Anatomy II Lecture Exam I Flashcards
Hip Bone
Hip Bone

• Hip bone is also called os coxae & the ridiculous innominate
bone (the latter means “unnamed”)
• There are 3 parts of the Coxal bone (the ilium, ischium and
pubis) that fuse at the acetabulum.
• Conjunction of ischium and pubis forms the Obturator Foramen
Important Landmarks on the Coxal bone 1: Ilium
➢ Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS)
➢ Anetrior Inferior Iliac Spine (AIIS)
➢ Posterior Superior Iliac Spine (PSIS)
➢ Posterior Inferior Iliac Spine (PIIS)
➢ Iliac Crest
➢ Iliac Fossa
➢ Greater Sciatic Notch
➢ Superior and Inferior Gluteal Lines
Important Landmarks on the Coxal bone: Ischium
➢ Ischial Spine
➢ Ischial Tuiberosity
➢ Ischial Ramus
➢ Lesser Sciatic Notch
Important Land marks on the Coxal bone: Pubis
➢ Superior Pubic Ramus
➢ Inferior Pubic Ramus
➢ Pubic Tubercle
➢ Pubic Crest
➢ Pectineal Line
Important Landmarks on the Coxal bone: Ilium
➢ Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS)
➢ Anetrior Inferior Iliac Spine (AIIS)
➢ Posterior Superior Iliac Spine (PSIS)
➢ Posterior Inferior Iliac Spine (PIIS)
➢ Iliac Crest
➢ Iliac Fossa
➢ Greater Sciatic Notch
➢ Superior and Inferior Gluteal Lines
Important Landmarks on the Coxal bone: Ischium
➢ Ischial Spine
➢ Ischial Tuiberosity
➢ Ischial Ramus
➢ Lesser Sciatic Notch
Important Land marks on the Coxal bone: Pubis
➢ Superior Pubic Ramus
➢ Inferior Pubic Ramus
➢ Pubic Tubercle
➢ Pubic Crest
➢ Pectineal Line

Important Landmarks on the Coxal bone: Ilium
➢ Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS)
➢ Anetrior Inferior Iliac Spine (AIIS)
➢ Posterior Superior Iliac Spine (PSIS)
➢ Posterior Inferior Iliac Spine (PIIS)
➢ Iliac Crest
➢ Iliac Fossa
➢ Greater Sciatic Notch
➢ Superior and Inferior Gluteal Lines
Important Landmarks on the Coxal bone: Ischium
➢ Ischial Spine
➢ Ischial Tuiberosity
➢ Ischial Ramus
➢ Lesser Sciatic Notch
Important Land marks on the Coxal bone: Pubis
➢ Superior Pubic Ramus
➢ Inferior Pubic Ramus
➢ Pubic Tubercle
➢ Pubic Crest
➢ Pectineal Line
Important Landmarks on the Coxal bone: Ilium
➢ Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS)
➢ Anetrior Inferior Iliac Spine (AIIS)
➢ Posterior Superior Iliac Spine (PSIS)
➢ Posterior Inferior Iliac Spine (PIIS)
➢ Iliac Crest
➢ Iliac Fossa
➢ Greater Sciatic Notch
➢ Superior and Inferior Gluteal Lines
Important Landmarks on the Coxal bone: Ischium
➢ Ischial Spine
➢ Ischial Tuiberosity
➢ Ischial Ramus
➢ Lesser Sciatic Notch
Important Land marks on the Coxal bone: Pubis
➢ Superior Pubic Ramus
➢ Inferior Pubic Ramus
➢ Pubic Tubercle
➢ Pubic Crest
➢ Pectineal Line

pelvis
pelvis
• The pelvis is the bony
ring made up by the
two os coxae and the
sacrum.
• Within this ring are
three articulations: the
2 sacroiliac joints and
the pubic symphysis.

sacroiliac joint 1
SACROILIAC JOINT
• Auricular surfaces of
ilium & sacrum form
synovial part of the SI
joint
• The sacroiliac joint is actually 2 types of joints. A
synovial joint inferiorly and a syndesmosis
posteriosuperiorly.
Syndesmosis is in superior .. portion of the joint! Interroseis

sacrioiliac joint 2
SACROILIAC JOINT
• Auricular surfaces of
ilium & sacrum form
synovial part of the SI
joint
• The sacroiliac joint is actually 2 types of joints. A
synovial joint inferiorly and a syndesmosis
posteriosuperiorly.
Syndesmosis is in superior .. portion of the joint! Interroseis
=–
It is not uncommon for the sacroiliac joint to undergo stenosis (ossify) with age.

sacroiliac ligaments
iliolumbar
Sacroiliac ligaments
Ventral & dorsal sacroiliac
• Thickened regions of the sacroiliac joint capsule
Iliolumbar
• From iliac crest to TVP of L5
• limit rotation & anterior gliding of L5 in relation to the sacrum
• Limits side-bending of L5 in relation to pelvis

sacroiliac ligaments
interosseus sacroiliac
sacrotuberous
sacrospinous
stability of sacrum
Sacroiliac ligaments
Interosseus sacroiliac: Between iliac tuberosity & sacrum
• This forms a syndesmosis
Sacrotuberous: sacrum to ischial tuberosity
Sacrospinous: sacrum to ischial spine
• Form greater & lesser sciatic foramina
Stability of sacrum
Downward compression of the sacrum, due to
the weight of the upper body
causes interosseus ligaments to pull
ilium bones together to tighten joint
Anterior sacral rotation limited by ligaments
• Sacrotuberous
• Sacrospinous
• Interosseus sacroiliac

Nutation of sacroiliac joint
Nutation of sacroiliac joint
• Nutation is rotation or
tilting of sacrum around
axis through interosseus
ligaments (horizontal axis)
• Anterior nutation:
promontory moves inferior
and anterior, coccyx
superior and posterior
• Posterior nutation is the
opposite; AKA counter
nutation
• Nutation brings the iliac
crests closer together and
the ischial tuberosities
further apart, increasing
the size of the pelvic outlet.

Femur
Femur
• Head
• Neck – separated from the shaft
anteriorly by the intertrochanteric
line
• Greater Trochanter - lateral
• Lesser Trochanter - medial
• Linea aspera – ridge on
posterior aspect of shaft
• Gluteal tuberosity
• Med & lat condyles and
epicondyles
• Adductor tubercle – small
prominence at superior

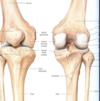
Hip Joint
& ligaments
Hip Joint
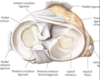
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket synovial
joint between the head of the femur and
the acetabulum of the coxal bone.
Head of femur & acetabulum are
connected by ligaments.
• Transverse acetabular lig & acetabular
labrum (C-shaped cartilage lining)
– enlarge articular surface
• Ligamentum teres of head of femur
– from head to transverse acetabular lig.

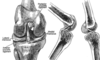
Hip Joint Capsule
iliofemoral, ischiofemoral, and pubofemoral ligaments
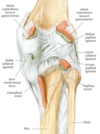
Hip Joint Capsule
There are 3 ligaments that make up the
main stabilizers of the hip joint.
• Iliofemoral - limits hyperextension of
femur
• Ischiofemoral – reinforces hip capsule
posteriorly
• Pubofemoral – reinforces hip capsule
inferiorly
All 3 ligaments wind around the hip joint
so that they tighten in extension.
The pubofemoral ligament also helps
limit abduction. Flexion of the hip
joint is limited primarily by the
hamstring muscles

Hip Joint vasculature
Hip Joint Vasculature
• Femoral neck derives blood from medial and lateral circumflex
femoral arteries. The femoral head receives blood from the
medial and lateral epiphyseal arteries. The medial epiphyseal
artery is also called the artery of the ligamentum teres and not
everyone has one. The lateral epiphyseal artery arises from the
medial femoral circumflex artery and is easily disrupted by
francture, dislocation, etc. This can lead to avascular necrosis of
femoral head.

psoas major
psoas minor
iliacus
PSOAS MAJOR
O: bodies, TVP’s of T12-L5
I: lesser trochanter of femur
N: L1-4 - “lumbar plexus”
A: lat flex vertebral column
flex femur at hip
PSOAS MINOR
O: bodies of T12-L1
I: pectineal line of the pubis
N: L1
A: weak flexor of the lumbar
spine
ILIACUS
O: iliac fossa
I: lesser trochanter
N: femoral n.
A: flex femur

gluteus maximus
gluteus medius
gluteus minimus
GLUTEUS MAXIMUS
O: iliac crest & sacrum/coccyx
I: gluteal tuberosity & iliotibial tract
N: inferior gluteal n.(L5, S1,2)
A: extend, lat rotate femur
Bursae are located between gluteus
max and ischial tuberosity & greater
trochanter
GLUTEUS MEDIUS
O: dorsal ilium
I: greater trochanter
N: superior gluteal n.(L5,S1)
A: abduct, med rotate femur;
during gait, supports body
on one leg while other leg
swings forward
GLUTEUS MINIMUS
O: dorsal ilium
I: greater trochanter
N: superior gluteal n.(L5,S1)
A: abduct, med rotate femur;
assists gluteus medius in
supporting the body during
gait

Tensor Fascia Lata
TENSOR FASCIA LATA
O: ASIS, Anterior Iliac Crest
I: Iliotibial tract–> lat condyle of tibia
N: superior gluteal n. (L4,5)
A: abduct, medially rotate, flex femur;
keep knee extended
Glut max and TFL both insert into iliotibial tract and maintain extended knee

Lateral Rotators
Obturator internus
superior & inferior gemelli
Quadratus femoris
obturator externus
Lateral Rotators
OBTURATOR INTERNUS
O: obturator membrane
I: greater trochanter (90degrees
around lesser sciatic notch)
N: nerve to obturator internus (L5,
S1)
A: lat rotate femur
SUPERIOR & INFERIOR GEMELLI
O: ischium
I: greater trochanter
N: nerves to obturator internus &
quad fem (L5,S1)
A: lateral rotate femur
QUADRATUS FEMORIS
O: ischial tuberosity
I: quadrate tubercle
N: nerve to quadratus femoris (L5,
S1)
A: lateral rotate femur
OBTURATOR EXTERNUS
O: obturator membrane (outer)
I: greater trochanter
N: obturator n. (L3,4)
A: lateral rotate femur

Another lateral rotator
OBTURATOR EXTERNUS
OBTURATOR EXTERNUS
O: obturator membrane (outer)
I: greater trochanter
N: obturator n. (L3,4)
A: lateral rotate femur

Another lateral rotator
piriformis
PIRIFORMIS
O: ant sacrum
I: greater trochanter
N: S 1,2
A: abduct, lat rotate
femur

Actions of Iliopsoas and Gluteal Muscles on the Femur
Actions of Iliopsoas and Gluteal Muscles on the Femur

Lumbar plexus
Lumbar plexus: ventral rami of L1-4

Sacral plexus
Sacral plexus: Ventral
rami from
L4,5 & S1,2,3
Sciatic nerve (L4,5 S1,2,3)
• Tibial nerve
• Common Fibular (Peroneal)
nerve
Superior gluteal nerve (L4,5 S1)
Inferior gluteal nerve (L5 S1,2)
Pudendal (S2,3,4)
• Anal & Urethral sphincters, External
genitalia
Posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh (S1,
2,3)
Nerve to quadratus femoris (L4,5 S1)
Nerve to obturator internus (L5 S1,2)

sciatic nerve
Sciatic nerve
• L4,5 S1,2,3 rami exit greater sciatic
foramen with piriformis
• Enters thigh between hamstrings &
adductor magnus
• Divides into common fibular & tibial
branches
• Muscles:
– hamstrings
– 1/2 adductor magnus
– muscles of leg/foot

Common fibular portion of sciatic nerve…
Common fibular portion exits below, above or through
piriformis muscle

superior gluteal nerve
inferior gluteal nerve
Superior gluteal nerve
• Gluteus medius,
minimus & TFL
• Exits superior to
piriformis
Inferior gluteal nerve
• Gluteus maximus
• Exits inferior to
piriformis

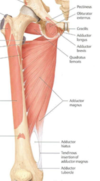
Thigh - Anterior Group
Sartorius
Quadriceps femoris (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius)
THIGH – ANTERIOR GROUP
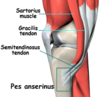
SARTORIUS
O: Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
I: medial surface upper tibia (pes anserine)
N: femoral n. (L2,3)
A: flex thigh(hip), lat rotate femur;
flex leg(knee) QUADRICEPS FEMORIS
O: rectus femoris: Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine
vastus lateralis: linea aspera
vastus medialis: linea aspera vastus intermedius: upper ant femur
I: tibial tuberosity via patellar tendon N: femoral n. (L2,3,4)
A: extend leg(knee);
flex femur (rectus femoris)