Anatomy and Physiology of Nose Flashcards
What is the nasal function?
–To function as an airway in respiration
–Particularly important in neonates who are obligate nasal breathers
Warms inspired air
Humidification
Filtration of large particulate matter by coarse hairs in the nasal vestibule
Mucus production trapping and ciliary clearance of particulate matter
Immune protection
Olfaction
Drainage/aeration of the middle ear via Eustachian tube
Drainage of paranasal sinuses and nasolacrimal duct
Voice modification
Pheromone detection via the vomero-nasal organ of Jacobsen
–Function debated in humans
What type of mucosa is sinonasal mucosa?
•Respiratory ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells
What is the function of sinuses?
- Help with vocal resonance
- Decrease the weight of skull and facial bones
- Act as buffer for trauma
Here are the landmarks of the external nose

More landmarks of external nose

What is the external nose composed of?
- 1/3rd bony, 2/3rd cartilage
- Frontal processes of maxilla and nasal part of frontal bones
What forms the midline partition of the internal nose?
Nasal septum
What forms the lateral walls of the internal nose?
Turbinates
What forms the roof of the internal nose?
Cribiform plate
What forms the floor of the nose?
Hard palate
What are the main components of the nasal septum?
Septal cartilage
Perpendicular plate of ethmoid
Vomer

What is the clinical relevance of the septum?
•Deviation
–Again congenital or acquired. Acquired being almost always caused by trauma
- Septal perforation
- Septal haematoma
Here are the turbinates

What are turbinates?
•Bony scroll-like projections from lateral wall of nose
What is each turbinate associated with?
•Each turbinate associated with its respective meatus
What is the clinical relevance of turbinates?
•Clinical relevance – usually inferior turbinate only
–Can cause nasal blockage due to
- Infection
- Inflammation e.g allergic rhinitis
–Usually managed medically with topical steroid sprays
–Can be managed surgically with turbinate reduction surgery
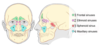
What are the paranasal sinuses?
- Frontal
- Maxillary x 2
- Ethmoid
–Anterior and posterior
•Sphenoid
What drains through the inferior meatus?
Nasolacrimal duct
What drains through the middle meatus?
–Frontal
–Maxillary
–Anterior ethmoid
What drains through the superior meatus?
–Posterior ethmoid
–Sphenoid
What is rhinosinusitis?
Inflammatory and infective process that affects the nasal passageway and contiguous paranasal sinuses
What are the forms of rhinosinusitis?
–Acute (bacterial)
–Chronic
- Allergic
- Non allergic
- –With polyps
- –Without polyps
What is the frontal and ethmoid sinus related to?
Anterior cranial fossa
What is the maxillary sinus related to?
Orbits
What is the sphenoid related to?
Optic nerve
Internal carotid artery
Cavernous sinus
What can result from spread of infection trhough a sinus?
Meningitis
Intracranial abscess
Orbital sepsis
What are risks of surgery on sinuses?
CSF leak
Orbital complications - worst case scenario - blindness
What is the blood supply of the nasopharynx?
•Anterior
–Derived from branches of internal carotid artery
•Ophthalmic > Anterior/posterior ethmoid arteries
•Posterior
–Derived from branches of external carotid artery
•Sphenopalantine
What is littles area?
A region in the anteroinferior part of the nasal septum where four arteries anastomose to form a vascular plexus.
Which arteries form littles area?
Anterior ethmoidal (branch of ophthalmic)
Sphenopalatine artery (branch of maxillary)
Greater palatine artery (branch of maxillary)
Septal branch of the superior labial artery (branch of facial artery)
Where does epistaxis normally occur?
Little’s area
What are common causes of epistaxis?
- Trauma aka nose picking
- Anticoagulants
- Iatrogenic – surgery
- Idiopathic
- Hypertension
What are the causes of olfactory dysfunction?
–Rhinosinusitis
–Post viral anosmia
–Trauma


