Biological Chemistry/Macromolecules Flashcards
1
Q
draw fructose in its ring form
A

2
Q
draw fructose in its linear form
A

3
Q
draw glucose in its ring form
A

4
Q
draw glucose in its linear form
A

5
Q
what is the nomenclature for carbohydrates?
A
- Number of carbons
- Aldose or ketose sugars
- Alpha or beta
- D and L isomers
6
Q
how do the aldose and ketose carbs vary?
A
- In an aldose group, the C with the carbonyl group is C1 (glucose)
- In a ketose sugar, it is on C2 (fructose)
7
Q
how do the alpha and the beta version vary for carbs?
A
- Alpha - below the plane: the hydroxyl is opposite the CH2OH
- Beta - above the plane: the hydrozyl is near the CH2OH
8
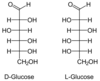
Q
What are the D and L versions - position of OH on penultimate carbon?
A
- Left is an L sugar (above the plane)
- Right is a D sugar (below the plane)- this is the type found in biological systems
9
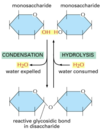
Q
How does a disaccharide form?
A
10
Q
what are the common disaccharides?
A
- glucose + glucose = maltose
- glucose + fructose = sucrose
- glucose + galactose = lactose
11
Q
what is a lipid?
A
they are hydrophobic and are used for energy store
12
Q
what is a fatty acid?
A
- monomer of lipids
- Amphipathic molecule
- Hydrophilic carboxylic acid head is ionized and polar
- All the carbons are single bonded - saturated
13
Q
what is a triaglycerol?
A
- Glycerol with 3 fatty acids that is used to store energy
- The double bonded unsaturated fatty acids adds kinks in tails
- The single bonded saturated fatty acids allows them to pack together efficiently
- Hydrophobic interactions between the tails

14
Q
what is a major component of biological membranes?
A
phospholipid bilayer
15
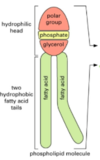
Q
what is a phospholipid?
A