Basic Calculus Flashcards
(29 cards)
What is the formula for integration by parts?

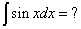
= -cos(x) + C

= tan(x) + C

= -cot(x) + C

= sin(x) + C

= sec(x) + C
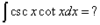
= -csc(x) + C
What is the substitution rule for definite integrals?
If g’ is continuous on [a,b] and if f is continuous on the range of u=g(x) then:
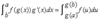
What is the basic substitution rule, not necessarily for definite integrals?
If u=g(x) is a differentiable function whose range is an interval I, and f is continuous on I, then
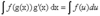
if the area is bounded by curves y=f(x) and y=g(x), and the lines x=a and x=b, where f and g are continuous and f(x) > g(x) for all x in [a,b];
What is the formula for the area between the two curves?

If the function is symmetric and f is continuous on
[-a,a] and f is even such that [f(-x)=f(x)] then


If the function is symmetric and f is continuous on
[-a,a] and f is odd such that [f(-x)=-f(x)] then

= 0
The fundamental theorem of calculus states that if f is continuous on [a,b], then:
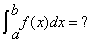
= F(b) - F(a)
Where F is any antiderivative of f. That is, a function such that F’=f.
Using the basic properties of integrals, and assuming that f and g are continuous:

= c (b-a)
Using the basic properties of integrals, and assuming that f and g are continuous:


Using the basic properties of integrals, and assuming that f and g are continuous:


Using the basic properties of integrals, and assuming that f and g are continuous:


Using the properties of definite integrals:


Using the properties of definite integrals:

= 0
Using the properties of definite integrals:


Using sigma notation rules:

= nc
Using sigma notation rules:


Using sigma notation rules:


Using sigma notation rules:












