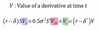Brownian Motion Flashcards
(22 cards)
What 4 things do you need to know about Brownian Motion?
- Z(0) = 0
- Z(t+s) - Z(t) ~ N(0,s)
- Changes in Z(t) are independant over time
- E[Z(t+h)|Z(t)] = Z(t)
What 3 multiplication rules do you need to remember when working with Brownian Motion?
- dt x dt = 0
- dt x dz = 0
- dz x dz = dt
ABM
dX(t) =
dX(t) = αdt + σdZ(t)
ABM
X(t+s) - X(t) ~
X(t+s) - X(t) ~ N(αs, σ2s)
GBM


GBM


GBM
ln[S(t)] ~ N(m, v2)
m =
v2 =
ln[S(t)] ~ N(m, v2)
m = ln[S(0)] + (α - δ - 0.5σ2)t
v2 = σ2t
GBM
E[S(t)] =
E[S(t)] = S(0)e(α-δ)t
GBM
S(t) =
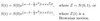
Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Process
dX(t) =
dX(t) = λ[α - X(t)]dt + σdZ(t)
What is Ito’s Lemma?
dV = Vsds + 0.5Vss(ds)2 +Vtdt
Sharpe Ratio
Φ =
Φ = (α - r)/σ
What do you know about two Ito Processes that depend on the same dZ(t) ?
Their Sharpe Ratios are equal.
If Φ1 > Φ2, how do you exploit arbitrage?
- Buy 1/(σ1S1) shares of S1
- Short 1/(σ2S2) shares of S2
- Invest (1/σ2 - 1/σ1) at the risk free rate
Risk Free Portfolio

Risk Free Portfolio


Risk Free Portfolio


Risk Free Portfolio
Three steps for creating a risk free portfolio?

Risk Neutral Vs True
Relate to dZ(t) & Z(t)
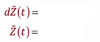
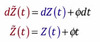


Black Scholes Equation

What is the Black Scholes PDE?