells
*since hypoxic cells are not actively proliferating, they are resistant to chemo which targets dividing cells
What are angiogensis inhibitors?
- angiostatin - cleavage fragment of plasminogen
- endostatin- cleavage fragment of collagen
- interferons
- platelet factor 4
- TIMPS- tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases
*it’s about finding a balance between these inhibitors and the proangiogenic factors release by tumours the tumor cells have an inbalance of these*
what is the ‘angiogenic switch hypothesis’?
this hypothesis states that regulation of angiogensis is a balance between pro- and anti- angiogenic factors
what is VEGF?
vascular endothelial growth factor
-stimulates angiogensis and vasculogenesis
it increases vascular permability, facilitating metastasis (often why tumors bleed however )
regulated by p53 and VHL tumour supressors - however, these are often lost in cancer
VEGF receptors are often over-expresed by tumour endothelium
what is the HIF1 pathway in hypoxia induced angiogensis?
HIF1 is a transcription factor that regulates many genes that are controlled via oxygen levles - when the tumor increases in size we reduce amount of oxygen available and HIF1 expression increases as well as VEGF- which is controlled by HIF 1
HIF1= hypoxia inducible factor 1
what is the HIF1 pathway in hypoxia induced angiogensis?
HIF1 is regulated by hypoxic conditions because it is stabilized by hypoxia and VHL cannot regulate it under hypoxic conditions
VHL= part of complex with ubiquitin ligase activity which degrades HIF1
what is the difference between tumour associated blood vessels and non-tumour associated blood vessels?
tumour associated= leaky allowing cells to spread easily into vasculature
non-tumour associated = regularly patterned and functioning - normal vessel wall and endothelium
describe the effect of the tumour microenvironment on cancer research/treatment
research in the past focused on experimenting with just tumour cells in a la condition - but tumours are not isolated in the body.
now we know there is an interplay between tumour cells and healhty cells, so we need to model these interactions to understand the real implications of cancer treatment
*we also know that a metastatic tumour and the primary tumour grow indifferent microenvironments, so a ‘one size fits all’ treatment might not even work in one person with multiple tumours



