Brain Development Flashcards
Neural Tube Development
(Diagram)

Alar Lamina
Dorsal thickening from neuroepithelium which contain nerve cell bodies that will form processes that exit thickening into marginal layer of neural tube
Basal Lamina
Ventral thickening from neuroepithelium which contain nerve cell bodies that will form processes that exit thickening into marginal layer of neural tube
3 Main functional types of Neurons
- Motor (efferent): from basal lamina of neural tube
- Association (interneurones): from alar lamina of neural tube
- Sensory (afferent): from neural crest
** All 3 having different functions (functional types), they all have a different developmental origin within the developing NS
-basal lamina is the source of all efferent neurons
Motor Neurons

- Convey messages from the CNS to the periphery of the body. (i.e. to supply muscles with motor neurons taking impulses from CNS to different limbs of body).
- Efferent.
- Carrying impulses out of the CNS to the periphery of the body
Association or Interneurons

- Neurons like this connect or associate one point in the CNS with another point in the CNS, but they never leave the CNS unlike the motor neurons. Could be anything, one bit of spinal cord to another bit of spinal cord. Associated one point of CNS with another.
- By far the most numerous in the Nervous system!
Sensory (afferent) Neurons

- bring information in from the periphery of the body.
- From the skin to the CNS.
- Doing the opposite thing to efferent neurons in terms of signal transfer.
3 Vesicles of “3 vesicle stage of Brain”
- Forebrain
- Midbrain
- Hindbrain
- Development of Brain I
- Ventricles contain cerebrospinal fluid
- shows 3 obvious expansions of this cranial end of neural tube
- hindbrain becomes the part continuous with the rest of the neural tube and this leads to the formation of the spinal cord

“5 Vesicle Stage of Brain”
- Soon after 3 vesicle stage:
- Forebrain region forms a growth pouch-like on either side
- two expansions of forebrain vesicles
- becomes 5-vesicle stage due to added expansions

Brain Regions

Pontine Flexure
- Hindbrain elongates somewhat and tends to grow in length so much that to accommodate it has to be folded. Becomes V-shaped or U-shaped –> Pontine Flexure
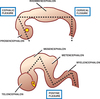
Pons and Medulla Oblongata

- the Pontine Flexure:
allows for 2 different parts of the brain to develop from the hindbrain vesicle. More rostral part is the pons. And the most caudal part becomes continuous with the spinal cord and is called the medulla oblongata.
Formation is due to elongation of the hindbrain vesicle
Secondary Neural Structures to Adult Neural Structures

Parts of the Brain
(including all that composes forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain)

Parts of the Telecephalon

- cerebral hemispheres (2)
- Largest parts of telencephalon. Form connections that join the left hemisphere with the right
- limbic system
- olfactory bulb
- interconnecting structures (commisures)
Parts of Diencephalon

Gross Description of parts of the brain
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
- Brainstem
-medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain

View of Brain Stem with Cerebellum Removed

Interventricular Foramen

- The lateral ventricles connected to the third ventricle by theinterventricular foramina
- In the brain, the interventricular foramina (or foramina of Monro) are channels that connect the paired lateral ventricles with the third ventricle at the midline of the brain
Corpus Callosum

- The corpus callosum is a thick band of nerve fibers that divides the cerebral cortex lobes into left and right hemispheres
- It connects the left and right sides of the brain allowing for communication between both hemispheres
Neural Tube
Formation: Notochord induces its overlying ectoderm –>neuroectoderm–> neural plate= Elongated thickening of ectoderm –>lateral parts rise–> neural folds process continues & ends meet & fuse–> Neural tube
- Marginal Layer: formed primarily of nerve Cell processes (white matter
- Mantle Layer: Cells
- Alar Lamina- cells here–> Interneurons (reside soley in CNS)
- Basal Lamina- cells here–> Motor (efferent) neurones
- Neuroepithelial (ventricular) Layer- major proliferative layer & 1st to develop
Neural Crest
Formation: During NT formation, some cells of the neural folds breakaway to form two continuous cords- the neural crests, which run almost the whole length of the NT at its dorsolateral aspects
- NC cells can differentiate into: Spinal ganglia (dorsal root), ANS ganglia & ganglia of some cranial nerves, sensory afferent neurones, chromaffin cells & Schwann cells
Development of Brain
- The neural tube forms 3 primary brain vesicles: forebrain, midbrain & hindbrain
- Outgrowths from the prosencephalon grow either side of the forebrain vesicle & form the telencephalon & diencephalon–> 5 vesicles
- From the hindbrain form the
- metencephalon (pons)&
- myelencephalon (medulla)
Parts of the Brain
Developmental- parts of the brain can be subdivided based on their embryonic origin. Divisions:
- Hindbrain- medulla oblongata, pons & cerebellum
- Midbrain
- Forebrain:
- Diencephalon (midline component): epithalamus, thalamus, hypothalamus
- Telencephalon (paired outgrowths): cerebral hemispheres (2), limbic system, olfactory bulb, Interconnecting structures (commissures)
Gross- parts of the brain can also be subdivided based on their appearance. Divisions:
- Cerebrum, Cerebellum & Brainstem (medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain)
- But diencephalon doesn’t fit into any of these groups



