Basic C++ Flashcards
(28 cards)
Mutable
Allow update non <test> static member from const function</test>
Compiler constant trick
Enum enum { dimension = 10}
double array[dimension];
Explicit Inlining
Class Test {
Inline void setdate();
};
void Test::setdate() { ….. }
Why function style cast
Optimize constructor call when return an object by function by value.
Complex getComplexnumber() {
return Complex( real, image)
}
Array initialization
int array[3] = {1,2,3}
Placement new
Syntax T *ptr = new (/* address */) T ( optional args )
inheritance: Access Privileges Public, Protected and private
if Public on derived class everything is the same, if Protected then Public of base class will be protected, if private then Public and protected of base class will be private
How to change inherited access for some function of base class?
By keyword “using :: under Public: or Protected: or Private:
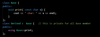
inheritance: Function Hiding
if derived class has the same function name then that function no longer access on base class. We can use “using ::; to make it available. or you can explicit specify ::
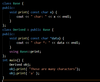
what function never inherited by derived class
Constructor, destructor and assignment operator
what is upcast and sliced off in term of Derived-to-Base class
upcast is casting pointer of derived class to base class sliced off is create base class by derived class
why do we need virtual function?
to able to have pointer of base class but the actual call will call derived class function.
Note: If derived class object call base class function and inside base class function call function that have the same name as base and derived then the function on base class will be called if it is not virtual function.
Ex:
class dog {
void bark() { cout << “I’m dog”; }
void seesomething() { bark(); }
}
class yellowdog : public dog {
void bark() { cout << “I’m yellow dog”; }
}
function bark should be virtual function
why destructor should declare as virtual function
to make sure that derived class destructor wiil get called.
Can we less restrict exception specification in virtual function?
No.

why use virtual in part of derivation process?
to solve problem of two subclass of class has common class (diamond problem). For instance, base class “Appliance” is derived by “AlarmClock” also derived by “Radio”. And class “AlarmClockRadio” derived both “Radio” and “AlarmClock”. We want to create only one base class “Appliance”
How to choose to call base class constructor?
Write base class name followed by a parenthetical list of arguments to be passed to constructor.

to use “atol”, what is include file?
is this program call copy constructor of MyClass?
MyClass a, b;
a = b;
No This program will call assignment operator on a=b.
Is copy constructor called or assignment operator called from the following snippet code:
MyClass a;
Const MyClass b = a;
Copy constructor is called because: Copy constructor is called when a new object is created from an existing object, as a copy of the existing object
What is Conversion Operator
We can also write conversion operators that can be used to convert one type to another type.
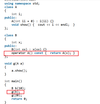
What will happen?
Test *ptr = new Test;
There are actually two things that happen in the above statement–memory allocation and object construction; the new keyword is responsible for both. One step in the process is to call operator new in order to allocate memory; the other step is to actually invoke the constructor. Operator new only allows us to change the memory allocation method, but does not do anything with the constructor calling method. Keyword new is responsible for calling the constructor, not operator new.
How can overload operator?
It is started by “operator” keyword then by symbol of operator.
int operator+(int y); // t+y means t.operator+(y)
We can use operator to convert object to other type
operator string() const { return to_string(a); }
What is global operator and why do we need it?
If that operator is not the memeber of that class then we need to create friend class in that object to support that operator.
Ex: operator “<<”, we want ostream to work with our object with ostream. ostream class is in the left side (cout << myobj; // cout.operator<<(myobj)).
We can’t change ostream class then we have to add global operator in our class then it will work with ostream.
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream &out, myclass) { ???; return out;}
When to use static_cast
- to convert object from one type to another, operator type conversion need to be defined
- convert pointer/reference from one type to related type


