Arbitrage Theory and Options Flashcards
(28 cards)
Define Asset Span
The set of different payoffs we can achieve in the future via trade in the existing assets today. Typically denoted by M
Define Complete markets
Market are complete if any newly issued security can be replicated by current assets. M = R^s
Wat is the relation between M and R^s in incomplete markets?
M is a subset of R^s
Define arbitrage
Making a certain profit with zero initial capital. hx >= 0 and ph’ <= where one holds with strict inequality
Define a strong arbitrage
Zero or positive payment tomorrow. Positive payment today
State the law of one price mathematically

State the law of one price qualitatively
Any two portfolios with the same payoffs must have the same price
Define a risk-premium
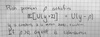
How toderive risk-neutral probabilities?
Define security price as a inear combination of the state prices. Divide and multiply by the sum of state prices. Each risk-neutral probability is the state-price divided by the sum of state prices
What is the Covered interest rate parity?
F = S * (1+r*)/(1+r)
F and S are forwards and spot prices measured as amount of fx per domestic currency
r* is foreign interest rate. r i domestic currency
How to derive the CIRP?
Borrow 1/(1+r) at home (need to repay 1)
Buy foreign FX
Invest abroad
Sell forward fx, 1/F
1/(1+r) * S * (1+r*) * (1/F)
Since you will have to repay only 1, the payoff to this strategy must be 1 for there not to be arbitrage
What are portfolio holding in vector form?
h = (h1, h2, … , hj)
What is portfolio payoff in vector-matrix notation?
hX
What is the regular formulation of the Fundamental Theorem of Finance?
Theorem 1:
Security prices exclude arbitrage iff there exist strictly positive state prices
Theorem 2:
Security prices exclude strong arbitrage iff there exist positive state prices
How does market completeness relate to ‘no arbitrage’?
No aribitrage requires existence, not uniqueness, of positive state prices. We can still price redundant assets in incomplete markets
Define Absolute Risk Aversion?
A(w) = - u’‘(w) / u’(w)
Define Relative Risk Aversion
RRA = - u’‘(w)/u’(w)*w = A(w) * w
What is the “general” fundamental theorem of finance=
Equillibrium is a sufficient condition for ‘no arbitrage’ which is a necessary and sufficient condition for positive state prices
What is dynamic completion and when is it possible?
It is completing the market by retrading. Allows for completing markets when number of assets is below number of states. Requires that the maximum number of states from each note does not exceed the number of securities
What is the upper bound for the price of a call?
c <= S
What is the lower bound for the price of a call?
c >= S - K/(1+r)
What is put call parity?
c + k/(1+r) = p + S
How can options complete the markets?
Imagine the market has one asset which pays a different payoff in each state. Then issue s-1 options with strike price at the assets payouts (except fore the largest)
What is the welfare effect of completing the markets?
Fully completing the markets will always have a positive welfare effect.
Partially completing the markets need not make people better off. May generate externalities, requiring regulation


