Biospectroscopy Flashcards
(266 cards)
What state of matter has rotational energy?
Gas only
What are the challenges of Raman spectroscopy?
Can be highly effected by fluorescence
Laser can destroy sample if power is too high
May require several modes of operation and different laser wavelengths to cover all applications
Define
Symmetric stretching
Simultaneous vibration of two bonds, in which the bonds elongate together and contract together
What happens when PCA is applied to spectroscopic data?
When applied to spectroscopic data, scores proved a map of the sample similarities/dissimilarities and the loadings represent the spectral features that cause the samples to group the way they do
Definition
Map of samples: Projected locations of objects onto the principal components
Scores (T)
Draw a FT/Raman Spectrometer

Define
Vibrational energy
The energy in a vibrating system, otherwise at rest; especially that in a molecule due to the vibrations of its atoms
What is the equation for Beer’s law?
A = ελ c l
Where:
A = Absorbance
- c* = concentration
- l* = path length
ελ = Extinction coefficient
Draw a Michelson Interferometer

Definition
a measure of the degree to which electrons are displaced relative to the nuclei (i.e. how much to the electrons slosh about)
Polarizability
Which has a higher frequency (and wavenumber)?
Stretching or Bending modes
Stretching modes
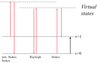
What are the two types of light scattering?
Rayleigh scattering: elastic - same frequency - weak
Raman scattering: inelastic - changed frequency - weaker
Definition
One of the possible Raman interactions that leads to the material losing energy and the emitted photon has a higher energy than the absorbed photon
Anti-Stokes Raman scattering
Definition
finds a data value by averaging the values within a segment of data points
Moving average
Why are the spectra for the same molecule different?

Different chemophores are enhancing different excitation wavelengths
Define
De-trending
Removing unwanted baseline effects by estimating a polynomial baseline
Which mode has the strongest absorbance?
Asymmetric stretching
What is the relationship between number of double bonds and the position of v(C=C)?
↑ congugation
=
↓ frequency v(C=C)
because
↑ electron delocalisation
=
↓ strength of double bonds
=
↓ force constant
↓ wavenumber
What two components make up molecular energy levels?
Electronic
Nuclear motion
Do all CO2 modes give rise to IR transitions?
No. The electric component of the electro-magnetic radiation must interact with an oscillating dipole of the same frequency. Asymmetric stretching and bending modes do but symmetric stretching does not.
- The fundamental transition of a diatomic molecule that is a harmonic oscillator is found at 3000 cm-1. Where would you expect to observe the 2nd overtone? (1 mark)
9000 cm-1
Which of the following statements about DNA is correct?
- DNA has a strong bands assigned to the symmetric phosphodiester stretching and the asymmetric stretching vibration at 1080 cm-1 and 1220 cm-1, respectively.
- In the hydrated state the B-DNA asymmetric stretch appears at 1240 cm -1 whereas in A-DNA the band appears at 1220 cm -1
- The A-DNA conformation is adopted by bacteria under hydrating conditions
- The B-DNA form is a more narrow and disordered form compared to A-DNA
- The A-DNA conformation is observed when DNA is hydrated
Which of the following statements about DNA is correct?
- DNA has a strong bands assigned to the symmetric phosphodiester stretching and the asymmetric stretching vibration at 1080 cm-1 and 1220 cm-1, respectively.
- In the hydrated state the B-DNA asymmetric stretch appears at 1240 cm -1 whereas in A-DNA the band appears at 1220 cm -1
- The A-DNA conformation is adopted by bacteria under hydrating conditions
- The B-DNA form is a more narrow and disordered form compared to A-DNA
- The A-DNA conformation is observed when DNA is hydrated
How can fluorescence be prevented?
Choosing an appropriate wavelength