Anatomy of the pituitary gland Flashcards
What are the main endocrine glands in the body?
Hint think:
- In the cranial cavity
- Neck
- Abdomen
- Pelvis
- Perineum
Cranial cavity:
- Hypothalamus and pituitary gland
Neck:
- 4 Parathyroids and throid gland
Abdomen:
- 2 adrenal glands
- Pancreas
Pelvis (female):
- 2 ovaries
Perineum (male):
- 2 testes
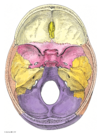
Label the main parts of the brain


What is the dinecephalon ?
- It is the Thalamus + the Hypothalamus
- It forms the central core of the cerebrum
Label the parts of the brain stem and the dinecephalon


What conencts the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland ?
The infundibulum

Where is the pituitary gland located in the cranial cavity ?
Located in the pituitary fossa which lies within the sella turcica
What structure does the pituitary gland lie immediately inferior too ?
The optic chiasm
What forms the optic chaism ?
The right and left optic nerves (CN II)
After the optic chaism describe the pathway of the optic tracts
- The right and left optic tracts pass posteriorly from the chiasm
- After synapsing in the thalamus the next axons in the chain pass via the optic radiation to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe
(The second point refers to the black dot on the pathway to the end of the pathway)
How can a pituitary tumour affect somones sight ?
It can compress on the optic chaism - resulting in a bitemportal hemianopia
(it results in a bitemporal hemianopia because the nasal retinae are the nerve fibres which cross over and swap which side of the optic pathway they are on at the optic chaism, and since in terms of seeing in the eye the nasal retinae produce sight in the temporal field (in the eyes its light opposites for nerves and what you see))

What are the 2 main surgical approaches which can be taken to reach the pituitary gland ?
- Transcranial approach (subfrontal – under the frontal lobe)
- Transsphenoidal approach (via nasal cavities & sphenoid sinus)
Blue line - transsphenoidal
Red line - transcranial

Go over this pic of the osteology of the nasal cavity
Go over the anatomy of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity

What are the paranasal sinuses ?
Air-filled spaces within the bones surrounding the nasal cavities (no. refer to the pic)
- Frontal sinuses
- Sphenoid sinuses
- Ethmodial sinuses
- Maxillary sinuses

Label the fractures shown


For learning the crianl nerves, there function and foramen then exist use the rafi ahmed brainscape and the table ive printed off.
Use them
What is the dura mater ?
The dura mater is the outermost layer of the meninges, lying directly underneath the bones of the skull and vertebral column. It is thick, tough and inextensible.

What is the diaphragm sellae ?
A tough sheet of dura mater forming a roof (diaphragm) over the pituitary fossa

What is the tentorium cerebelli ?
A tough sheet of dura mater “tenting” over the cerebellum within the posterior cranial fossa but with a central gap to permit the brainstem to pass through)

What foramens do the vertebral arteries and the internal carotid arteries enter the cranial cavity in ?
- Vertebral arteries - formane magnum
- Internal cartotid arteries - carotid canal
Go over this pic

What is the dural venous sinus ?
Venous channels within the dura mater that drain most of the venous blood from the cranial cavity (including the brain) into the internal jugular veins

What is the pituitary gland surrounded by ?
Surrounded by the cavernous and intercavernous sinuses



