C4 Part 2 Flashcards
(45 cards)
Chlorine, fluorine, bromine and iodine are in which Group and are known collectively as what?
Chlorine, fluorine, bromine and iodine are in Group 7 and are known collectively as the halogens.

Describe the physical appearance of the halogens chlorine, bromine and iodine at room temperature.
At room temperature, chlorine is a green gas, bromine is an orange liquid and iodine is a grey solid.

Group 7 elements have lots of everyday uses. Describe a common use for chlorine, bromine and iodine.
Chlorine is used to sterilise water (e.g. swimming pools, water purification tablets) and used to make pesticides and plastics, iodine is used to sterilise wounds, bromine is used in pesticides and pharmaceuticals (medicines).

Group 7 elements react vigorously with elements from which other group in the periodic table, and why?
Group 7 elements e.g. F, Cl, Br, I, react vigorously with Group 1 elements e.g. Na, Li, K. Group 1 elements want to lose their outer electron and Group 7 want to gain an electron to complete their outer shell, which they do very easily and rapidly. They form the halide salts e.g. Sodium flouride (NaF), Lithium chloride (LiCl), Potassium bromide (KBr).
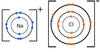
Write the word equations for the reactions between:
1) sodium and chlorine
2) potassium and iodine
3) lithium and bromine
1) Sodium + chlorine → sodium chloride
2) Potassium + iodine → potassium iodide
3) lithium + bromine → lithium bromide

Write the balanced symbol equations for the reactions between:
1) sodium and chlorine
2) potassium and iodine
3) lithium and bromine
1) 2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
2) 2K + I2 → 2KI
3) 2Li + Br2 → 2LiBr

What happens to the reactivity of the halogens as you go down Group 7 from fluorine to iodine?
Reactivity of the Group 7 elements decreases down the group. Flourine is most reactive, astatine (At) is the least reactive.

In a reaction between chlorine and sodium bromide, which halogen is displaced and why? What would you observe in the test tube?
In a reaction between chlorine and sodium bromide, bromine is displaced by the chlorine as chlorine is more reactive than bromine.
Sodium chloride and bromine are formed as a result.
You would observe the solution in the test tube turning orange/brown as the bromine is displaced and dissolves into solution.

Write a balanced symbol equation to explain what happens when
a) chlorine and sodium bromide and
b) bromine and potassium iodide react together.
Describe what you would see in the test tube.
a) Cl2 + 2NaBr →2NaCl + Br2 (solution would turn orange/brown as the less reactive bromine is displaced by the chlorine and goes into solution.
b) Br2 + 2KI →2KBr + I2 (solution would turn purple as less reactive iodine is displaced by the bromine and goes into solution.

Why do all halogens have similar properties?
All halogens have similar properties because they all have 7 electrons in their outer shell, all tend to gain an electron to form 1- ions (completing their outer shell of electrons, making them stable) and as a result all react readily with Group 1 elements.

What is happening to each of the halogens in these equations? What is this called?

The halogens are all gaining electrons to become negative ions (with full, stable outer shells). The gain of electrons is called “reduction” (the opposite - loss of electrons - is called “oxidation”). The halogens are all being reduced.
What is the purple block of elements commonly known as? Give some examples.
The elements in the purple block on this periodic table are known as the “transition metals”.
Examples include Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu), Zinc (Zn), Vanadium (V), Silver (Ag), Gold (Au), Lead (Pb), Nickel (Ni), Platinum (Pt).

Describe some of the properties of transition metals.
Transition metals have the following properties:
- good conductors of electricity,
- high melting points (except mercury, Hg, which is liquid at room temperature),
- good conductors of heat,
- malleable (can be beaten into shape),
- shiny when cut
- ductile (can be pulled into wires).

Transition metals tend to form coloured compounds. What are the colours of copper compounds, iron(II) compounds and iron(III) compounds?
Copper compounds are often blue/turqouise
Iron(II) compounds are often light green
Iron(III) compounds are often orange/brown.

Transition elements and their compounds are often good catalysts. Iron and nickel are the two you need to know. What are they used for?
Iron is used as a catalyst in the Haber process to make ammonia.
Nickel is used as a catalyst in the manufacture of margarine (to hydrogenate vegetable fats).

What is a thermal decomposition reaction?
Thermal decomposition as a reaction in which a substance is broken down into at least two other substances by heat.

Transition metal carbonates thermally decompose on heating. Write the word equations for the thermal decomposition of iron, copper, zinc and manganese carbonates.
Iron carbonate → Iron oxide + carbon dioxide
Copper carbonate → Copper oxide + carbon dioxide
Zinc carbonate → Zinc oxide + carbon dioxide
Manganese carbonate → manganese oxide + carbon dioxide.

Construct the balanced symbol equations for the thermal decomposition of the following transition metal carbonates - FeCO3, CuCO3, MnCO3 and ZnCO3.
FeCO3 → FeO + CO2
CuCO3 → CuO + CO2
MnCO3 → MnO + CO2
ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2

This would happen if you bubbled the gas produced when you heat a transition metal carbonate. What is the test and what is the gas?
This is the limewater test for carbon dioxide. When carbon dioxide is bubbled through limewater, it turns cloudy.

What does the term “precipitation” mean when referring to a chemical reaction?
Precipitation is a reaction between two solutions that produces an insoluble solid (a “precipitate”) which comes out of solution and is visible.

Sodium hydroxide solution is used to identify the presence of transition metal ions in solution, as coloured “precipitates” are formed. What are the colours of the following precipitates? Cu2+, Fe2+ and Fe3+.
Cu2+ gives a blue precipitate, Fe2+ gives a grey/green precipitate, Fe3+ gives an orange/brown precipitate.

Construct balanced symbol equations for the precipitation reactions between Cu2+, Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions and hydroxide (OH–) ions.
Cu2+ + 2OH- → Cu(OH)2
Fe2+ + 2OH- → Fe(OH)2
Fe3+ + 3OH- → Fe(OH)3

Why is iron used to make cars and bridges, but copper is used to make electrical wiring?
Iron (in steel) is used to make cars and bridges because it is strong, copper is used to make electrical wiring because it is ductile and is a good conductor of electricity.

List the physical properties of metals.
The physical properties of metals are:
• lustrous, hard and high density
• high tensile strength
• high melting and boiling points
• good conductors of heat and electricity.




















