Antibiotics 2 Flashcards
Rifampin MOA, Spectrum & Resistance
Mechanism:
BacteriCIDAL- Binds bacterial RNA polymerase at the active center, blocking the elongation of the mRNA
Spectrum: WIDE - Gram + and -, Mycobacteria tuberculosis
Resistance:
Intrinsic resistance- in some bacterial strains the drug is unable to bind to the β subunit of RNA polymerase
Acquired resistance- the strain acquires mutations in rpoB gene preventing drug binding
Treat Mycobacteria tuberculosis with 4 antibiotics due to the high rate of resistance
Rifampin AE’s
Adverse effects:
GI side effects, Hypersensitivity- Fever
Hepatotoxic-
Use caution when administering to patients with chronic liver disease
Induction of cytochrome P450 enzymes can induce the metabolism of other medicines leading to organ rejection and loss of seizure control. Important to monitor liver enzymes for int’x w/ anticonvuslants.
Turns body fluids orange-red and can stain contact lens
______ of Rifampin increases its excretion in the feces leading to what?
Impairment of liver function leads to higher blood serum levels
Fidoxamicin Mechanism & Spectrum
Mechanism: BacteriCIDAL- Inhibits RNA polymerase by binding to sigma subunit of RNA polymerase. – diff subunit than rifampin; cross resistance from rifampin-resistant strains is NOT very likely.
Spectrum: narrow spectrum sparing many of the gut flora, Gram positive anaerobes, C. difficile - better at preventing recurrent infections.
Fidoxamicin Resistance & AE’s
Resistance: Point mutation in RNA polymerase has been observed in vitro
Side effects:
Low absorption
Nausea, vomiting
Fluoroquinolones Mechanism & Spectrum
Mechanism: BacteriCIDAL- Inhibit DNA replication by binding bacterial DNA topoisomerases. topoisomerase II (gyrase): Gram -‘s, topoisomerase IV: Gram +
Spectrum:
Broad spectrum- Gram+, Gram-, and atypical organisms like Mycoplasma
Flouroquinalones Resistance, AE’s and Special Facts
Resistance:
*Overprescribed
*Active efflux of the drug
*Mutations in topoisomerases
Adverse Effects:
*GI side effects, confusion and photosensitivity
Tendon Rupture
*Contraindicated in pregnant women
*Prolongation of the QT interval
Important Facts:
*Chelate cations so don’t take with calcium, iron, aluminum, and zinc
*avoid dairy products or calcium-fortified juice - decrease absorption
*Adjust for renal dysfunction for all agents except moxifloxacin, which is not excreted into the urine
____ ____ of infection is impacted by concentration of drug at site of infection. Levofloxacin as good _____ making it extremely affective in tx UTI’s.
Failure rate; bioavailability
Folate antagonists: _____ & _____ Indirectly inhibit DNA synthesis by inhibiting
Sulfamethoxazole & trimethiprim indirectly inhibit DNA synthesis by inhibiting dyhydropterase synthetase (SMX) and dyhydrofolate reductase (TMP) in folate synthesis. Remember folate cofactors are vital in NT synthesis.
Bacteria and fungi that synthesize their own
dihydrofolic acid are sensitive to Sulfonamides.
Mammals obtain dihydrofolic acid in their diets
Bacteria that uptake dihydrofolic acid
are resistant to Sulfonamides as long as there is
enough dihydrofolic acid around.
Sulfonamides Mechanism & Resistance
Mechanism:
BacterioSTATIC- drug is a para-aminobenzoic acid analog and acts as a competitive inhibitor of Dihydropteroate synthetase
Resistance: change in dehydropteroate synthetase, increased efflux
increased production of PABA
Sulfonamides AE’s
Adverse effects:
*Hypersensitivity- Rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Cross reaction to other drugs containing sulfonamide moieties
*Crystalluria leading to acute renal failure
*Hemolysis if Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficient
*Kernicterus (bilirubin-induced brain dysfunction) Hyperbilirubinemia may cause bilirubin to accumulate in the gray matter of the CNS, potentially causing irreversible neurological damage
Sulfonamides can compete for binding to _____leading to ______ in infants and complications with drugs like _____.
Albumin, kernicterus, warfarin
Trimethoprim MOA, Spectrum, Resistance & AE’s
Mechanism: BacterioSTATIC- Inhibits bacterial dihydrofolate reductase. Bactericidal w/ sulfa
Resistance:
Altered dihydrofolate reductase
Increased amounts of dihydrofolate reductase.
Alternative metabolic pathways
Adverse effects:
Bone marrow suppression
Hyperkalemia
Trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole [TMP-SMX] (Bactrin)Sequential blockade is _______.
BacteriCIDAL
Mechanism: Sequential blockage of the folate synthesis pathway
Spectrum: broad treatment of UTIs, Shigella, Salmonella, Pneumocystis – a weird fungi.
Low/High MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) of antibiotics lead to more affective treatment.
LOW MIC’s mean less drug is needed to kill a certain amount of bacteria.
Metronidazole, Tinidazole MOA, Spectrum, Resistance & AE’s
Mechanism: BacteriCIDAL- metronidazole reduced (electron sink). The activated form generates free radicals leading to DNA strand breaks and cell death.
Spectrum: Protozoa, Anaerobic bacteria including Clostridium difficle & giardia
Resistance: Rare
Adverse effects:
Nausea, diarrhea, headache, and metallic taste.
*Avoid during pregnancy *
Disulfiram-like reaction with alcohol
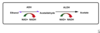
Unique limiting factor re: Metronidizole:
Metronidazole is only metabolized to the active form in anaerobes and not in aerobes
In aerobes, most of the ferredoxin is in the oxidized form.
Don’t have enough reduced form to activate metro.
The disulfiram-ethanol reaction
Metro acts here
I
I
Hangover from acetaldehyde
The disulfiram-ethanol reaction is due to increased serum acetaldehyde. Metronidazole blocks aldehyde dehydrogenase, inhibiting the oxidation of acetaldehyde and causing a marked increase in acetaldehyde concentrations after ethanol consumption.
*Sx of the disulfiram reaction include throbbing headache, nausea, vomiting, sweating, hypotension, confusion.
What other antibiotic class did we discuss that can cause disulfiram reaction and should not be consumed with alcohol?
2nd-generation Cephalosporins
A 21 year old woman presents with a 3-day duration of discomfort with urination and increased urinary frequency. Microscopic examination of the sediment of a centrifuged urine sample reveals 10-15 white blood cells per high power field and numerous Gram negative bacteria.
E. coli accounts for as much as 95% of UTI’s
Resistance patterns of E. coli to TMP-SMX and fluoroquinolones is variable and clinicians should understand resistance patterns in their community.
Nitrofurantoin is preferred
Nitrofurantoin (aka macrobid, macrodantin) MOA & Spectrum
Mechanism: BacteriCIDAL - Nitrofurantoin is reduced by bacterial flavoproteins to reactive intermediates, which inactivate or alter bacterial ribosomal proteins and other macromolecules. Leading to an inhibition of the synthesis of DNA, RNA, cell wall, and protein – generally non-specific MOA.
Spectrum: Broad Spectrum, Rapidly excreted in the urine in an active form
***Only reach high concentrations in the urine
Nitrofurantoin Resistance, AE’s and Important facts
Resistance: Lack of bacterial resistance since the drug interferes with a variety of processes.
Adverse effects: Vomiting and Pulmonary Toxicity
Important facts: Ineffective for infections outside of lower urinary tract
Nucleic Acid Inhibitor Summary
Rifampin – Beta subunit of RNA Polymerase – WIDE - Gram + and -, Mycobacteria tuberculosis
Fluoroquinolones – Topo II & Topo IV involved w/ DNA synthesis – recurrent RTI’s, UTI’s
Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole –inhibition of folate synthesis in bacteria that don’t consume folate –> Indirect inhibition of DNA snythesis – UTI’s, Shigella, Salmonella, Pneumocystis – a weird fungi.
Metronidiazole – Metabolite formation of free radicals that lead to DNA strand breaks & cell death – Anaerobes, C. diff
Nitrofurantoin – Many MOA involving DNA, RNA & protein synthesis due to crx of free radicals – ONLY UTI’s; High urine conc/poor tissue levels
Upregulation of para-aminobenzoic acid synthesis is associated with the development of drug resistance toward which antibiotic
Sulfamethoxazole
Which of the following drugs is most likely to cause anemia in individuals with glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency?
Sulfisoxizole
Alex’s tears have turned a reddish color. What is the mechanism of action of the antibiotic she is currently taking?
Inhibits RNA polymerase – from rifampin
Resistance to which drug occurs following the acquisition of mutations in DNA topoisomerase?
any of the flouroquinalones
Which of the following antibiotics would you use for empiric therapy in a patient with signs and symptoms of a urinary tract infection with a positive urinalysis?
Nitrofurantoin


