Antimicrobial Drugs Flashcards
How Antibiotic Resistance Happens
- Antibiotics were discovered and first really used in the 20s
- Every decade there is resistance that has started to appear
- We have companies that want drugs to be used a lot (this is their product!), but we HAVE to limit our use of antibiotics
- note: dont use the word germs
- there is always resistant bacteria around, but we need to keep some competition present!

Examples of how Antibiotic Resistance Spreads
- eating meat with antibiotic resistant bacteria
- hard to know the exact role of pets in all this but they are part of it and can get resistant bacteria from owner!

Goal of Antibacterial Therapy
- not every infection needs antibiotics
- when we use them appropriately, they are to HELP the host rid of the infectious organism
- bacterial cells are different to the mammalian cell
- where as: it is hard to treat cancer cells as they are similar to the host and the drug is therefore somewhat toxic

Antibiotic therapy is most effective when…

Natural Defence Mechs of Patient
- If M.E. is damaged, they are very prone to building respiratory tract infections
- UTIs can occur for people with renal issues

Bacterial Resistance and Antibacterial Agents
- bacterial resistance existed well before antibiotics were invented!

Bacterial resistance
- Bacteria have been killing eachother with “antibiotics” for ages to kill other bacteria!
- A good amount of the antibiotics come from fungi (e.g. penicillin)

Resistance and Antibiotic selection
- resistance does not just emerge at the site of infection but the normal flora in the gut and the skin

The Gut Microbe- What does it do and why do we care?
- what happens if the gut/skin microbiome are altered by antibiotics
- both (esp. gut) is very important for the immune system and body function
- basically signals to the immune system what is ok to have in body and what isnt

Immune system and cohabiting microbiota

- Dysbiosis= when microbiome of the gut/skin become disordered and arent at the amount they should be
- loss of control by the gut and immune system
- often a mix of all these
Bigger Picture: increased prevelance in people
- Increasing in prevelance despite the fact of knowing more and more about these diseases

People with Immune Mediated Diseases
- Diseases we didnt think were immune mediated did start as immune mediated in many cases
- start with a different microbiota
- meaning antibiotics can have an effect in these situations

Antibiotics and the microbiome

Whether an antibiotic is used appropriately or not…
- we will cause resistance either way
- is the benefit going to outweigh the fact that you are going to change the microbiota
- use of antibiotics in the early stages of life seem to have the largest impact on the immune system and functionality of animal/human

Responsibility of Veterinarian
- antibiotics dont cause many side effects as they are aimed at bacterial cells, not mammalian cells (different to anti-cancer drugs, NSAIDS)
- Vets have used lightly before as there arent really any side effects to mammalian cells
- disease prevention: worming suggestions, diet, etc.
- conservatively: treat with the right dose at the right time only when needed!

Issues for food animals

Horses
- MUST be signed out or it has to be treated as a food animal

Food animals and Drug Residues
- Drugs have a calculated withdrawal time: time where drug administration has stopped and when the animal is able to be slaughtered
- REALLY try to avoid the use of antibiotics in food animals, or be very strict about it!
- even the smallest bit of antibiotics (ex: penicillin) can cause an allergic reaction in people who consume products

Food Animals and Withdrawal times
- times are stated for all registered drugs
- the criteria MUST be followed for that withdrawal period to work
- If you are giving antibiotics for an animal destined for slaughter and production, you MUST look at data sheet

If not licensed: The Cascade

- There are a lot of times where the drugs may not be licensed for a certain condition or species
- you as a vet need to make a risk based clinical judgement: happens all the time!
- need to get owner consent
- for food animals: need to have an MRL and need to be able to specify the MINIMUM withdrawal time
- also keep records of treatment

If not licensed in food animals?
- these withdrawal periods are set by LAW
- use in food animals still applies the needed use of antibiotics in general, but the added layer of withdrawal times

Gram Staining

Microbial Spectrum
- 4 quadrants
- gram (-) aerobe: like E.Coli
- Penicillinase producing staph is really important!

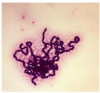
- gram + aerobic bacteria - STREP
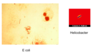
- Gram Negative aerobic bacteria

- Staph aureus
Atypical Bacteria Species
(6)
- they don’t gram stain!
enormously important as a causes of a variety of diseases depend on which area you are practicing in

Antimicrobial classes: Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis
(3)
- knowing the mech of action doesnt reallyyy change how much we use them, but it is important in our clinical reasoning
- bacitracin: in ear drops

Antimicrobial Classes: Inhibition of Cell Membrane Function
(4)
- most of these are anti-fungal drugs and not antibiotics!

Classes: Inhibition of Protein Synthesis
(5)
- chloramphenicol
- macrolides
- lincosamides
- tetracyclines -commonly used
- aminoglycosides
- these do have the capacity to change mammalian protein synthesis but much lower affinity for mammalian cells!

Classes: Inhibition of Nucleic Acid Synthesis
(5)
- chunking them doesnt matter a lot of the time, but helps to put them into groups to remember them!

When to use antimicrobials?
- only when you definitely diagnose a bacterial infection that needs treatment
- would cause critical illness and would progress if we do not treat it

Key Q’s and Clues: bacterial infection
- what are you looking for in clues? - signs of bacterial infection!
- increased body temp can ALSO occur in situations of cancer, or other illnesses (not a hard fast sign)
- neutrophil increase can happen in non-bacterial inflammation, stress, cancer

Antibiotics not indicated for….
- vomiting/no diarrhea: likely do not have a bacterial disease even if they ingested most disgusting items
- urine in cats is very hostile to bacteria (echo) - often environmental/stress. OVER ten years, urine becomes more dilute and then they are more prone to bacterial infections
- huge misconception: blood in feces needs antibiotics. not necessarily a bacterial infection causing blood to be in feces
- peridontal disease: commonly given AB’s before, during, after–> mechanically clean teeth!! don’t use the AB’s- biofilms

Choosing the right antibacterial drug
- can use guidelines, but you need to understand why those drugs are appropriate
- prescribe based on what is the most likely bacteria you are going to run into in the area of issue
- culture and sensitivity? is it recurrent?

Key Questions to Ask
(8)
*


Factors Affecting the Success of Antibacterial Therapy

Where do infections come from?
- A lot of the time the bacteria comes from within and gets to a place where it shouldnt be or they are in same area but the is not enough restriction placed by the body–> become a pathogen

Infection based on location
- gram (-) aerobes and anaerobes in large bowel?
- liver: coming from up the biliary tract or systemically (which would be staph)
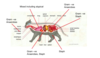
What groups of bacteria live in the gut?
What Bacteria live on the skin?
Examples of gram (-) bacteria that cause disease in animals























































