Apicomplexan parasites Flashcards
1
Q
apicomplexa
A
- ancient - origin 400-800mya
- diverse
- eukaryotes
- obligate intracellular life stage
- likely evolution from colpodellids - single cell photosynthetic symbionts
2
Q
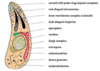
features of apicomplexan cells
A
- polarised with apical complex
- dense granules, micronemes and rhoptries (secretory)
- apicoplasts
- pellicle
- sub-pellicular microtubules
3
Q
apicoplast
A
- relic chloroplast-like organelle
- can’t photosynthesise
- fatty acid biosynthesis
- potential pesticide target
4
Q
pellicle
A
- plasma membrane surrounding double membrane
- double membrane = inner membrane complex
- defines cell movement
5
Q
sub-pellicular microtubules
A
- highly stable and sheet-like skeleton that defines cell shape
- long polymers of alpha and beta tubulin
- lie under outer compartment
- between 22 and 26 microtubules
- maintain cell surface integrity
- microtubule inhibtors often have no effect (stable)
- shape changes during invasion or division
6
Q
paired apical rhoptries
A
- sac-like and club-shaped
- protein and lipid
- anterior region (apex)
- variable number, usually 2, changes in life cycle
- vacuole formation during invasion
- no rhoptries - no invasion
- secrete contents upon invasion
7
Q
micronemes
A
- small secretory organelles
- secrete to extracellular environment or cell surface
- role in motility - abundance in gliding cells
- at apical pole
- adhesive proteins released for motility and attachmnet
8
Q
conoid vs aconoid
A
- conoid - toxoplasma
- microtubule rich basket like structure at cell tip
- role unknown
- when extruded cell moves
- when withdrawn cell stops
- aconoid - plasmodium
9
Q
lifecyle features
A
- typically 2 hosts
- one is definitive host
10
Q
definitive host
A
- organism in which pathogen undergoes sexual reproduction
- putative evolutionary origin
11
Q
toxoplasma lifecycle
A
- sporozoite oocyst in external environment e.g. soil
- oocyst ingested and bursts
- sporozoites penetrate midgut → tachyzoites
- dissemination throughout body
- bradyzoite cyst formation can occur
- carnivorous ingestion by definitive host of cyst
- cyst rupture
- trophozoite invasion of midgut epithelium → merozoites
- sporogony forming oocysts
12
Q
cryptosporidium lifecycle
A
- extracellular environmental stage
- highly resistant aquatic spores
- one host stage
- taken in through stomach lining
- sporulation and epithelium invasion
- replication and sexual development
13
Q
apicomplexan innovations
A
- antigenic variation
- host cell remodelling
- tight junction
- motility
14
Q
host cell remodelling
A
- plasmodium secretion of proteins into RBC
- alters RBS to provide parasite with what it needs to survive
- requires signal sequence PEXEL
15
Q
PEXEL
A
- plasmodium export signal
- RxLxE/Q/D sequence
- required for entry into host cell using protein release
- mutation of R to A prevents entry
- cleaved in ER by aspartic acid protease between L and E
- acetylated product recognised and translocated by translocon complex
- translocon sits in vacuole membrane
- unique to plasmodium
- host cell is effective biological extension of parasite
- conserved - similar motifs in other apicomplexa e.g. toxoplasma shuttlign ot host cell nucleus
16
Q
tight junction
A
- forms at meeting point between host cell membrane and parasite
- transient seal required for invasion
- RON2 and AMA1 (microneme proteins) injected, anchored and interact
- handshake between AMA1 and RON4 pulls parasite in to host cell
- RON 4 - rhoptry neck protein 4
- localised in ring of tight junction
17
Q
role of tight junction
A
- definite anchor point
- potential molecular sieve
- coat proteins are shed but why?
- prevent bursting of host cell


