Brain pathways Flashcards
(100 cards)
Label the neuroanatomical axes 1 and 2
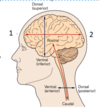
1 - rostral 2 - caudal
Label the neuroanatomical planes 1-3

1 - horizontal/axial 2 - coronal 3 - sagittal
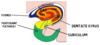
Label the subdivisions of the CNS 1-5

1 - diencephalon 2 - midbrain 3 - pons 4 - medulla 5 - cerebellum
Label the features of the brain 1-5

1 - precentral gyrus 2 - central sulcus 3 - postcentral gyrus 4 - lateral (Sylvian fissure) 5 - superior tempiral gyrus
What are some of the basic functions of the frontal lobe?
Movement, rational thought, decision making and planning
Where is the primary motor cortex found within the brain?
Pre-central gyrus
What are some of the basic functions of the temporal lobe?
Processes auditory signals, involved in learning and memory
What are some of the basic functions of the parietal lobe?
Processes sensory information, involved in attention and spatial awareness
Where is the primary somatosensory cortex found?
Post-central gyrus
What are some of the basic functions of the occipital lobe?
Visual processing (the primary visual cortex is found here)
Label these medial structures of the brain 1-3

1 - optic chiasm 2 - fornix 3 - corpus callosum
Label these medial structures of the brain 1-3

1 - olfactory bulb 2 - cingulate gyrus 3 - calcacrine fissure
Label these medial structures of the brain 1-3
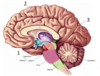
1 - hypothalamus 2 - thalamus 3 - pineal body
What is the overall basic function of the thalamus?
It relays all sensory information (except olfactory information) before passing it onto the appropriate area of the cortex
Label the thalamic nuclei 1-4

1 - anterior nucleus
2 - lateral posterior nucleus
3 - pulvinar nucleus
4 - reticular nucleus
Label the thalamic nuclei 1-5

1 - dorsomedial nucleus
2 - medial geniculate nucleus
3 - lateral geniculate nucleus
4 - ventral posteromedial (VPM) nucleus
5 - ventral posterolateral (VPL) nucleus
What is the function of the anterior nucleus?
It is connected to the hippocampus so is thought to be involved in memory
What is the function of the dorsomedial nucleus?
Emotional behaviour
What is the function of the ventral anterior and ventrolateral nuclei?
Involved in motor function
What is the function of the ventral posterolateral (VPL) and ventral posteromedial (VPM) nuclei?
They act as relay nuclei for sending somatosensory information to the somatosensory cortex
What is the function of the lateral posterior nucleus?
Integrates sensory input with cognitive functions
What is the function of the pulvinar nucleus?
Processes visual stimuli
What is the function of the medial geniculate nucleus?
Relays auditory information
What is the function of the lateral geniculate nucleus?
Relays visual information