Anatomy Flashcards
85 year old woman with multi-infarct dementia is either unwilling to or unable to make any movements of the left hip joint passively or actively.
Ipsilateral active knee extension and all active ankle movements are grossly normal, all contralateral limb movements are grossly normal.
Where is the pathology?
- lumbar disc vertebrae
- contralateral internal capsule of the brain
- ipsilateral femur
- contralateral medulla oblongata
- contralateral anterior roots
Ipsilateral femur
45 year old man presents with an uncomfortable swelling visible and palpable in relation to the posteromedial aspect of the knee
Where is the pathology?
- great saphenous vein (phlebitis)
- tibial nerve (neuroma)
- small saphenous vein (varicosity)
- biceps femoris tendon
- popliteal artery (aneurysm)
Great long saphenous vein - more superficial, more likely to be seen and palpated
Tibial nerve is unlikely, within the deep fascia
Small saphenous vein and biceps femoris tendon are both more lateral
Pop artery is more central and deeper, less likely to be palpable

Patient in a road traffic accident has sustained a severe compression injury to the lower limb. Compartment syndrome is diagnosed.
In compartment syndrome, pain is maximal on stretching the muscles within the affected compartment. On examination, constant and severe pain is noted, maximal on testing the function of the muscles supplied by the tibial nerve.
Which compartment is affected?
- Anterior compartment of the leg
- Lateral compartment of the leg
- Medial compartment of the thigh
- Posterior compartment of the thigh
- Posterior compartment of the leg
Anterior compartment of leg - dorsiflexion, done by the deep fibular nerve. This is the correct answer, because as the question states pain is maximal in the affected compartment when the muscles are stretched, i.e. the other side is being tested, in this case the tibial nerve causing plantarflexion and corresponding stretch of the anterior compartment
Lateral compartment of the leg - eversion, superficial fibular nerve
Medial compartment of the thigh - adduction of the hip, obturator nerve
Posterior compartment of the thigh - flexion of knee and extension of hip, sciatic nerve
Posterior compartment of the leg - plantarflexion, tibial nerve

It is noted during lower limb examination that when the patient is asked to stand on their right leg, their pelvis tips inferiorly towards their left side.
Which of the following would give this sign?
- ankylosing spondylitis
- iliopsoas sprain
- congenital hip dislocation
- a femoral hernia
- osteoporotic fracture of L1
Describing +ve Trendelenberg meaning gluteus medius is affected (supplied by the superior gluteal nerve, arises from L4, L5 and S1)
Only option that would affect glut medius is congenital hip dislocation
Joe, aged 70, has spinal stenosis as demonstrated on MRI. Which activity would Joe find least likely to exacerbate the leg pain associated with this condition?
- walking downstairs
- cycling
- back extension exercises
- painting a ceiling
- jogging downhill
Cycling would be least likely to exacerbate (not extending the back)
Patient has an urgent femoral arteriogram performed after peripheral vascular examination revealed a cold, pulseless right foot. The arteriogram showd a complete blockage of the most distal point at which complete occlusion is most likely to lead to ischaemia of the whole foot.
- anterior tibial artery
- femoral artery
- fibular artery
- popliteal artery
- posterior tibial artery
Popliteal artery
NB - fibular artery doesn’t contribute to the foot

With the patient lying prone, the examining physician flexes the patient’s knee and extends the hip. The patient feels pain in the anterior aspect of the thigh
Which of the following neural structures is involved in transmitting the action potentials that carry the pain signals?
- lumbosacral plexus
- precentral gyrus
- posterior rami
- anterior roots
- corticospinal tract
Vignette alludes to the femoral nerve (L2, L3, L4) - part of the lumbrosacral plexus
Posterior rami - supplies the skin on the back
Anterior roots - motor fibres and signals
Corticospinal tract deals with motor function
70 year old man is brought to A&E after being found by his neighbour. He had a fall yesterday and was unable to get up. Neurological exam…
Power - right 4/5 hip/knee/ankle, left 5/5 hip/knee/ankle
Reflexes - right increased knee and ankle and plantar response equivocal, left normal with flexor plantar response
Sensation - right normal, left normal
Tone - right increased, left normal
- cerebrovascular accident involving the left internal capsule
- epidural haematoma affecting the right anterior roots
- myasthenia gravis
- progressive muscular atrophy
- tumour compressing the ipsilateral lumbosacral plexus
Cerebrovascular accident involving the left internal capsule
Neuro exam suggests UMN lesion on the left side, every other option is LMN
Hamish is a 74 year old man who has stimbled as he walked off the pavement to cross the road just outside his house. He was helped back into his house by some neighbours. Today he has found it difficult to lift his right leg out of bed. When you see him he is able to weight bear pain-free, but says his right leg is “weak at the knee” and won’t do what he wants it to. O/E he is unable to SLR
- fractured neck of femur
- ruptured iliopsoas tendon
- ruptured quadriceps tendon
- biceps femoris tear
- adductor muscle strain
Ruptured quadriceps tendon - spans both the knee and the hip joint
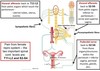
38 year old woman undergoes a routine pap smear. During the colleciton of cells from the uterine cervix, she feels mild pain. Which location is she most likely to experience a referral of pain to?
- umbilical region
- suprapubic region
- perineum and posterior thigh
- epigastric region
- inguinal region and anterior thigh
Perineum and posterior thigh - cervix is below the pelvic pain line (pelvic organ that does not touch the perineum). Visceral afferents go back via S2-S4
Dermatomes for S2-S4 are perineum and posterior thigh
DVT originating in the posterior tibial vein has extended to the level of the inguinal ligament. Further proximal progression will extend the thrombus into which vein next?
- common iliac
- deep femoral
- external iliac
- femoral
- great saphenous
External iliac

Patient presents with pain on active flexion of the hip. Which muscle is the most likely source of the pain?
- Glut medius
- Iliopsoas
- Piriformis
- Sartorius
- Semitendinosis
Iliopsoas - main flexor of the hip joint
Patient presents with anaesthesia in the first web space only. Which part of the nervous system is most likely to be functioning abnormally?
- Deep fibular nerve
- Internal capsule of the brain
- L5 posterior nerve root
- Superficial fibular nerve
- Tibial nerve
Deep fibular nerve - cutaneous nerve
Superficial fibular nerve does dorsum of the foot, and the saphenous nerve does the medial leg

Patient presents with inability to extend the left wrist joint. You also find parasthesia of the skin of the posterior forearm and hand. WHich fracture is most likely to cause this clinical picture?
- fracture of the anatomical neck of the humerus
- fracture of the olecranon
- fracture of the surgical neck of the humerus
- midshaft fracture of the humerus
- supracondylar fracture of the humerus
Vignette is describing wrist drop - radial nerve pathology, typically the elbow joint is spared because the radial nerve has already given off branches to supply the triceps
Midshaft fracture of the humerus
Reminder: radial nerve supplies…
Muscles - posterior forearm, posterior arm
Skin - posterior forearm, posterior arm, posterior hand
Which of these structures would be transected as a consequence of a standard laminectomy?
- annulus fibrosus
- anterior longitudinal ligament
- dura mater
- ligamentum flavum
- posterior longitudinal ligament
Ligamentum flavum

The ankle jerk (calcaneal tendon) reflex specifically tests which named nerve/spinal nerve roots?
- common fibular nerve/L5
- deep fibular nerve/L5
- saphenous nerve/L3,4
- lateral plantar nerve/S1,2
- tibial nerve/S1,2
Tibial nerve/S1,2
Ankle jerk - tibial/S1,2
Knee jerk - saphenous/L3,4
Biceps brachii - musculocutaneous/C5,6
Triceps brachii - radial nerve/C7,8
Dave is running forward during a basketball game when he goes over his ankle. O/E you find an inversion injury to his right ankle. What is most likely?
- Achilles tendon rupture
- Avulsion fracture of medial malleolus
- Rupture of anterior talofibular ligament
- Rupture of calcaneofibular ligament
- Rupture of deltoid ligament
Rupture of anterior talofibular ligament - most commonly injured ligament in inversion and plantar flexion
NB - deltoid ligament is most commonly injured ligament in eversion

Angela had severe left sciatica for 4 weeks. Which is most likely?
- reduced/absent knee jerk
- decreased power of hip flexion
- decreased power of plantar flexion
- impaired sensation on medial side of thigh
- impaired sensation on medial side of leg
Sciatic nerve (L4-S3)
Knee jerk is L3,4
Hip flexion is femoral nerve, L2,3,4
Plantar flexion is tibial, L4-S3
Sensation on medial thigh is obturator nerve, L2,3,4
Sensation on medial leg is saphenous nerve (from femoral), L2,3,4

Patient complains of pins and needles in his right little finger and adjacent palm, and ‘weakness’ of his right hand. O/E you find wasting of the muscles between the metacarpal bones of his right hand dorsally and flattening of the anteromedial border of the forearm. In which region is the affected nerve most likely to be compressed?
- carpal tunnel
- cubital tunnel
- Guyon’s canal
- tarsal tunnel
- thoracic outlet
Vignette describes pathology of the ulnar nerve (wasting of the muscles in the hand supplied by the ulnar nerve is called “guttering”)
Everything in the anterior forearm is supplied by the medial nerve EXCEPT the ulnar half of flexor digitorum profundus and flexor carpi ulnaris, which are both supplied by the ulnar nerve.
The ulnar nerve runs through the cubital tunnel
NB - Guyon’s canal does affect the ulnar nerve but just in the hand, and is seen in cyclists.

Describe the nerve supply of the following…
- posterior arm
- anterior arm
- posterior forearm
- anterior forearm
- hand and intrinsic muscles
- LOAF muscles
Posterior arm - radial nerve
Anterior arm - musculocutaneous nerve
Posterior forearm - radial nerve
Anterior forearm - median nerve
Hand and intrinsic muscles - ulnar nerve
LOAF muscles - median nerve
Which of the following is a cause of left foot drop?
- fractured neck of femur
- fractured neck of fibula
- left femoral nerve compression
- ruptured left achilles tendon
- stroke affecting the right internal capsule of brain
Fractured neck of fibula - common fibular nerve runs here, which splits into superficial fibular nerve (lateral leg) and deep fibular nerve (anterior leg)



