Bariatric Surgery Flashcards
Indications for Bariatric surgery?3
- BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2 without comorbidities
- BMI 35-39.9 kg/m2 with comorbidity
- BMI 30-34.9 kg/m2 (w/specific comorbodities)
BMI 35-39.9 kg/m2 with comorbidity which comorbities? 13
- Type 2 DM 2. OSA
- HTN
- Hyperlipidemia
- Obesity-hypoventilation syndrome (OHS)
- Pickwickian syndrome (OSA+OHS)
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
- Pseudotumor cerebri
- GERD
- Venous stasis disease
- Severe urinary incontinence
- Debilitation arthritis
- Impaired quality of life
BMI 30-34.9 kg/m2 with what comorbidites? 2
- Uncontrollable Type 2 DM
- Metabolic syndrome Lack of evidence to support long term benefit in this group
Contraindications to bariatric surgery? 10
- History of bulimia
- Age > 65 or less than 18
- For lipid or glycemic control
- For CV risk reduction
- Untreated major depression or psychosis
- Binge-eating disorders
- Current drug or alcohol abuse
- Severe cardiac disease with prohibitive anesthetic risks
- Severe coagulopathy
- Inability to comply with requirements including (life-long nutritional supplements) & dietary changes**
Preoperative assessment includes what? 3
- Psychological
- Medical
- Anesthetic risk
Preoperative assessment requires a team approach Who? 5
- Nutritionist
- Medical bariatric specialist
- Psychologist/Psychiatrist
- Clinical nurse specialist
- Surgeon
Goals of the psychologic assessment 4
- Is the patient able and willing to make the necessary changes?
- Identification of mental disorders
- Social history in regards to previous weight loss attempts, physical activity, substance abuse, compulsive eating
- Does the patient have the cognitive ability to do this and the support to carry it through?
Components of the psychological assessment 4
- Behavioral
- Cognitive/emotional
- Current life situation
- Expectations
Medical assessment includes? 2
Complete history and physical exam
Mechanisms of weight loss with surgery 3
Restriction
Malabsorption
Both
Restrictive surgeries do what? What are the three general processes?
Limit caloric intake by reducing the stomach’s capacity:
- Resection
- Bypass
- Creation of a proximal gastric outlet
Specific Restrictive surgeries? 3
- Vertical banded gastroplasty
- Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding
- Sleeve gastrectomy
Malabsorptive surgeries do what? How is this accomplished? 2
Decrease the effectiveness of nutrient absorption by shortening the length of the functional small intestine:
- bypass of the small bowel absorptive surface area
- diversion of the biliopancreatic secretions that facilitate absorption
Malabsorption surgeries 2
- Jejunoileal bypass
- Duodenal switch operation
Combination restrictive/malabsorptive surgeries 3
- Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB)
- Biliopancreatic diversion
- Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch
3 Most common bariatric surgeries
- Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (47%)
- Sleeve gastrectomy (28%)
- Laparoscopic adjustable gastric band (18%)
Roux-en Y gastric bypass (RYGB)
Most commonly performed bariatric surgery in the US
47% of weight loss surgeries done in 2011
Describe this?
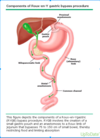
RYGB surgery
- Gastric pouch is how big?
- Gastric pouch attached to a section of small bowel ______cm in length (gastrojejunostomy)
- Cut ends of the _____________and the __________are then connected 75 to 150 cm distal from the gastrojejunostomy
- Gastric pouch less than 30 ml
- 75-150 cm in length (gastrojejunostomy)
- biliopancreatic limb, the Roux limb
RYGB
Major digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs where?
in the common channel where pancreatic enzymes and bile mix
Weight loss mechanism
- What part of restrictive?
- What contributes to the malabsorption part?
- What suppressses the appetite?
- What two substances are increased post bypass? and what will this promote?
- Small pouch is restrictive
- There is malabsorption because of the “removed” small bowel
- Ghrelin inhibition (suppresses appetite)
- GLP-1 and CCK increased post bypass (may promote an anorectic state)
Gastrojejunostomy can result in ____________with high sugar meals
Describe this?
- Dumping syndrome
- lightheadedness, nausea, diaphoresis and/or abdominal pain, and diarrhea
Expected weight loss with RYGB
Up to 70% of extra weight in 2 years
Describe the Sleeve gastrectomy?
Second most common weight loss surgery performed worldwide
28% of all procedures in 2011

Sleeve Gastrectomy
- Most of the what is removed?
- Advantages? 2
- New stomach is resistant to what?
- Contains a few _______producing cells
- Most of the greater curvature of the stomach is removed
- Safer and technically less difficult to perform than RYGB
- New stomach is resistant to stretching without the fundus
- ghrelin
Weight loss mechanism: for sleeve gastrectomy?
4
- Restrictive
- Alterations in gastric motility
- Decreased ghrelin levels
- Increased GLP-1 and PYY (promote less hunger)
Expected weight loss with sleeve gastrectomy?
60% of excess weight lost in 2 years
Laparoscopic adjustable gastric band surgery
Describe this?
18% of bariatric surgeries done in 2011

- What is the lap band and where is it placed?
- How does it work?
- Goal of band adjustments? 2
- Soft silicone ring connected to an infusion port placed in the subcutaneous tissue
- Ring is inflated with saline to cause variable degrees of restriction
- Goal of band adjustments
- Allow a cup of dried food
- Satiety for at least 1.5 to 2 hrs after a meal.

- Lowest mortality rate among bariatric pts?
- Lap band
Weight loss mechanism for Lap Band?
Purely restrictive
Expected weight loss for lap band?
50-60% of excess weight lost at 2 years
Expected short term weight loss following bariatric surgery for:
Gastric bipass?
Gastric band?
Sleeve gastrectomy?

Post surgical diet?
Usually have a liquid diet that progresses to soft then full diet over a period of weeks to months
- When should we monitor weight and blood pressure?
- Watch for what? especially if the pt is vomiting?
- How often should they F/U? 3
1, Monitor at every follow up visit
- Watch for hypotension (especially if persistent vomiting)
- Check BP and weight every 4-6 weeks for the first 6 months
- Then at 9 and 12 months post surgery
- Then annually
Macronutrient needs? 3
Which surgery does not cause significant macronutrient deficiencies?
1, Protein**,
- carbohydrates and
- fats
RYGB
- Lap band common deficiency?
- Sleeve geastrectomy common deficiency?
- RYGB? 7
(but how many vit? 6)
- Lap Band
Folate deficiency
- Sleeve gastrectomy
B12
- RYGB
- Vit A, D, E, K, B1 (thiamine), B12
- Iron,
- Copper,
- Zinc
- Folic acid,
- Biotin,
- Selenium
Routine labs at 3, 6, 12 months then annually
10
- CBC
- CMP
- Iron studies, ferritin
- B12
- Lipids
- 25 OH-Vit D, PTH*
- Thiamine
- Folate
- Zinc
- Copper
Medication management post surgery
- Change meds from delayed release to immediate release. How?
- How should we manage glycemic control?
- How should we manage antireflux symptoms?
- Crush or liquid formulation
- In general should DC oral antidiabetic meds and use insulin therapy for glycemic control
- Usually can DC antireflux meds except after sleeve gastrectomy reflux symptoms increase
Medication management post surgery
- What kind of pills may be less effective?
- In general avoid_____?
- OCP
- NSAIDs
In general avoid NSAIDs:
- Especially in who?
- Why?
- Especially in patients who have had a Roux-en-Y
- They have very little stomach area and are a set up for ulcers!
Factors that affect glycemic control post surgery
- How many calories a day for the first month?
- Average weight loss in the first month?
- 400-800 kcal diet/day for the first month
- Average weight loss in first month is 20-40 pounds
Further improvement in glycemic control post RYGB
- Improvement in DM control happens regardless of what?
- DM remission can occur in the first month
But in 1/3 of patients recurs when?
- Exposure of distal jejunum to the undigested nutrients. This causes increased what? 3
- the amount of weight loss
- 5 years
3.
- peptid YY,
- GLP-1
- GIP
Late complications (post 30 days)
4
- Cholelithiasis
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Neurologic complications
- Psychological complications
Complications of RYGB
11
- Gastric remnant distention
- Stomal stenosis
- Internal hernias
- Short bowel syndrome
- Dumping syndrome
- Metabolic/nutritional derangements
- Renal failure
- Post-op hypoglycemia
- Change in bowel habits
- Failure to lose weight and weight regain
- Ventral incisional hernias**
Which complication would present with these symptoms?
Upper abdominal pain
Hiccups
LUQ tympany to percussion
Shoulder pain
Abdominal distention
Tachycardia
Shortness of breath
Large gastric bubble on Xray
Gastric remnant distention
Gastric remnant distention is what? 2
Treatment?
- Gastric pouch severe distention secondary to mechanical obstruction or paralytic ileus
- Progressive distention and rupture
- Treatment – emergent surgery
MAY BE FATAL
Stomal stenosis
presents how?
6
- Several weeks post op
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Dysphagia
- GE reflux
- Inability to tolerate oral intake
Stomal stenosis
- is what?
- Workup? 2
- Tratment?
- Narrowing at the anastomosis (pouch to Roux limb)
- Work up: endoscopy or UGI series
- Treatment: endoscopic balloon dilation
Marginal ulcers
- Occur near where?
- What is it? 2
- Causes? 5
- Occur near the gastrojejunostomy
2.
- Acid injury to the jejunum or
- associated with gastrogastric fistula
3. Causes: - Poor tissue perfusion
- Excess acid
- NSAIDs
- H. pylori*
- Smoking
Marginal ulcers
- symptoms? 4
- diagnosis and
- treatment? 5
- Symptoms:
- Nausea,
- pain,
- bleeding and/or
- perforation - Diagnosis:
Upper endoscopy
- Treatment:
- Acid suppression
- Sucralfate
- DC NSAIDs
- DC smoking
- Test and treat H. pylori
Acute cholecystitis/cholelithiasis
signs and symptoms?
7
- RUQ pain
- R shoulder pain or pain in the R upper back
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Pain may worsen with deep inspiration
- Pain may last longer then 6 hr and start post eating
- Tender RUQ on exam
Acute cholecystitis/cholelithiasis
- Can be prevented by what?
- Dx?
- Tx?
- Can be prevented by post operative ursodiol
- DX: ultrasound
- TX: surgical removal of the gallbladder
What is this?
Patient presented with abd pain post gastric bypass

- Short bowel syndrome results in what?
- In severe cases it may require what?
- Results in severe micro and macronutrient deficiencies
- In severe cases may require intestinal transplantation
Early dumping syndrome presents how?
4
What percent of pts develop this?
What causes it?
15 min after eating development of
- colicky abdominal pain,
- diarrhea,
- nausea and
- tachycardia
Up to 50% of patients develop either early or late dumping syndrome
Prominent post ingestion of simple carbohydrates
Late dumping syndrome
- How long after meal?
- Symptoms? 4
- 2-3 hours after a meal
2.
- Dizziness,
- fatigue
- Diaphoresis
- weakness
What complication would this patient have?
Blackouts and Seizures
Severe hypoglycemia
Severe hypoglycemia
- May be secondary to what?2
- What may resolve these symptoms?
1.
- May be secondary to insulinoma
- May be secondary to islet cell hypertrophy
2. Slowing food transit time may resolve the symptoms
Change in bowel habits
- Whats common in RYGB?
- Whats common in gastric banding?
- Diarrhea or loose stools common post RYGB
- Constipation common post gastric banding
Pt complains
“I’m not losing weight” or “I’m gaining weight”
what could this be?
4
- Maladaptive eating patterns
- Gastrogastric fistula
- Gradual enlargement of the gastric pouch
- Dilation of the gastrojejunal anastomosis
Complications from gastric banding
8
- Pouch dilation
- Stomal obstruction
- Band slippage, infection or erosion
- Incisional hernias
- Port-tubing disconnections
- Port infections
- Esophagitis
- Esophageal dilation
What would these symptoms indicate?
Persistent nausea, vomiting and inability to tolerate secretions or oral intake?
Stomal obstruction
Stomal onstruction
- Can occur when?
- Mayb be secondary to what?2
- Dx?
- Tx?
- Can be acute (shortly following surgery)
- May be secondary to
- edema or
- due to the band being too tight - DX: UGI
- TX: NG tube to decompress until edema subsides or surgery for band revision
Band erosion
will cause what kind of sympotms?
5
- Infection
- Failure of weight loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- Epigastric pain
- Hematemesis
Band erosion
- Occurs at a mean of how many months?
- Dx?
- Tx?
- Occurs at a mean of 22 months
- DX: endoscopy
- TX: surgical removal
Most common sleeve gastrectomy complications
4
- GERD
- Bleeding
- Stenosis of the stoma
- Leaks
What is the most serious complication of SG?
gastric leaks
Occur in up to 5.3% of patients
Gastric Leaks usually due to local factors that impede healing?
- Inadequate blood supply at the staple line
- Gastric-wall heat ischemia
- There can be high intragastric pressure


