Anatomy Flashcards
Erythrocyte

- Carries O2 to tissues and CO2 to lungs.
- Anucleate and biconcave
- large surface area-to-volume ratio for rapid gas exchange
- Life span of 120 days.
- Source of energy is glucose (90% used in glycolysis, 10% used in HMP shunt).
- Membrane contains chloride-HCO3− antiporter, which allows RBCs to export HCO3− and transport CO2 from the periphery to the lungs for elimination.
Eryth = red; cyte = cell.
Erythrocytosis = polycythemia = incr hematocrit. Anisocytosis = varying sizes.
Poikilocytosis = varying shapes.
Reticulocyte = immature erythrocyte, marker of proliferation.
Platlet (thrombocyte)

- Involved in 1° hemostasis.
- Small cytoplasmic fragment derived from megakaryocytes.
- Life span of 8–10 days.
- When activated by endothelial injury, aggregates with other platelets and interacts with fibrinogen to form plug.
- Contains dense granules (ADP, calcium) and α granules (vWF, fibrinogen).
- Approximately 1⁄3 of platelet pool is stored in the spleen.
- Thrombocytopenia or decr platelet function results in petechiae.
- vWF receptor: GpIb.
- Fibrinogen receptor: GpIIb/IIIa.
Leukocyte

- Granulocytes (neutrophil, eosinophil, basophil)
- Mononuclear cells (monocytes, lymphocytes).
- Responsible for defense against infections.
- Normally 4000– 10,000 cells/mm3.
- WBC differential from highest to lowest (nl per USMLE):
Neutrophils (54–62%)
Lymphocytes (25–33%)
Monocytes (3–7%)
Eosinophils (1–3%)
Basophils (0–0.75%)
Leuk = white; cyte = cell.
Neutrophils Like Making Everything Better.
Neutrophil

- Acute inflammatory response cell.
- Increased in bacterial infections.
- Phagocytic.
- Multilobed nucleus.
- Small, more numerous specific granules contain ALP, collagenase, lysozyme, and lactoferrin.
- Larger, less numerous azurophilic granules (lysosomes) contain proteinases, acid phosphatase, myeloperoxidase, and β-glucuronidase.
- Hypersegmented polys (5 or more lobes) are seen in vitamin B12/ folate deficiency.
- Incr band cells (immature neutrophils) reflect states of incr myeloid proliferation (bacterial infections, CML).
Monocyte

Differentiates into macrophages in tissues.
Large, kidney-shaped nucleus.
Extensive “frosted glass” cytoplasm.
Mono = one (nucleus); cyte = cell.
Monocyte: in the blood.
Macrophage

- Phagocytoses bacteria, cellular debris, and senescent RBCs and scavenges damaged cells and tissues.
- Long life in tissues.
- Macrophages differentiate from circulating blood monocytes.
- Activated by γ-interferon.
- Can function as antigen-presenting cell via MHC II.
- CD14 is a cell surface marker for macrophages.
- Macro = large; phage = eater.
- Important component of granuloma formation (e.g., TB, sarcoidosis).
- Macrophage: in the tissue.
Eosinophil

- Defends against helminthic infections (major basic protein).
- Bilobate nucleus.
- Packed with large eosinophilic granules of uniform size.
- Highly phagocytic for antigen antibody complexes.
- Produces histaminase and arylsulfatase (helps limit reaction following mast cell degranulation).
Eosin = a dye; philic = loving.
Causes of eosinophilia = NAACP: Neoplasia Asthma Allergic processes Connective tissue diseases Parasites (invasive)
Basophil

- Mediates allergic reaction.
- Densely basophilic granules containing heparin (anticoagulant), histamine (vasodilator), and leukotrienes.
- Basophilic—staining readily with basic stains.
- Isolated basophilia is uncommon, but can be a sign of myeloproliferative disease, particularly CML.
Mast Cell
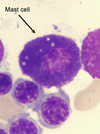
- Mediates allergic reaction in local tissues.
- Mast cells resemble basophils structurally and functionally but are not the same cell type.
- Can bind the Fc portion of IgE to membrane.
- IgE cross-links upon antigen binding, causing degranulation, which releases histamine, heparin, and eosinophil chemotactic factors.
- Involved in type I hypersensitivity reactions.
- Cromolyn sodium prevents mast cell degranulation (used for asthma prophylaxis).
Dendritic Cell

- Highly phagocytic APCs.
- Functions as link between innate and adaptive immune systems.
- Expresses MHC class II and Fc receptor on surface.
- Called Langerhans cell in the skin.
Lymphocyte

-Divided into B cells, T cells, and NK cells. -B cells and T cells mediate adaptive immunity. -NK cells are part of the innate immune response. -Round, densely staining nucleus with small amount of pale cytoplasm.
B Lymphocyte
- Part of humoral immune response.
- Arises from stem cells in bone marrow.
- Matures in marrow.
- Migrates to peripheral lymphoid tissue (follicles of lymph nodes, white pulp of spleen, unencapsulated lymphoid tissue).
- When antigen is encountered, B cells differentiate into plasma cells that produce antibodies, and memory cells.
- Can function as an APC via MHC II.
B = Bone marrow
T lymphocyte
- Mediates cellular immune response.
- Originates from stem cells in the bone marrow, but matures in the thymus.
- T cells differentiate into:
cytotoxic T cells (express CD8, recognize MHC I); helper T cells (express CD4, recognize MHC II); and regulatory T cells.
- CD28 (costimulatory signal) necessary for T-cell activation.
- The majority of circulating lymphocytes are T cells (80%).
T is for Thymus.
CD is for Cluster of Differentiation.
CD4+ helper T cells are the primary target of HIV.
MHC × CD = 8
(e.g., MHC 2 × CD4 = 8, and MHC 1 × CD8 = 8).
Plasma Cell

-Produces large amounts of antibody specific to a particular antigen. -Eccentric nucleus, clock-face chromatin distribution, abundant RER, and well-developed Golgi apparatus. Multiple myeloma is a plasma cell cancer.


