Analysis, Design and Comparison of Algorithms Flashcards
(20 cards)
What are two things to check when Analysing an Algorithm
- Time Complexity
- Space Complexity
What is the Time Complexity of an Algorithm
How much time an algorthim takes to solve a particular problem relative to the number of inputs it recieves
What is Time Complexity measured in
- Big-O notation
- Big-o notation shows the effectiveness of an algorithm
- It shows an upper limit for the amount of time taken relative to the number of data elements given as an input
How is Big-O notation written
In the form 0 (n), where n is the : the number of inputted entities, and 0 (n) is the time relationship
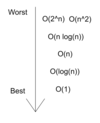
What are the examples of Big-O Notation
- 0 (k) - Constant Time Complexity - the amount of time taken to complete an algorithm is independent from the number of elements inputted
- 0 (n) - Linear Time Complexity - the amount of time taken to complete an algorithm is directly propoertional to the number of elements inputted
- 0 (n2) - Polynomial Time Complexity (example) - the amount of time taken to complete an algorthim is directly propertional to the sqaure of the elements inputted
- 0 (nn) - Polynomial Time Complexity - the amount of time taken to complete an algorithm is directly proportional to the elements inputted to the power of n
- 0 (2n) - Exponential Time Complexity - the amount of time taken to complete an algorithm will double with every additional item
- 0 (log n) - Logarithmic Time Complexity - the time taken to complete an algorithm will increase at a smaller rate as the number of elements inputted increases
Give an Algorithm example of each Big-O Notation
- Constant Time - print (“hello”)
- Linear Time Complexity - for ([a,b,c … n] print(“hello”)
- Polynomial Time Complexity - for ([a,b,c … n] for ([a,b,c … n]) print (“hello”)
- Exponential Time Complexity - recursive algorithms with size n
- Logarithmic Time Complexity - a divide and conquer algorithm
Describe the Consant Time Complexity Graph

Describe the Linear Time Complexity Graph

Describe the Polynomial Time Complexity Graph

Describe the Exponential Time Complexity Graph

Describe the Logarithmic Time Complexity Graph

Which are the best and worst time complexities
What is the Space Complexity of an Algorithm
The amount of storage the algorithm takes
How is Space Complexity written
- Big O notation
- Algorithms store extra data whenever they make a copy, this isn’t ideal
- When working with lots of data it is not a good idea to make copies as they takes up storage which is expensive
What is an Algorithm
A series of steps that complete a task
When does time complexity take priority and when does space complexity take priority
- If you have a lot of processing power then focus on space complexity
- If you have a lot of data that needs to be processed quickly you would focus on time complexity
How do you reduce Space Complexity and Time Complexity
- Reduce Space Complexity - perform all of the changes on the original piece of data
- Reduce Time Complexity - reduce the number of embedded loops, reduce number of items you have to complete operations on (divide and conquer algorithm)
What Big-O Notation does the Linear Search Algorithm have
0 (n)
What is the Big-O Notation for the Binary Search Algorithm
0 (log(n))
What is the Big-O Notation for a Bubble Sort Algorithm
O (n2)


