Attenuation & Decibels Flashcards
___ is How the strength of the ultrasound changes as is moves through the medium
attenuation
____ is the Rate that work is done, energy
in US it is a wave of energy
Some energy is released into the medium during propagation
Measured in _____
Determined by the _____
power
Watts (mW)
source
_____ is the Power of the wave per area over which it is spread. what is it determined by?
intensity
source
what is the formula for intensity? what is it measured in?
I (W/cm2) = Power (W)/ Area (cm2)
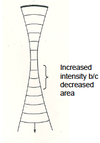
what is intensities relationship to power and area?
Increasing power increasing Intensity
Decreasing area increasing Intensity - focusing
Example: Sun on dry leave, focused through a lens will increase the intensity and cause leaves to burn – power is unchanged, only area changed
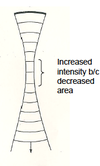
what increases w/ increasing power and intensity?
what improves the image quality?
potential bioeffets.
Image quality – Will generally be improved by increasing power because you get stronger reflections back
_____ is the Maximum variation of an acoustic variable
Unit depends on the variable being measured
amplitude
what is the relationsihp b/t amplitude and intensity?
Intensity = amplitude2
Amplitude = square root of Intensity
If amplitude increased by 2x, then intensity increased 4x
what are power and attenuation described in ?
decibels
what is a decibel?
what does it represent?
what do you need to compute a decibel change? why?
Bel – logarithmic ratio of the relative powers of 2 beams.
Decibel is 1/10 of a bel, it is a unit of measurement used in sound applications
Represents the smallest degree of difference in loudness the normal human ear can hear
Relative values, not absolute – need 2 powers or intensities to compare in order to compute a decibel change
*50% off of $100 = $50 it has changed by 50$. if it’s 3 decibels, it has increased 2x from where it started
what is a logarithms
Different way to look at numbers, called log base 10
The log of a number is the amount of times 10 has to multiplied together to get the number.
Also described as the power to which 10 must be raised to get the number
Look at the chart

what is
Log10 of 10 =
Log10 of 100 =
Log10 of 1000 =
Log of a fraction is –
Log10 of .01 = -2
why are these used?
1
2
3
Logs are used when dealing with very large numbers (to many 0). In sound application we are comparing 2 like quantities, such as power, intensity or amplitude
When comparing power, intensity or amplitude change
if there is an increase, it is a ____
If there is a decrease, it is an _________
gain
attenuation

Input power is 10W, output power is 100W. What is the decibel change? Is it a gain or attenuation?
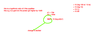
Input power is 100W, output power is 10W. What is the decibel change? Is it a gain or attenuation? What is the power ratio?

Beginning intensity is 100 mW/cm2, ending intensity is 10 mW/cm2. What is the decibel change? Is it a gain or attenuation? What is the intensity ratio?

Beginning intensity is 100 W/cm2, ending intensity is 10 mW/cm2. What is the decibel change? Is it a gain or attenuation? What is the intensity ratio?
Units must match.

When comparing voltage and amplitude, you must use ___in the equation
Because intensity = amplitude2
Because Power = voltage2
20

Beginning voltage is 100 mV, ending voltage is 10 mV. What is the decibel change? Is it a gain or attenuation? What is the voltage ratio?
The input intensity is 10 times less than the output intensity. What is the intensity ratio? What is the “relative intensity?”
This is asking for dB change.

The transmitted intensity is 1000 times greater than the reflected intensity. What is the relative intensity?
This is asking for dB change.

Power one is 100 W and power two is 50 W. What is the decibel change?
Power one is 100 W and power two is 200 W. What is the decibel change?

what are the intensity power ratios for 3, 6, 10

Power one is 100 W and power two is 25 W. What is the decibel change?
Power one is 100 W and power two is 400 W. What is the decibel change?











