Anatomy Flashcards
What is the normal width of the small bowel, large bowel and cecum?
Small bowel - 3cm
Large bowel - 6cm
Cecum - 9cm
What are the three most common causes of small bowel obstruction?
- Adhesions
- Hernia
- Tumour
What are the two most common causes of large bowel obstruction?
- Tumour
- Diverticulitis
Where do bowel cancer mets tend to appear?
Liver
Where is the lymphatic drainage of the large bowel and proximal 2/3 of the rectum?
Inferior mesenteric lymph nodes
Where is the lymphatic drainage of the distal 1/3 of the rectum?
Either the same as the rest of the rectum or to the internal iliac and superficial inguinal lymph nodes
Where is the lymphatic drainage of the small bowel?
Superior mesenteric lymph nodes and cisterna chyli
What are the two anal sphincters?
Internal and External

What are the characteristics of the internal anal sphincter:
- Control
- Type of nerve innervation and nerve
- Position
- Function
- Involuntary autonomic (S4)
- Sympathetic
- Upper 2/3 of canal
- It maintains the resting control by being kept shut and preventing incontience
What are the characteristics of the external anal sphincter:
- Control
- Type of nerve innervation and nerve
- Position (layers and continuation of..?)
- Function
- Voluntary (striated)
- Pudendal S2-S4 keeps it closed, we relax it
- Three layers - Subcutaneous, superfical, deep (continuation with puborectalis)

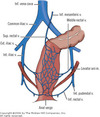
What is the arterial blood supply to the anus?
Superior Rectal artery via the IMA
Middle rectal artery via the internal iliac
Inferior rectal artery via the internal iliac and inferior pudendal

What is the venous drainage of the anus?
Superior rectal vein to IMV (Portal)
Middle rectal vain to internal iliac vein (systemic)
Inferior rectal vein to the internal iliac (systemic)
What is Alcocks canal?
A anatomical area where the pudendal nerve, internal pudendal artery and internal pudendal vein travel through

What is the key nerve in the pelvis and what does it do?
Pudendal (S2-S4)
- Sensation to external genitalia
- Maintains anal tone via external ana sphincter
- Controls external urethral sphincter
What system does the SRV drain to?
Portal

