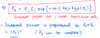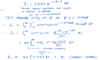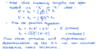Bramwell Flashcards
(68 cards)
What is “Condensed Matter”?
Matter in a high-density state (i.e. solid, liquid, glass, colloid etc.) such that many-body (10^23) effects are important.
What is “order”?
Typically characterised by restricted phase space, low entropy and discrete symmetries; crystalline state is the paradigm.
What are “excitations”?
Excited quantum states reflect many-body nature: quasiparticle excitations in crystals are the paradigm.
Why X-ray and neutron scattering ?
Our understanding of condensed matter is intimately bound up with these experimental techniques, which are among the most important in science.
Why order and excitations in magnetism ?
Magnetic order and excitations are very diverse and illustrate all the general principles extremely well.
X-rays are
EM radiation, wavelength ~1 Angstrom
‘Thermal’ neutrons are
free quantum particles with wavelength ~1 Angstrom
X-ray photon, p k E
p = hbar*k, k = 2*pi/lambda, E = hbar*k*c

Thermal neutron, p k E
p = hbar*k, k = 2*pi/lambda, E = hbar^2*k^2/2m
Reciprocal Lattice Vector G of a cubic lattice
G = 2pi/a (h k l)
Reciprocal Lattice Vector G
By definition, G is a wavevector with the periodicity of the crystal, so
G=2pi/d_hkl
Direct Space and Reciprocal Space

orthorhombic structure
a=/=b=/=c, alpha=beta=gamma=90deg orthogonal
Basis vectors of reciprocal lattice

Sketch the basic experimental geometry of X-ray or neutron scattering in the ‘W’ (or ‘M’)- configuration. Appropriately annotate the different parts of your sketch
sample angle determines q (Wavevector)
analyser angle determines energy transfer deltaE = h*w_q
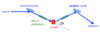
Scattering triangle for X-ray or neutron scattering.
Scattering vector def Q = k’ - k

Laue Condition
For a and Q to be parallel
Q.a=2pi*h
Where Q is the scattering vector
Show that the the scattering triangle is isoscelese for elastic scattering. Hence show that |Q| = 4pi sin theta/lambda. Write down the Laue condition for a and Q parallel and use the result just derived to demonstrate its equivalence to Bragg’s law.

First order (n = 1) Bragg reflection from an analyser crystal is used to measure the energy of a scattered X-ray or neutron.
Express how the energy of (i) the scattered photon and (ii) the scattered neutron depends on the scattering angle theta’ at the analyser crystal (d-spacing d_a).
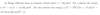
Explain why the neutrons produced by a reactor or spallation source are typically passed through a hydrogenous material and what the process is called.
Neutrons produced by a reactor or spallation source are very high in energy and so have wavelengths too short to be useful in probing condensed matter. Passing them through a hydrogenous material slows the neutrons through collisions (hydrogen has a large scattering cross section) and the neutrons eventually equilibrate with the material, with a much lower energy. The process is called moderation and the material is called the moderator.
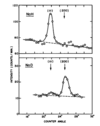
Argue that the Bragg peak becomes extremely intense and sharp in a real crystal
In real crystals, many atmoic planes are interfereing. This gives very sharp peaks surrounded by mostly destructive interference.
Scattering Amplitude A

Fourier Analysis

Fourier Analysis of electron density