anneuploidy- genetics 1 Flashcards
what is the function of a chromosome?
vessels of genetic inheritance
Allow DNA to be stably maintained Package 2.17m long DNA into 40μm nucleus
Allows DNA to be replicated and segregated
how many genes do humans have?
3.2 billion bp, ~20.000 genes
label the following


what are the 3 different types of chromosomal structures?
Metacentric - centromere placed in middle
Sub-metacentric - closer to one telomere
Acrocentric - centromere near telomere

describe the human karyotype
2 haploid sets of 23 chromosomes
44 autosomes, 2 sex chromosomes
arranged according to G banding and size
what are the 2 main types of chromosomal abnormalities?
Aneuploidy – too many or too few chromosomes
Structural – chromosome rearrangements
what is the most common cause of anneuploidy?
maternal non dysjunctin in meiosis 1
what are thedifferent combinations of abnormal gametes that can arrise?
- trisomic conceptus
- monosomic conceptus
- uniparental disomy

what is mosacism?
Mosaicism is when a person has 2 or more genetically different sets of cells in his or her body- some cells may have 46 chromosomes and some may have either more orless-
describe the daughter cells if nondysjunction occurs in meiosis 1
- 2 gametes with an extra chromosome
- 2 gamaetes with a chromosome missing

describe the daughter cells if non dysjunction occurs in meiosis 2
1 daughter cell with an extra chromosome
1 daughter cell with missing chromosome
2 daughter cells with normal chromosomes
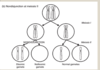
what are the 2 different ways that mosaicism can occur that will result in conditions like downsyndrome?
- post zygotic non- dysjunction
- this is when a normal coceptus zygote will undergo non dysjunction during mitosis and this will lead to some cells having 47 chromosomes and others having 45- the cells with 45 chromosomes are less likely to survive, but the cells with 4 7 chromosomes will go on to proliferate- if nondyjunction occurs earlier on more cells will have trisomy, but if it occurs later on less cells will hav trisomy - Anaphase lag
- this is when the zygote starts with trisomy 21, the sister chromatids do not seperate properly from eachother resulting in soem cells with 48 chromosomes and some cells with 46
the cells with 48 chromosomes die off, but the cells with 46 chromosomes continue to proliferate. this increases the number of cells with a normal chromosome number
what is the downsyndrome phemotype?
learning difficulties,
dysmorphic features,
heart defects
Alzheimer’s 20-30 years earlier
which chromosome is affected in downssyndrome?
trisomy 21
what are the 3 different types of karyotypes that can occur in don syndrome?
- 95% primary (full) trisomy : 47,XX,+21 (or 47,XY,+21)
- 1-2% mosaicism: 46,XX/47,XX,+21 (or XY)
- 4% translocation: 46, XX,der(14;21)(q10),+21 (or XY)
what is the name given to those with trisomyy 21
edwards syndrome
what is the phenotype for edwards syndromes?
- SEVERE MENTAL DISABILITY
- DYSMORPHIC FEATURES: MICROGNATHIA, PROMINENT OCCIPUT
- ROCKER-BOTTOM FEET,
- CLENCHED FISTS WITH OVERLAPPING FINGERS
- CONGENITAL HEART DEFECTS
MANY DIE WITHIN WEEKS, 90% WITHIN 1 YEAR








