Basic Algorithm Scripting Flashcards
(10 cards)
Return the length of the longest word in the sentence provided to a function.
Your response should be a number.
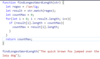
Create a function that takes a string as an argument and returns a string of the argument reversed.
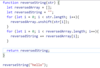
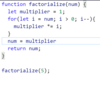
Return the factorial of the provided integer.
If the integer is represented with the letter n, a factorial is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to n.
Factorials are often represented with the shorthand notation n!
For example: 5! = 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5 = 120
Only integers greater than or equal to zero will be supplied to the function.
Return an array consisting of the largest number from each provided sub-array. For simplicity, the provided array will contain exactly 4 sub-arrays.
Remember, you can iterate through an array with a simple for loop, and access each member with array syntax arr[i].
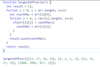
Check if a string (first argument, str) ends with the given target string (second argument, target).
This challenge can be solved with the .endsWith() method, which was introduced in ES2015. But for the purpose of this challenge, we would like you to use one of the JavaScript substring methods instead.

Repeat a given string str (first argument) for num times (second argument). Return an empty string if num is not a positive number. For the purpose of this challenge, do not use the built-in .repeat() method.

Truncate a string (first argument) if it is longer than the given maximum string length (second argument). Return the truncated string with a … ending.

Create a function that looks through an array arr and returns the first element in it that passes a ‘truth test’. This means that given an element x, the ‘truth test’ is passed if func(x) is true. If no element passes the test, return undefined.
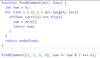
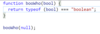
Check if a value is classified as a boolean primitive. Return true or false.
Boolean primitives are true and false.