Buck converter Flashcards
What are assumptions made for the buck converter circuit?
> Switch is ideal
> Diode is ideal
> Vi is constant
> C0 is large so the load no current flows through it
> The inductor has a continuously flowing current and is in a steady state operation
> The inductor current can be assumed to be changing linearly with time because the switching frequency is high enough.
> The circuit has negligible resistance
What happens when the switch is closed?
> Diode is reverse biased and no current flows through it
> The current flows through the inductor and load.
> We assume no current flows through the capacitor
What happens when the switch is open?
> The magnetic field stored in the inductor is released and current flows through the diode and the load.
> We assume no current flows through the capacitor
Draw the waveforms for the inductor current, switch voltage, diode voltage, and switch current
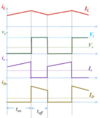
What is the equation for the voltage across the inductor and thus the equation for the current through the inductor?
V = L × di/dt
∫ (V/L)dt = i
What is the equation to calculate the overall current waveform of the current through the load/inductor?
ID + IS = IL
What is the relationship for the on current and off current?
∆ion = -∆ioff
What is KVL when the switch is closed?
Vi = VL + VO
or
Vi - VL = VO
What is the equation for the inductor voltage based on the duty and the time period?
VL = L(∆ion / KTS)
What is KVL when the switch is open? What about when the diode is ideal?
VO = VL - VD
When ideal: VO = VL
What is the equation for the output voltage when the switch is closed?
VO = VI - L(∆ion / ton)
What is the equation for the output voltage when the switch is open
VO = -L(∆ioff / toff)
What is the equation for the voltage relationship dependent on the duty cycle?
K = VO / Vi
Derive the voltage relationship equation
Vi - VO = L(∆ion / KTS)
(Vi - VO)KTS / L = ∆ion
- VO = L(∆ioff / (1 - K)TS)
- VO(1 - K)TS / L = ∆ioff
(Vi - VO)KTS / L = VO(1 - K)TS / L
(Vi - VO)K = VO(1 - K)
ViK - VOK = VO - VOK
ViK = VOK = VO / Vi
For a lossless computer, what are the input and output relationships?
Pin = Pout
VOIO = ViIi
For a lossless computer, what is the equation for the current relationship?
K = Vi / VO
What factors do you need to know to calculate a value for the inductor?
> Input voltage (Not requred)
> Output voltage
> PWM Duty cycle
> PWM frequency
> Current ripple
What is the equation for the value of the inductor?
L = (Vi - VO)K / (fs × ∆I)
Derive the equation for the value of the inductor
Vi - VO = L∆ion / KTS
(Vi - VO)K = L∆ion / TS
(Vi - VO)K / fS = L∆ion
(Vi - VO)K / fS∆ion = L
What is the equation for the inductor value without requiring the input voltage? Derive it
L = (1 - K)VO / fS∆ion
L = (Vi - VO)K / fS∆ion
L = (ViK - VOK) / fS∆ion
L = ((Vi/VO)K - K)VO / fS∆ion
L = ((1 / K)K - K)VO / fS∆ion
L = (1 - K)VO / fS∆ion
What is the assumption with CO?
> CO is so large that we can ignore it (No current flows through it so the voltage across CO is 0).
> In reality this is not the case, assumptions only apply if the buck converter is ideal
What is the equation for the rate of change in voltage across the capacitor? Derive it
dV0 / dt = [1 / C0] ic
Q = C0V0
dQ / dt = d/dt(C0V0)ic = C0× dV0 / dt
dV0 / dt = [1 / C0] ic
When we assume the output current is constant, what is the assumption with the capacitor? What is the equation to describe this?
> It is assumed that all the fluctuations in the current is compensated by capacitor.
> I0 = iL - ic
What is the equation for the voltage across the output?
vO = ∫([1 / C0] ic)dt
vO = Area under the graph for the output current ripple through the inductor



