Anaesthetics Flashcards
What are the causes of airway obstruction?
Vomit/ Tongue
Angioedema
Laryngospams
Epiglotitis
Tumours
Trauma
How many breaths per minute is normal?
12
What volume of air is tidal volume?
500 ml
What is total lung capacity?
6 Litres
What volume of air is normal functional residual capacity?
2.5 L
What is functional residual capacity?
Amount of air left behind after tidal volume
In obese patients, what lung volume is reduced?
Functional residual capacity
Describe what the terms “variable” and “fixed” are used for when describing oxygen masks?
Variable - Unable to determine the amount of oxygen administered
Fixed - Able to determine the amount of oxygen administered
What is the maximum amount of oxygen that can be put into nasal speculums?
4 Litres
What type of mask is a Hudson mask?
Variable performance mask
What type of mask is a non-rebreather mask?
Fixed performance mask
What is this ? What is its use?

Guedel airway (oropharyngeal airway)
Used to open airway and depress tongue
How is a guedel oropharygenal airway inserted?
Reverse side first, then turned around
What is this?

Nasopharyngeal airway
What is an “LMA” and what is its use?
Laryngeal mask airway
Sits over the laryngeal inlet - keeping open and supplies oxygen
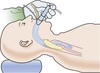
What is an “igel”?
Supraglottic airway
Sits above laryngeal inlet

What is used to guide endotracheal tube placement through vocal cords?
Laryngoscope
What is an example of a definitive airway?
Endotracheal tube
What factors make intubation difficult?
Airway obstruction
Kids
Hyperbarric patients
Beards
Rotten teeth
TMJ dysfunction
Jaw fracture
Receeding jaw
What is caprogrpahy?
Measurement of CO2 from endotracheal tube
Shows that tube is placed in the correct place
Shows that there is normal cardiac output

How would a patient who could not normally be intubated be intubated?
Awake fiberoptic endoscope
What airway manoeuvre should be used if there is a queried C spine fracture
Jaw thrust
What airway manoeuvre should be done to open the airway of a normal patient?
Head tilt chin lift
What are the three pilars of anaesthesia?
Hyponosis
Muscle relaxation
Analgesia
How is cardiac output calculated?
CO = Stroke volume X Heart rate
What is normal cardiac output?
4-8 L per minute
Where is spinal anaesthesia injected?
L3/L4
Injected into the subarachnoid space
What is epidural injected into?
Epidural space (vertebral canal)
What does an epidural needle pass through?
Supraspinous
Interspinous
Ligamentum flavum
Epidural space
What does a spinal needle pass through?
Supraspinous
Interspinous
Ligamentum flavum
Dura matter
What makes CSF?
Choroid plexus:
Lateral ventricles
Third ventricles
Fourth ventricles
An epidural above which spinal level may lead to bradycardia?
T4
What are the advantages of endotracheal tube over a laryngeal mask?
Endotracheal tube seals the airway. Provides airway patency + protection
Consider in patients who are at risk of aspiration
How is the minute volume of lungs calculated?
VM= Tidal X Respiratory rate
What is alveolar ventilation?
Alveloar ventilation is the portion of the minute volume that takes part in gas exchange at alveolus.
Proportion of gas is wasted - remains in large airways or lung dead space
VM = Alveolar ventilation + Dead Space Ventilation


