Anatomy Flashcards
In the image of the pelvis below, what does the number 1 denote?

- iliac crest

In the image of the pelvis below, what does the number 2 denote?

- anterior superior iliac spine
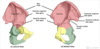
In the image of the pelvis below, what does the number 3 denote?

- anterior inferior iliac spine

In the image of the pelvis, what does number 4 denote?

- pubic tubercle

In the image of the pelvis, what does number 5 denote?

- pubic symphasis

In the image of the pelvis, what does number 1 denote?

- iliac tubercle

In the image of the pelvis, what does number 2 denote?

- iliac crest

In the image of the pelvis, what does number 3 denote?

- anterior superior iliac spine
- abbreviated as ASIS

In the image of the pelvis, what does number 4 denote?

- inguinal ligament

In the image of the pelvis, what does number 5 denote?

- pubic tubercle

Where does the transphloric plane run?
- transversely (horizontal)
- between pubic symphasis and jugular notch
- aproximaltey at L1

Where does the trans-tubercular plane, also known as the intertubercular plane run?
- between the superior aspect of the iliac crest

What is the inguinal region?
- inguinal means groin in latin
- groin area
What is and where is the inguinal canal located?
- short passage that runs superior and parrael to the inguinal ligament

What is the anatomical and physiological importance of the inguinal canal?
- serves as a pathway for genitalia
- weak point for potential hernias

What is the mid-lingual point?
- halfway between the pubic symphysis and the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)

Where is the mid-point of inguinal ligament?
- halfway between the pubic tubercle and the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)

There are 2 openings of the inguinal canal, known as rings. These are the superficial and deep rings, where are they located?
- deep (internal) ring is found above the midpoint of the inguinal ligament
- superficial (external) ring marks the end of the inguinal canal, and lies just superior to the pubic tubercle

What is a direct inguinal hernia?
- caused by weakeness of posterior wall of the inguinal canal
- abdominal contents push through weak area into inguinal canal
- abdominal contents exit at superficial ring and emerge within the scrotum

What is an indirect inguinal hernia?
- abdominal contents pass through the deep inguinal ring
- abdominal contents enter the inguinal canal
- abdominal contents exit at superficial ring and emerge within the scrotum

What is the outer most central layer of the abdominal musccular wall called?
- rectus abdominas

When looking at the rectus abdominas, what are the white lines that run horizontally and seperate rectus abdominas called?
- tendinous intersections

When looking at the rectus abdominas, what are the white lines that run vertically either side of the rectus abdominas called?
- linea semilunaris
- a tendinous intersection separating the lateral edge of the muscle from the external oblique and internal oblique muscles
- usually extends from tip of the ninth costal cartilage to the pubic tubercle

What is the white line that runs vertically down the centre of the abdominal wall between the rectus abdominal muscles?
- formed by the lateral tendon sheaths of lateral muscles aponeurosis
- later muscles are the internal and external oblique muscle and transversus abdominis muscle
- meet in the middle forming the linear alba























