Anatomy of the Larynx Flashcards
Where is the larynx located?
between pharynx and trachea
Opposite C3-C6
What are the structures that form the framework of the larynx?
epiglottis, thyroid cartilage, cricoid and arytenoids
What connects the hyoid bone to the larynx?
Larynx slung from the hyoid bone by the thyrohyoid membrane and the thyrohyoid muscle
Where is the thyroid cartilage located?
Where are the membranes asssociated with it?
What is its joint?
Superior border at C4
- Thyrohyoid membrane-
- median thyrohyoid ligament- anteromedial thickening
- Lateral thyrohyoid ligament- posterolateral thickening
- Thyrohyoid muscle
Cricothyroid joint- inferior horns articulate with cricoid cartilage

What is the key characteristic that differentiates the cricoid cartilage from other cartilages in the larynx
What vertebral level is the cricoid cartilage at?
What structures is it attached to and how?
Signet ring shaped- only complete ring of cartilage
C4
Sup.- thyroid cartliage
Inf- first tracheal ring- cricotracheal membrane
Posterior signet- arytenoids

What are the two cartilage nodules located at the inlet of pharynx?
cuneiform- within margins of aryepiglottic fold
Corniculate cartilage- lying at the apex of arytenoids
no functional importance

Where is the epiglottis located and what are its attachments?
The epiglottis is a leaf shape lying behind root of tongue
Sup.ant.- hyoepglottic ligament- hyoid
Inf.- thyroepiplottic ligament ( immediately above the vocal cords)- thyroid cartilage
Lat.- aryepiglottic folds (runs backwards to form the entrance of larynx)- aryetenoids
Upper anterior surface projects above hyoid bone
its mucosa is reflected forwards to base of tongue

How does the epiglottis attach to the base of tongue?
At base of tongue raised up to median glossoepiglottic folds and lateral pharngoepiglottic folds
Depression between the two- vallecula

What is the significance of cricothyroid membrane and what are its attachements?
Connects thyroid, crocoid and arytenoid cartilages
- composed of elastic tissue
- Attachements
- Sup.- posterior surface of thyroid cartilage
- Inf.- vocal process of arytenoid
- between attachments- upper edge thickened- vocal ligament
- Anteriorly, membrane thickens as cricothyroid ligament

Use of cricothyroid ligament in emergency
cricothroid ligament is subcutaneous, easily felt and used in emergency cricothyroid puncture for laryngeal obstruction
Where are the vocal cords located and what are the two folds of mucosa?
Arytenoids to back of thyroid- below epiglottic attachements
- Upper
- Vestibular fold
- Small amount of fibrous tissue
- false vocal cords
- Lower
- True vocal cords
- vocal ligament
- muscosa firmly adherent to to vocal ligament. No intervening submucosa. Gives pearly white avascular appearance of vocal cords seen on laryngoscopy
- Space between vocal cords-rima glottidis
What is the piriform fossa and what is its significance?
Piriform fossa- recess on either side of larynx, in which swallowed foreighn bodies tend to lodge

What is the function of muscles of larynx
- open glottis in inspiration
- close vestibule and glottis in deglutition
- alter tone of true vocal cords in phonation
What is the role of intrinsic muscles?
Close larynx during swallowing
List the intrinsic muscles and their levels of attachment
- Aryepiglottic and oblique arytenoids- close aryepiglottic folds (which define the laryngeal inlet)
- Thyroepiglottic muscles close the walls of vestibule of larynx
- Lateral cricoarytenoids, interarytenoids- close the vocal cords

What is the only intrinsic muscle that does not have a sphincter mechanism?
Posterior cricoarytenoid- upon contraction, this rotates the arytenoids outwards and seperates the vocal cords
What is the only extrinsic muscle of the larynx?
Cricothyroid muscle
- between cricoid and thyroid cartilage
- lowers the thyroid cartilage forwards, distance between the vocal process of arytenoids is increased, vocal cords stretched

What are the 3 ways in which food is prevented from entering the larynx
- Closure of sphincter mechanism of larynx
- Tucking the larynx behind the overhanging mass of the tongue
- Using the epiglottis to guide the bolus away from the laryngeal entrance
How does “tucking the larynx behind the overhanging mass of the tongue” work?
Larynx elevated and pulled forwards by actions of the suprahyoid muscles, thyrohyoid and stylopharyngeus muscles
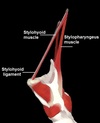
Process of preventing food from entering larynx
- As head of bolus reaches epiglottis, it is tipped backwards against pharyngeal wall and momentarily holds up the passage of food
- Larynx then elevated and pulled forwards by muscles
- Epiglottis stand erect, guiding bolos into streams along the piriform fossa and away from laryngeal orifice
- Then epiglottis flaps backwards as cover over the laryngeal inlet, but this only occurs after the main bolus of food has passed beyond it
Nervous supply to the larynx
Vagus
-
Superior laryngeal nerve
- External- passes into cricothyroid muscle and supplies this
- Internal- pierces thyrohyoid membrane with superior laryngeal vessel- supply mucosa of larynx down to vocal cords
-
Recurrent laryngeal nerve- intrinsic muscles and mucosa below vocal cords
- Right- arises as vagus n. crosses in front of right subclavian a., then passes back into larynx
- Left- winds below aorta and ascends up

What happens when the superior laryngeal nerve is damaged?
Weakness in phonation due to loss of tightening effect of cricothyroid muscle on the cord
What happends if the recurrent nerve is bruised or partially damaged?
Semon’s law: The abductors ( posterior cricoarytnoids) are affected more than the adductors ( the rest of intrinic sphinctors)
The affected cord adopts to midline adducted position
In bilateral complete paralyis, the cords come together, stridor (high pitched, wheezing sound) is intense and tracheostomy may be essential
What happens in complete division of the recurrent laryngeal nerve?
Cords on the affected side take up neutral position between abduction and adduction. Usually the other cord is able to compensate and speech is not greatly affected
If both nerves are affected, voice is completely lost and breathing becomes difficult through the only partially opened glottis


