ANAT - Heart & Mediastinum Flashcards
1
Q
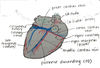
HEART CHAMBERS
A
-
Blood flow
- SVC/IVC –> RA –> tricuspid valve –> RV –> pulmonary vein –> lungs –> pulmonary artery –> LA –> mitral valve –> LV –> aortic valve –> aorta –> system
- Right chamber = pulmonary circuit (decreased BP, 15-20 mmHg)
- **Left chmaber ** = systemic circuit (increased BP, 100 mmHg)
- Blood volume must be equal on both sides or else will cause backup
- LV failure = pulmonary edema
- RV failure = peripheral edema
- Aortic stenosis
- Aortic valve doesn’t fully open
- LV must contract harder (heart grows and gets stronger as a result)
- So, they sometimes don’t fix it until symptomic because its advantageous to have a strong heart
2
Q
CARDIAC CYCLE
A
- Diastole = Filling
1. A/P valves close
- T/M valves open
- Atria contract
* Systole = Emptying - T/M valves close
- Ventricles contract
- A/P valves open
3
Q
CHEST CAVITIES
A
- Two pulmonary cavities (1 per lung) and mediastinum
- Pulmonary cavities surrounded by parietal pleura
- Mediastinum surrounded by fibrous pericardium
-
Fibrous pericardium = dense CT sac around heart
- Lined by parietal pericardium
- Limited distensibility (but can stretch it over time)
- If it fills with fluid (blood), puts pressure on ventricles –> tamponade
4
Q
DIAPHRAGMATIC SURFACE OF THE HEART
A
- Esophagus runs posterior to pericardial sac; therefore, transesophageal US’s can be used to visualize the heart
- costomedial recess formed by the parietal leural from costal side reflecting over fibrous pericadium creating a space
- Heart attches to diaphragm at is central tendon
- R/L of heart = phrenic nerves and pericardiacophrenic vessels
- Pericardiacophrenic vessels supply fibrous pericardium and parietal pericardium
5
Q
MEDIASTINUM
A
- Divided into superior/inferior at T4/Angle of Louis
-
Superior
- Aortic arch
- Esophagus
- Trachea
- Roots of great vessels
- Phrenic, vegus, and cardiac nerves
-
Inferior
-
Anterior
- Fat, branches of internal thoracic artery
- Thymus (in children)
-
Middle
- Pericardial sac and heart
- Pulmonary trunk
- Ascending aorta
- SVC
-
Posterior
- Everything anterior to vertebrae and in between parietal pleural of lungs
-
Anterior
6
Q
FORMATION OF THE PERICARDIAL SAC

A
- Heart grows, invaginating the serous pericardium
- Creates 2 layers with a serous fluid filled space in between
- Inside to out:
- Endocardium
- Myocardium
- Epicardium
- Visceral pericardium
- Parietal pericardium
- Fibrous pericardium
7
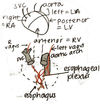
Q
BORDERS OF HEART IN SITU
A
- Phrenic nerves = between fibrous pericardium and parietal pericardium (therefore, not technically in the mediastinum)
- Left vagus nerve = runs along aortic arch, branches into left recurrent pharygneal
- Right vagus nerve = runs behind SVC
- Left and right vagus meet and mix in the esophageal plexus
- During fetal period, blood =/= pumped to lungs, but heart still needs to receive blood on L side to grow strong…
- Shunt between L & R atria = ductus arteriosis
- Closes before birth
- Base of heart = LA (mostly, but a little bit of RA)
- Apex = where L & R ventricles meet (on diaphragm)
8
Q
SINUSES
A
- Tranverse sinus - anterior to SVC and posterior to pulmonary trunk and aorta
- Oblique sinus - between parietal pericardium and posterior heart

9
Q
VARIATIONS IN CORONARY CIRCULATION
A
- Left Dominant Heart - PD comes off of left coronary artery
- Right Dominant Heart - PD comes off right coronary artery
10
Q
RIGHT ATRIUM
A
- Outer wall = pectinate muscles
- Inner wall = smooth
- Fossia ovalis = fetal R-L shunt
- Valve & ostium or coronary sinus
- Atrial appendage = auricle
11
Q
LEFT ATRIUM
A
- All smooth walls
- Remnant of septum primium
- Left appendage = auricle
- Afrib –> clot formation –> easily throws
12
Q
VENTRICLES
A
-
Papillary muscles
- Connect to valve flaps via chordae tendineae
- Prevent valve inversion during contraction to prevent regurgitation by contracting –> tension on chordae
- Regulated by modulatory band arising from heart conduction system
- During contraction, pull apex up toward cardiac skeleton = fibrous disc between atria and ventricles from which valves arise
- During contraction, all valves (A, P, T, M) in same plane
- Muscles on ventricular wall = traberculae carneae
- Left Ventricle
- Anterior and posterior papillary muscles
- Anterior and posterior valve flaps
- THICK walled
- Right Ventricle
- Septal, anterior, and posterior papillary muscles
- Septal, anterior, and posterior papillary muscles
13
Q
VALVES
A
-
Aortic/Pulmonary
- Diastole: OPEN
- Systole: CLOSED
- Inversion prevented by SEMILUNAR SHAPE
-
Mitral/Tricuspid
- Diastole CLOSED
- Systole OPENED
- Inversion prevented by PAPILLARY MUSCLES
14
Q
ANGIOGRAM
A
- Inject dye through ostium of coronary artery in aorta
- Fills during diastole because the aortic valve flaps are down, exposing the ostium
15
Q
FIBROUS SKELETON
A
- Attachment point of cardiac muscle fibers
- Electrical insulator between atria/ventricles