Anatomy Quiz Flashcards
Name the view seen here

Lateromedial view of Equne hoof
Name the view seen here

Dorsopalmar View of Equine Hoof
Name the Structure

First phalanx (long pastern)
Name the Joint

Proximal interphalangeal joint (pastern joint)
Name the Structure

Second Phalanx (short pastern)
Name the Joint

Distal interphalangeal Joint (coffin joint)
Name the Structure

Third Phalanx (coffin bone)
Name the Structure

Navicular Bone
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow

Extensor process of P3
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow

common digital extensor
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow

impar ligament
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow

Digital cushion
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow

Deep digital flexor
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow

straight sesmoidean ligament
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow

insertion of oblique sesmoidean ligament
which view is good for assessing solr margins of P3 and the navicular bone
Dorsal proximal to palmar distal (upright pedal)

Identify the structure indicated by the arrow

navicular bone
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow

wings of the coffin bone
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow

solar margin
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow

semilunar canal
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow (light blue lines)

vascular channels
Identify the structure indicated by the yellow dotted line

dirt in the white line on bottom of the hoof
name the structure indicated by the orange line

crena margins of solearis
WTF is the crena margins solearis
smooth round concavity of the distal phalanx solar margin (more prominent in hindlimb)
which view is used to asses the flexor surface and medullary cavity of the navicular bone
palmar proximal to palmar distal (skyline)

Identify the structure indicated by the arrows

wings of coffin bone
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow

navicular bone
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow

medullary cavity
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow

flexor surface
what is a dorsoproximolateral to palmarodistomedial view used for in equines
to throw out the lateral wing of P3

Identify the structure indicated by the X

radial carpal bone
Identify the structure indicated by the X

Intermediate carpal bone
Identify the structure indicated by the X

Accessory Carpal Bone
Identify the structure indicated by the X

Ulnar Carpal Bone
Identify the structure indicated by the X

4th carpal bone
Identify the structure indicated by the X

3rd carpal bone
Identify the structure indicated by the X

2nd carpal bone
Identify the structure indicated by the X

Metacarpal 3
Identify the structure indicated by the X

Metacarpal 2
Identify the structure indicated by the X

Metacarpal 4
Indicate the lateral side

B
The accessory bone is on the lateral side
Name the view seen here

Lateromedial
T/F: radiographs are the most sensitive on the edges
true
name the view seen here

flexed view
why are flexed used (2 reasons)
Manipulation of the limb to better image anatomic structures of interest.
Visualization of articular surfaces
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow (outlined in blue)

Intermediate carpal bone
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow (outlined in yellow)

radial carpal bone
identify the structure indicated by the arrow (purple outline)

carpal bone 4
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow (outlined in pink)

carpal bone 3
indentify the structure indicated by the arrow

ulnar carpal bone
identify the joint indicated by the arrow

radial carpal joint
identify the joint indicated by the arrow

middle carpal joint
identify the joint indicated by the arrow

carpal metacarpal joint
describe the view seen here

dorsolateral to palmaromedial
what structures are easily seen with dorsolateral to palmaromedial views
palmar-lateral structures e.g lateral splint bones
How can you distinguish between DLPM view from a DMPL view?
C4 and MC4 on DLPM are not aligned

describe the view seen here

Dorsomedial to palmarolateral (DMPL)
T/F: C2 and MC2 are stacked on top of each other in the DMPL view
true

Identify structure #1

carpal bone 2
Identify structure #2

carpal bone 1
identify structure #3

metacarpal bone 2
Identify Structure #1

tibia
Identify Structure #2

calcaneous
Identify Structure #3

chestnut
Identify Structure #4

tarsocrural joint
Identify Structure #5

proximal intertarsal joint
Identify Structure #6

Distal intertarsal joint
Identify Structure #7

tarsometatarsal joint
Identify Structure #8

metatarsal 3
describe the view seen here

DLPMO (dorsolateral to palmaromedial oblique)
Identify structure indicated by the arrow

medial mallelous
Identify structure indicated by the arrow

distal intermediate ridge of the tibia
Identify structure indicated by the arrow

MT2- medial splint bone
Identify structure indicated by the arrow

MT4- Lateral splint bone
Identify structure indicated by the arrow

fourth tarsal bone
Identify structure indicated by the arrow

calcaneous
identify the structure outline by the green line

lateral trochlear ridge of the talus
(aka gonzo’s nose- how to disinguish between DMPLO from DLPMO views)
identify the structure outlined in pink

sustentaculum tali
identify the structure outlined in yellow

T1 and T2 fused
Identify structure indicated by the arrow

dorsolateral surface of tarsometatarsal joint
Identify structure indicated by the arrow

medial condyle
Identify structure indicated by the arrow

medial tibial condyle
Identify structure indicated by the arrow

medial intercondylar eminence
Identify structure indicated by the arrow

fibula
Identify structure indicated by the arrow

lateral condyle
what is another term for MC3
cannon bone
MC2 and MC4 in horses are also known as
splint bones
what is the fetlock
metacarpal phalangeal joint
what is the pastern joint
proximal interphalangeal joint
what is the distal interphalangeal joint know as
coffin joint
what are the general principles for small animal radiography
At least 2 orthogonal views
Primary beam centered on area of interest with collimation.
Good positioning – sedation
Placement of markers:
- Lateral views: dorsal or cranial surface
- Craniocaudal view: lateral surface
common disorders of shoulder seen on radiographs (2)
osteochondrosis
neoplasia
what are the routine views of the shoulder (2)
mediolateral and caudocranial
name the view seen here

mediolateral shoulder
name the view seen here

caudocranial shoulder
identify structure #1
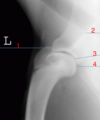
supraglenoid tubercle
identify structure #2

spine of the scapula
identify structure #3

glenoid cavity
identify structure #4

caudal head of the humerus
identify the structure indicated by the arrow

spine of the scapula
identify the structure indicated by the arrow

glenoid cavity
common disorders of the elbow seen on radiographs
Elbow dysplasia, fractures/trauma
routine views of the elbow
Mediolateral, craniocaudal and Flexed mediolateral
name the view seen here

mediolateral elbow
name the view seen here

craniocaudal elbow
identify the structure indicated by the arrow

anconeal process
(better visualized on the flexed mediolateral view)
identify the structure indicated by the arrow

medial epicondyle
identify the structure indicated by the arrow

medial coronoid process
identify the structure indicated by the arrow

olecranon
identify structure #1

medial epicondyle
identify structure #2

medial coronoid process
identify structure #3

lateral epicondyle
common problems in the manus
truama especially subluxations
name the view seen here

mediolateral manus
name the view seen here

dorsopalmar manus
Identify structure #1

antebrachiocarpal joint
Identify structure #2

middle carpal joint
Identify structure #3

carpometacarpal joint
Identify structure #4

dorsal sesamoid bone
Identify structure #5

accessory carpal bone
Identify structure #6

ulnar carpal bone
Identify structure #7
proximal sesamoid bone
Identify structure #1

ulnar carpal bone
Identify structure #2

4th carpal bone
Identify structure #3

intermedioradial carpal bone
Identify structure #4

proximal sesamoid bone
what views are used for the hips and pelvis
Routine: lateral and extended ventrodorsal views
Optional: frog legged ventrodorsal view
common problems in the hips and pelvis
trauma, hip dysplasia (large dogs), and Legg-Calves-Perthes (small dogs)
name the view seen here

lateral hips and pelvis

name the view seen here

VD extended hipls/pelvis
Identify structure #1

lumbosacral junction
Identify structure #2

superimposed ilia
Identify structure #1

leftt ilium
Identify structure #2

left greater trochanter
Identify structure #3

left pubis
Identify structure #4

pubic symphysis
Identify structure #5

left ischium
what views are routinly used to view the stifle
mediolateral and craniocaudal
common reasons for taking a radiograph of the stifle
trauma-fractures, cranial cruciate tears
name the view seen here

caudocranial stifle
indicate the medial side

B (the fibula is located on the lateral side)
Identify structure #1

lateral condyle
Identify structure #2

extensor fossa
Identify structure #3

fibula
Identify structure #4

patella
Identify structure #5

medial fabella of gastrocnemius
name the view seen here

mediolateral stifle
Identify structure #1

patella
Identify structure #2

fabella of the gastrocnemius
Identify structure #3

caudal fascial plane
Identify structure #4

popliteal sesamoid bone
Identify structure #5

infrapatellar fat pad
what are the routine views of the tarsus
mediolateral and dorsoplantar
common reasons to radiograph the tarsus
trauma, OCD (large dogs)
name the view seen here

mediolateral tarsus
Identify structure #1

calcaneus
Identify structure #2

tarsocrural joint
Identify structure #3

proximal intertarsal joint
Identify structure #4

distal intertarsal joint
Identify structure #5

tarsometatarsal joint
name the view seen here

dorsoplantar view of the tarsus
identify the lateral side

A (4th tarsal bone and calcaneous are on the lateral side)
Identify structure #1

lateral malleolus
Identify structure #2

4th tarsal bone
Identify structure #3

medial trochlear ridge of the talus
Identify structure #4

medial malleolus
Identify structure #5

central tarsal bone
Identify structure #6

3rd tarsal bone
Identify structure #7

superimposed 1st and 2nd tarsal bones
name 7 radiation safety procedures
avoid hand holing cassesttes
all unnecessary persons should leave
lead apparel
adjustable light collimator
rotate personnel
age and pregnancy status
radiation monitoring
T/F the fibula can have multiple separate centers of ossification
True (don’t mistake these as fractures)
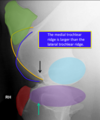
T/F: the medial trochlear ridge is larger than the lateral trochlear ridge in the lateromedial view of the equine stifle
True (the medial trochear rigde is outlined and yellow and the lateral trochear ridge is outlined in blue)
T/F in a DMPLO of the equine carpus the first carpal bone is sometimes present and the fifth carpal bone is rarely present. They are non-articular, will vary in size, have smooth margins and may be present on one side only
true
T/F the only way to know medial vs. lateral and which limb was radiographed of the equine metacarpal-phalangral joint (fetlock) is if the film was correctly labled at the time the image was taken
true


