Anatomy Eye, retina and colour vision Flashcards
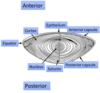
what is the external anatomy of the eye?


what are the different types of tears?
basal
reflex
emotional
how are basal teats produced?
by lacrimal system at a constant level- even in absence of irritation or stimulation
when are reflex tears produced?
increased tear production in response to ocular irritation
what is the lacrimal reflex pathway made up of?
- afferent pathway, CNS, efferent pathway and lacrimal gland
- Afferent- cornea, innervation = sensory nerve fibres via cranial nerve V1- ophthalmic trigeminal
- Trigeminal nerve relays signals to CNS
- Efferent- parasympathetic
- Neurotransmitter- acetylcholine
- Afferent- cornea, innervation = sensory nerve fibres via cranial nerve V1- ophthalmic trigeminal
what are tears produced by?
lacrimal gland
where is the lacrimal gland located?
within orbit
latero-superior to globe

where do tears drain?
2 puncta, opening on upper and lower medial lid margins
where do puncta drain to?
- Puncta form opening of superior and inferior canaliculi within lower and upper eyelids
- Both canaliculi converge as single common canaliculus and drain tear into tear sac
- Tear drained out of tear sac into nasal cavity through tear duct
what is the cornea covered with?
tear film- thin layer fluid
what is the function of the tear film?
- Maintains smooth cornea-to-air surface
- Important for maintaining clear vision and removing surface debris during blinking
- bactericide
- Source of oxygen and nutrient supply to anterior segment
- Cornea has no blood vessels
what are the layers of the tear film?
superficial lipid layer
aqueous tear film
mucinous layer

what is the superficial lipid layer?
- Responsible protecting tear film from rapid evaporation
- Secreted by Meibomian glands situated along eyelid margins
what is the aqueous tear film?
- Main bullk of tear film
- Delivers oxygen and nutriet to surrounding tissue
- Contains factors against potentially harmful bacteria
what is the mucinous layer?
- Ensures tear film sticks to eye surface
- Renders surface eye ‘wettable’
- Mucin molecules act by binding water molecules to hydrophobic corneal epithelial cell surface
what is the conjunctiva?
thin, transparent tissue that covers outer surface of eye
- Begins at outer edge of cornea, covers visible part of eye and lines inside of eyelids
- Nourished by tiny blood vessels that are nearly invisible to naked eye
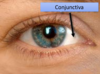
what happens in conjunctivitis to the visible conjunctiva?
infection of the conjunctiva
blood vessels become visible to naked eye
what is the anterio-posterior diameter of eye in adults?
24mm
where does the eye sit?
anatomical space of the oribit
what is the eye enclosed by?
bone walls
what is the posterior coat of the eye
sclera
choriod
retina
what is the anatomy of the eye in lateral view?


what is the sclera responsible for?
- Sclera- hard and opaque
- Protection
- Shape maintenance of eye
- High water content
what is the choroid responsible for?
- Choroid- pigmented and vascular
- Providing circulation to eye
- Shielding out unwanted scattered light
what is the retina responsible for?
- Retina- neurosensory tissue
- Converting light into neurological impulses
- Transmitted to brain via optic nerve
what is the cornea?
- Transparent, dome shaped window covering front of eye
- Low water content
- Refracting surface providing 2/3 eye focusing power
- Clear window to look through