Biochemical Indicators of MI Flashcards
(26 cards)
When should bloods be taken following a MI
Not until 4 hrs have elapsed
SPIN
Specificity high & positive result
=> Rules disease in
SNOUT
Sensitivity high & negative result
=> rules disease out
TnC binds to
Ca2+
TnI binds to
INHIBITS binding of actin to myosin
TnT binds to
Tropomyosin
Similarities between cardiac troponins and skeletal muscle troponins
Cardiac TnC = skeletal TnC
Differences between cardiac troponins and skeletal muscle troponins
Cardiac TnT and TnI are different
- Marker of choice for detection of MI
When do TnTs and TnIs appear in plasma
4-8 hrs after MI
Protracted release from disintegrating myofilaments
What does [Tn] on admission correlate with
6 week mortality
Structure of creatine kinase
DIMER
Muscle type - 2M
Brain type - 2B
MB - myocardium (CK-MB) but 1-3% skeletal muscle
When does CK-MB increase
1-3 hrs post MI
How is CK-MB expressed
What should the value be
CK-MB:total CK activity
Should exceed 5% total activity
Why is Troponin preferred over CK-MB
Total CK has poorer specificity due to presence in skeletal muscle
- injury due to trauma, surgery

Enzymes in serum following an uncomplicated MI
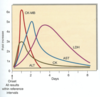
What is Myoglobin used for
To exclude MI
Rises early following MI but not specific for cardiac muscle

Time sequence of change in plasma cardiac markers after acute myocardial infarction

Name the 3 cardiac enzymes
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (HBD)
- Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) - isoenzymes measured
What are isoenzymes
- Products of different genes
- Share similar AA sequences
- Catalyse the same rxn
- Multiple subunits - LDH = tetramer, H type and M type
What is the marker of choice in detection of reinfarction within the 1st week
CK-MB
Optimal timing of sample
Blood sampling @ presentation, then @ 6-9 hours and again 12-24 hours (if earlier samples are -ve)
Effect of ischaemia on albumin
N-terminus of albumin is altered
Probably occurd through a series of chemical rxns involving free-radical damage-altered albumin (IMA)
What is IMA unable to bind to
Metals (e.g. cobalt) @ N-terminus
When is albumin converted to IMA
When albumin circulating in blood comes in contact with ischaemic tissue in the heart


