Brain Stem and Cranial Nerves Flashcards
(39 cards)
Parasympathetic fibres from which 3 nerves are distributed with branches of the trigeminal nerve (V)?
Oculomotor (III), Facial (VII), Glossopharyngeal (IX)
Which 2 cranial nerves run in the same line as they both arise from the somatic motor column?
Abducens and hypoglossal
Which clinically important tract descends in the pyramids of the medulla?
Corticospinal tract
Cranial nerves 6, 7 and 8 emerge at which junction?
Pontomedullary junction
What paired structures project down into the interpeduncular fossa?
The mamillary bodies
Coma might result from damage to which diffuse network in the brain stem tegmentum?
Reticular formation
What is the clinical significance of the area postrema, and which group of drugs act on receptors in this region?
The area postrema is the vomiting centre of the medulla. It is one of the few areas of the brain lacking a blood-brain barrier, which allows detection of the blood contents.
Anti-emetics act on the area postrema receptors.
How is the spinal accessory nerve tested clinically?
idk
Which thalamic nucleus recieves the optic tract?
Lateral geniculate nucleus
The superior and inferior colliculi on the dorsal surface of the mibrain is part of which generalised region of the brainstem?
Tectum - meaning roof
What is the clinical term for inhalation of stomach contents?
Aspiration - e.g. in aspiration pneumonia
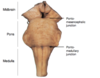
Identify the labelled junctions in the brain stem.

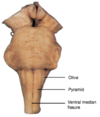
The rootlets emerging from the ventrolateral sulcus of the olive constitute which nerve?
Hypoglossal (CNXII)
Why is unilateral pupil dilation a warning sign following head injury?
Indicates generalised swelling and compression
Which cranial nerve is the only one to emerge from the dorsal surface of the brainstem?
Trochlear - emerges lateral to the frenulum between the inferior colliculi
The middle meningeal artery enters the skull via which foramen?
Foramen spinosum
The dorsolateral sulcus posterior to the olive is the site of filaments contributing to which cranial nerves?
9, 10, 11
Which cranial nerves are mainly responsible for the afferent and efferent limbs of the gag reflex?
Afferent: glossopharyngeal
Efferent: vagus
Which cranial nerve arises from the lateral pontine region?
Trigeminal
Which limbic lobe nucleus recieves olfactory pathway projections?
Amygdala
Sensory and motor fibres to the pharynx and larynx are supplied by which 3 cranial nerves?
9, 10, 11
The most posterior portion of the thalamus is known as what?
Pulvinar
Compare the clinical signs in an upper versus lower motor neuron facial nerve lesion?
idk
Which pontine nerve is especially vulnerable to stretch in raised intracranial pressure? What signs and symptoms would you expect from damage to this nerve?
Trochlear damage: blurry vision, diplopia, rotational (torsional) disturbances in visual field