Aortic dissection Flashcards
(28 cards)
What is Aortic dissection?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vrbsxsadiwI
Tear in the inner wall of the aorta. Blood penetrates the diseased medial layer and then cleaves the intimal laminal plain leading to dissection
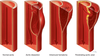
What is the area called in a dissection between the intima and media which forms?
False lumen
What are causes of aortic dissection?
AcquiredH
- Hypertension (most common)
- Trauma; deceleration injury
- Syphilis
- Use of amphetamines and cocaine
- Atherosclerosis
Congenital
- Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Bicuspid aortic valve
- Coarctation of the aorta
What are signs/symptoms of aortic dissection?
Symptoms
- Tearing/severe chest pain radiating to the back
- Collapse
Signs
- Reduced/abscent peripheral pulses
- Hypotension/hypertension
- Soft early diastolic murmur (AR)
- Pulmonary oedema
What complications of aortic dissection can cause a patient to present with sudden collapse?
- Tamponade
- Acute AR
- External rupture
Why might there be reduced/absent peripheral pulses in someone with aortic dissection?
As the dissection extends, branches of the aorta occlude sequentially leading to unequal arm pulses, acute limb ischaemia, and other signs of obstructive ischaemia
If someone with aortic dissection had anuria, what might have happened?
Dissection has spread down to the renal arteries and has occluded them
What classification systems are used to classify aortic dissections?
- Debakey - Type I, II, III
- Stanford - Type A, B

If someone with aortic dissection had hemiplegia, what may have happened?
Occlusion of the carotid artery
What is the difference between a type A and type B dissection (based on stanford classification)?
- Type A - all dissecitons involving ascending aorta, regardless of site of origin
- Type B - all dissections not involving ascending aorta
What classifies as a type I debakey dissection?
Originates in the ascending aorta, and propagates at least to the aortic arch and often beyond it distally
What classifies as a type II debakey dissection?
Originates in and is confined to the ascending aorta
What classifies as a type III debakey dissection?
Originates in the descending aorta and extends distally downwards.
Can rarely move retrograde into the arch and ascending aorta
How would you investigate someone with a suspected aortic dissection?
- ECG - exclude MI
- Initial test - CXR - Mediastinum may be widened
-
Definitive
- Contrast enhanced CT angio - if stable
- Transoesophageal Echocardiocraphy - if unstable
How does AR occur in aortic dissection?
Could cause dilation of the ascending aorta

If someone presented with a Stanford Type A aortic dissection, what would you do to manage them?
Surgery - immediately call cardiothoracic surgeons
How would you manage someone with a Stanford type B aortic dissection?
Generally managed conservatively
Meticulous BP control - aim SBP 90-120 mmHg
- IV Sodium Nitroprusside
- β-blockers - IV labetalol, esmolol or propranalol
What debakey classification is the following aneurysm?

Type I - involves ascending and descending aorta (= Stanford A)
What debaey classification is the following dissection?

Type II - involves ascending aorta only (= Stanford A)
What debakey classification is the following dissection?

Type III - involves descending aorta only, commencing after the origin of the left subclavian artery (= Stanford B)
What debakey classification is the following dissection?

Type III - involves descending aorta only, commencing after the origin of the left subclavian artery (= Stanford B)
What stanford classification is the following type of dissection?

Type A - A affects ascending aorta and arch
What stanford classification is the following dissection?

Type B - B begins beyond brachiocephalic vessels
How would you generally manage someone with suspected aortic dissection?
Determine need for surgical intervention
- Crossmatch
- ECG
- CXR
- CT/MRI/TOE
- Hypotensives


