Biochem - Carbohydrate Digestion Flashcards
1
Q
How many units make up:
- monosaccharides
- oligosaccharides
- polysaccharides
A

2
Q
Name the sugar

A
mannose
3
Q
name the sugar

A
D-Ribose
4
Q
name the sugar
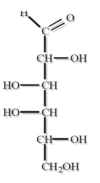
A
D-Galactose
5
Q
name the sugar

A
D-Glucose
6
Q
name the sugar

A
D-Fructose
7
Q
Maltose
- What two monosaccharides compose maltose
- How are they linked together
- Where is maltose derived from
A
- 2 alpha-D-glucose
- alpha 1,4 glycosidic link
- maltose is derived from starch

8
Q
Sucrose
- What two monosaccharides compose sucrose
- How are they linked together
A
- alpha-D-glucose + beta-D-fructose
- Glc-alpha-1-2Fru

9
Q
Lactose
- What two monosaccharides compose Lactose
- How are they linked together
A
- Beta-D-Gal + Alpha-D-Glc
- Beta-1,4 glycosidic link

10
Q
Starch
- is this a homopolysaccharide, heteropolysaccharide, or a glycoconjugate?
- where is it commonly found?
- How are the components linked together?
- name the two types and how they are different
A
- homopolysaccharide
- main storage of plant sugar
- linked with alpha glucose
- Amylose - 1,4 glc links - helical configuration
Amylopectin - 1,4 glc & 1,6 glc - branched structure

11
Q
Glycogen
- is this a homopolysaccharide, heteropolysaccharide, or a glycoconjugate?
- where is it commonly found?
- How are the components linked together?
A
- homopolysaccharide
- main glc storage form in animals
- 1,4 and 1,6 alpha

12
Q
Cellulose
- is this a homopolysaccharide, heteropolysaccharide, or a glycoconjugate?
- where is it commonly found?
- How are the components linked together?
- Why can’t humans digest this?
A
- homopolysaccharide
- chief constituent of plant cell walls
- linked by Beta-1,4 linkage
- Humans lack cellulase, which is needed to hydrolyze Beta-1,4 bonds

13
Q
Heteropolysaccharides
- Are these branched or unbranched?
- List the common components of heteropolysaccharides
- What are the most abundant heteropolysaccharides int he body?
- Describe the charge of the most abundant heteroploysaccharides
A
- long unbranched containing a repeating disaccharide unit
- Disaccharide unit of a modified sugar and a uronic acid
Such as: N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) or N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc)
&
Glucuronate or iduronate - Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
- highly negative charged molecules
14
Q
Hyaluronates, chondroitin 4- and 6-sulfates, keratan sulfates, dermatan sulfates, and heparin & heparan sulfates are examples of….
Homopolysaccharides
Heteropolysaccharides
Glycoconjugates
A
Heteropolysaccharides
15
Q
What are the three main types of glycoconjugates?
A
Proteoglycans
Glycoproteins
Glycolipids