Bones and Joints Lecture Flashcards
(43 cards)
What is haematopoiesis?
Haematopoisesis is the formation of red blood cells
Where does haematopoises happen?
Haematopoises happens in the medullary cavity
What are condyles?
Condyles are smooth lines where bones join
What do muscles, tendons and ligaments attach to?
They all attach to epicondyles
What are epicondyles?
Epicondyles are the protruding area above or below the condyle for attachment of ligamnets and muscles that act on the joint
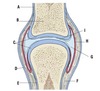
What is A?

Condyles
What is B?

Epicondyles
What is C?

Supracondylar region
What is a fossa?
A fossa is a shallow depression, accomodates the full movement of the bones when they are together
What is a process?
A process is any projection or bump
What is a foramen?
A foramen is a rounded aperture for vessels and nerves
Why do bones form around vessels?
Bones form around vessels because vessels cannot penetrate bones once they are formed
Where are process and foramen found?
Process and forament are found on the skull
What is a salcus?
A salcus is a shallow groove
What is a tubercle?
A tubercle is a small rounded projection
What is a tuberosity?
A tuberosity is a rough projection
What is a spine?
A spine is a pointed process
What are the 3 types of fibrous joints?
The 3 types of fibrous joints are:
Sultures between skull bones
Syndesmoses between certain long bones
Gomphoses that attach the roots of human teeth to the jaw
What are the two types of cartilaginous joints?
The 2 types of cartiliginous joints are:
Primary cartilaginous joint (synchondroses)
Secondary cartilaginous joint (symphysis)
What are synchondroses cartilaginous joints?
Synchondroses cartilaginous joints connect to bones by hyaline cartilage
What are examples of synchondroses cartilaginous joints?
Examples of synchondroses cartilaginous joints are:
Epithyseal growth plate
Rib to costal cartilage
What are symphysis cartilaginous joints?
Symphysis cartilaginous joints involve both hyaline and fibrocartilage, so are stronger than primary cartilaginous joints
How do the hyaline and fibrocartilage interact with each other in a symphysis cartilaginous joint?
The articular surface of each bone is covered with a thin layer of hyaline cartilage, with fibrocartilage uniting the two laters