AQA GCSE Additional Biology Flashcards
What is the scientific name for a simple cell?
Epithelial cell
What do we call a cell with special features
A specialised cell
Nucleus, ribosomes and mitochondria are examples of what?
Cell organelles
What is the function of a cell nucleus?
Controls the cell and contains genetic information
What is the function of mitochondria?
Mitochondria are where energy is released for the cell through respiration.
What is the function of ribosomes?
Ribosomes carry out protein synthesis. This is where proteins are built up from amino acids.
What is the function of a cell membrane?
The cell membrane controls what can enter and exit the cell.
Name 4 specialised animal cells.
Sperm cell, nerve cell, muscle cell, ciliated epithelial cell.
Identify the parts of an animal cell.

A - Mitochondria
B - Cytoplasm
C - Ribosome
D - Nucleus
E - Cell membrane
What controls the chemical reactions inside a cell?
Enzymes
How is a muscle cell specialised for its function?
Muscle cells have fibrils that can shorten in length allowing the cell to contract.
How is a sperm cell adapted to carry out its function?
Sperm cells have a tail to swim towards and egg. They also have a streamlined shape and a large number of mitochondria to provide energy for movement.
How are nerve cells adapted to carry out their function?
They have long fibres to carry impulses and branches at nerve endings to communicate with other nerve cells.
How are ciliated epithelial cells adapted ot carry out their function?
They have cilia which can move. This allows dust and mucus to be brushed along cell surfaces e.g. mucus can be moved out of the lungs.
What type of cell is this?

Muscle cell
What type of cell is this?
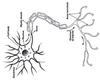
Nerve cell
What type of cell is this?
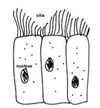
Ciliated epithelial cell
Label the plant cell.

A - Cell wall
B - Cell membrane
C - Ribosome
D - Chloroplast (containing chlorophyll)
E - Vacuole
F - Nucleus
G - Cytoplasm
H - Mitochondria
What type of cell is this?

Root hair cell
Why does this cell form a plant not contain chloroplasts?

Becaue it is a root hair cell, found in root, which do not receive sunlight so do not photosynthesise
What is a xylem vessel?
Empty tubes made from dead plant cell walls. These tubes are used to transport water from the roots up to the stem and leaves.
What is the function of a cell wall?
To strengthen and support a cell
What is the function of chloroplasts?
Chloroplasts are the organelles in which photosynthesis takes place.
What do chloroplasts contain?
Chlorophyll, which captures sunlight so that the chloroplast can carry out photosynthesis





