Basic Science & Non-Tumor pathology Flashcards
Which bone graft substitue disappears the most quickly in vivo?
Calcium sulfate
What is the rate of decay in bone mass after skeletal maturity?
After menopause in women?
0.3-0.5% per year after skeletal maturity
a further 2-3% for untreated women during the decade after menopause
What kind of collagen is fibrocartilage?
Type 1
same as bone
So scar = type 1 collagen
What cell type accounts for 90% of the adult skeleton?
osteoCYTE
rhBMP-2 is approved for what uses?
Single level ALIF from L2-S1 in DDD with a fusion device
open tibial shaft fratures stabilized with an IM N and treated with 14 days of initial injury
What is the bending rigidity of a plate proportional to?
Thickness ^3
What is false about osteocalcin?
- It is the most abundant noncollagenous protein of bone
- It is secreted by osteoclasts
- It is involved in mediating calcium homeostasis
- It has been used as a biochemical marker of bone formation
- It is part of the organic matrix of bone
2
It is secreted by osteoBLASTS
What is the increase in mortality risk after a fragility fracture of:
vertebra
hip
Vertebral fragility fracture: 15% increase
Hip fragility fracture: 20% increase
How much devascularization does reaming cause?
It devascularizes 50-80% of the cortex
Muscle duration and speed of contraction are most dependent on what?
Fiber type
Type II (fast twitch) contract faster, stronger and fatigue quicker
What happens with removal of the AER?
Limb truncation
AER controls longitudinal growth

Name the rare, but deadly, complication of Paget’s
What is the prognosis?
Paget’s Sarcoma
secondary transformation into osteosarcoma > chondrosarcoma > spindle cell sarcoma
<1%
5 year survival <5%
Distraction osteogenesis - bone forms by what type of ossifciation?
intramembranous (primary) ossifciation
Name 4 results of joint immobilization on articular cartilage
cartilage thinning
tissue softening
reduced proteoglycan content
cartilage erosion
What’s the role of collagen in artiular cartilage?
Prevent swelling of articular cartilage that would otherwise occur due to the effect of aggrecan in drawing in water
What is the mechanism of botox?
Inhibition of ACh release from presynaptic vesicles
How do local anesthetics works?
Interfere with conduction (depolarization)
Rate of decrease of vertebral fragility fractures after bisphosphonate treatment at 1 & 3 years?
1 year: 60% decrease
3 years: 40% decrease
Also decreased non-vertebral fraglity fractures 40%
Area of growth plate pathology in rickets
zone of provisional calcification
This is why there is a widening of physis on xray, bc the physis doesn’t ossify!
3 radiographic findings in osteopetrosis
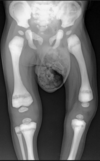
Rugger jersey spine
Erlenmeyer flask distal femur
Thickened cortex/lack of a IM canal
Phases of ligament healing
inflammatory
- neutrophils & macrophage mediated with growth factors involved
Proliferative
remodeling
maturation
What happens to water content of cartilage with normal aging? in OA?
Decreases with normal aging
Increases with OA
What supplies the inner and outer parts of bone? (blood vessels)
Nutrient artery system supplies inner 2/3
is a high pressure system
Periosteal system supplies outer 1/3
is a low pressure system
50 year old DM patient comes in with sudden onset of unilateral leg weakness, absent reflexes on that side and weight loss of about 15 - 20 lbs. No history of radiculopathy or back issues. Diagnosis? 1 differential
Diabetic lumbosacral plexopathy (basically diabetic neuropathy)
Acute, stepwise onset of unilateral weakness
Associated with poor diabetic control, absent reflexes and weight loss (up to 40 lbs)
dDx: tumour