Appendicular Skeleton Flashcards
Clavicle
Junction of neck and anterior thorax (S-shaped bone).
Acromial end (clavicle)
Flattened lateral end that articulates with medial aspect of acromion via acromioclavicular joint

Sternal end (clavicle)
Location:
• Clavicle (medial end)
Description:
• Enlarged, medial end
• Projects above manubrium of sternum to deepen jugular notch
• Has smooth, articular surface

Scapula
Location:
• Posterior thorax
• Overlies ribs 2-7
Description:
• Large, triangular, flat bone
• Characteristic features include spine, acromion, coracoid process, and glenoid cavity
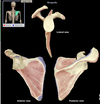
Spine (scapula)
Location:
• Scapula
Description:
• Prominent ridge on posterior surface of scapula
Comment:
• Provides attachment for trapezius and deltoid muscles
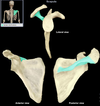
Acromion (scapula)
Location:
• Scapula
Description:
• Flattened, lateral part of scapular spine
Comment:
• Articulates with clavicle
• Subcutaneous superior point of shoulder (easily palpated)
• Provides attachment for trapezius and deltoid muscles
• Landmark for intramuscular injections

Glenoid cavity/fossa (scapula)
Location:
• Scapula
Description:
• Shallow depression at superior end of lateral border
Comment:
• Articulates with head of humerus to form glenohumeral (shoulder) joint
• Made “deeper” by rim of fibrocartilage (labrum)

Coracoid process (clavicle)
Location:
• Scapula (anterior)
Description:
• Prominent protuberance inferior to acromion of scapula
Comment:
• Provides attachment for pectoralis minor, coracobrachialis, and short head of biceps brachii muscles
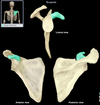
Lateral border (clavicle)
Location:
• Scapula
• Between inferior angle and glenoid cavity
Description:
• Border of scapula inferior to glenoid cavity
• Superior end has infraglenoid tubercle
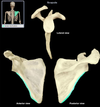
Medial border (clavicle)
Location:
• Scapula
Description:
• Border of scapula parallel to vertebral column
Also known as:
• Vertebral border of scapula
Comment:
• Provides attachment for levator scapulae, rhomboid major and rhomboid minor, and serratus anterior muscle

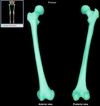
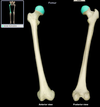
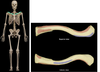
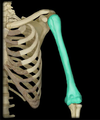
Humerus
Location:
• Arm
Description:
• Long bone
• Characteristic features include head, neck, greater and lesser tubercles, shaft, medial and lateral epicondyles, capitulum, and trochlea
Comment:
• Largest bone of upper limb
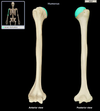
Head (humerus)
Location:
• Humerus (proximal)
Description:
• Rounded articular surface
• Continuous with anatomical neck
Comment:
• Articulates with glenoid cavity of scapula to form glenohumeral (shoulder) joint
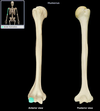
Deltoid tuberosity (humerus)
Location:
• Humerus (shaft)
Description:
• Roughened area near mid-shaft on anterolateral surface
Comment:
• For attachment of deltoid muscle

Medial epicondyle (humerus)
Location:
• Humerus (distal)
Description:
• Medial subcutaneous projection near elbow
Comment:
• Provides attachment for hand flexor muscles
• Ulnar nerve subcutaneous on posterior aspect (“funny bone”

Lateral epicondyle (humerus)
Location:
• Humerus (distal)
Description:
• Small lateral projection near elbow
Comment:
• Provides attachment for hand extensor muscles

Trochlea (humerus)
Location:
• Humerus (distal)
Description:
• Grooved surface medial to capitulum
Comment:
• Articulates with trochlear notch of ulna
• Contributes to elbow joint

Capitulum (humerus)
Location:
• Humerus (distal)
Description:
• Dome-shaped surface lateral to trochlea
Comment:
• Articulates with head of radius
• Contributes to elbow joint
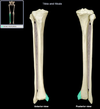
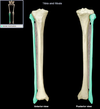
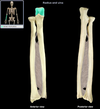
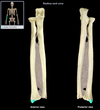
Ulna
Location:
• Forearm (medial) Ariculates with pinky!
LOOKS LIKE ICECREAM SCOOP
Description:
• Long, thin bone
• Articulates proximally with trochlea of humerus and radius
• Articulates distally with radius and carpal bones (lunate and triquetrum)
• Characteristic features include olecranon, trochlear notch, tuberosity, shaft, and styloid process
Comment:
• Fibrocartilage separates distal end from carpal bones

Trochlear notch (ulna)
Location:
• Ulna (proximal, anterior aspect)
• Between olecranon and coronoid process
Description:
• Prominent notch
• Has smooth articular surface
Function:
• Provides articulation with trochlea of humerus
Radial notch (ulna)
Holds ulna
Smaller notch right below trochlear notch
Where radius attaches

Head (ulna)
Adjacent to styloid process of ulna. Distal to trochlear notch.

Styloid process (ulna)
Location:
• Ulna (distal)
Description:
• Pointed distal projection
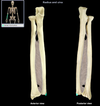
Radius
Articulates with capitulum of humerus. Also articules with the thumb (lateral)

Head (radius)
Location:
• Radius (proximal)
Description:
• Disk-shaped, with concave superior surface
• Articulates with capitulum of humerus and radial notch of ulna

Styloid process (radius)
Location:
• Radius (distal)
Description:
• Pointed distal projection
Comment:
• Provides for attachment of brachioradialis muscle
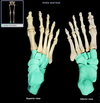
Hand
Consists of 8 carpal bones, metacarpals and phalanges

Carpals
Location:
• Hand
Description:
• Eight, small, irregular-shaped bones
• Form the wrist
Comment:
• Arranged in two rows of four
• Proximal row (scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform) articulates with radius and ulna
• Distal row (trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate) articulates with metacarpals
• Hand comprises wrist, palm, dorsum, and fingers

Scaphoid (carpal)
Location:
• Wrist
Description:
• “Boat-shaped” carpal bone
• Articulates with radius, trapezium, trapezoid, and capitate

Lunate (carpal)
Location:
• Wrist
Description:
• Crescent-shaped carpal bone
• Articulates with radius, hamate, capitate, triquetrum, and scaphoid

Triquetrum (carpal)
Location:
• Wrist
Description:
• Pyramidal carpal bone
• Articulates with lunate, hamate, and pisiform
Comment:
• Provides attachment for extensor retinaculum
• Carpal bones arranged in two transverse rows: proximal bones (lateral to medial) are scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform; distal row (lateral to medial) are trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate
• Latin: triquetrus = three-cornered (describes shape)
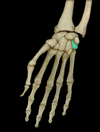
Pisiform (carpal)
Location:
• Wrist
Description:
• Pea-shaped carpal bone
• Articulates with triquetrum
Comment:
• Embedded in tendon (sesamoid bone) of flexor carpi ulnaris muscle
• Provides attachment for flexor and extensor retinacula, and flexor carpi ulnaris and abductor digiti minimi muscles
• Carpal bones arranged in two transverse rows: proximal bones (lateral to medial) are scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform; distal row (lateral to medial) are trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate
• Latin: pisum = pea (describes shape)

Trapezium (carpal)
Location:
• Wrist
Description:
• Irregular-shaped carpal bone
• Articulates with trapezoid, scaphoid, and metacarpals I-II
Comment:
• Provides attachment for flexor retinaculum
• Carpal bones arranged in two transverse rows: proximal bones (lateral to medial) are scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform; distal row (lateral to medial) are trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate
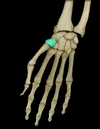
Trapezoid (carpal)
Location:
• Wrist (smallest carpal)
Description:
• Four-sided carpal bone
• Articulates with trapezium, scaphoid, capitate, and metacarpal II
Comment:
• Carpal bones arranged in two transverse rows: proximal bones (lateral to medial) are scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform; distal row (lateral to medial) are trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate
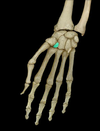
Capitate (carpal)
Location:
• Wrist
Description:
• Largest carpal bone
• Proximal surface has prominent head
• Articulates with scaphoid, lunate, trapezoid, hamate, and metacarpals III and IV
Comment:
• Latin: capitate = head
• Carpal bones arranged in two transverse rows: proximal bones (lateral to medial) are scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform; distal row (lateral to medial) are trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate

Hamate (carpal)
Location:
• Hand
Description:
• Wedge-shaped carpal bone of wrist
• Process (hamulus) projects from palmar surface
• Articulates with triquetrum, capitate, and metacarpals IV-V
Comment:
• Hamulus provides attachment for flexor retinaculum of hand
• Carpal bones arranged in two transverse rows: proximal bones (lateral to medial) are scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform; distal row (lateral to medial) are trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate
• Latin: hamatus = hooked (describes shape)
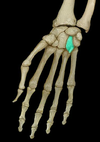
Metacarpals
Location:
• Hand
Description:
• Five small, long bones between carpal (wrist) bones and phalanges (fingers)
• Designated by Roman numeral (I-V) from lateral (thumb) to medial (little finger)
• Characteristic features are base (proximal), shaft, and head (distal)
Comment:
• Knuckles formed by heads of metacarpals

Phalanges of the Hand
Location:
• Hand (fingers)
Description:
• Small bones of fingers
• Medial four fingers have three phalanges each (proximal, middle, and distal)
• Thumb has two phalanges (proximal and distal)
Comment:
• Singular of phalanges is phalanx

Proximal phalanx (phalanges)
Location:
• Finger
• Medial four fingers: between middle phalanx and metacarpal
• Thumb: between distal phalanx and metacarpal I
Description:
• Small bone at base of fingers
Comment:
• Medial four fingers each have three phalanges (proximal, middle, and distal)
• Thumb has two phalanges (proximal and distal)
• Plural of phalanx is phalanges

Middle phalanx (phalanges)
Location:
• Finger
• Medial four fingers: between proximal and distal phalanges
Description:
• Small bone in fingers
Comment:
• Medial four fingers each have three phalanges (proximal, middle, and distal)
• Thumb has two phalanges (proximal and distal)
• Plural of phalanx is phalanges
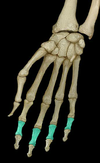
Distal phalanx (phalanges)
Location:
• Fingers
• Medial four fingers: distal to middle phalanx
• Thumb: distal to proximal phalanx
Description:
• Small bone at tip of finger
• Covered by nail on dorsal surface
Comment:
• Medial four fingers each have three phalanges (proximal, middle, and distal)
• Thumb has two phalanges (proximal and distal)
• Plural of phalanx is phalanges

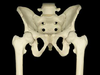
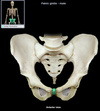
Os Coxa
hips