Anaerobic Metabolism Flashcards
What is the only way of producing energy without oxygen and mitochondria?
Glycolysis
Where does glycolysis take place in the cell?
In the cytosol
What is the net production of glycolysis?
From 1 molecule of glucose (6C):
- Loss of 2 x ATP
- Gain of 2 x Pyruvate (3C)
- Reduction of 2 x NAD to NADH
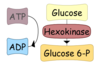
Describe the 1st step of Glycolysis
Hexokinase uses ATP to phosphorylate Glucose into Glucose-6-P.
This reaction is irreversible and traps Glucose inside the cell.
Hexokinase is regulated through inhibition when the concentration of Glucose-6-P increases.
Describe the 2nd step of Glycolysis
Phosphohexoisomerase converts Glucose-6-P to Fructose-6-P
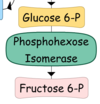
Describe the 3rd step of Glycolysis
Phosphofructokinase *uses* *ATP* to phosphorylate Fructose-6-P into Fructose 1,6-biphosphate.
This reaction is irreversible.
Phosphofructokinase is inhibited by high levels of intracellular ATP

Describe the 4th step of Glycolysis
Aldolase splits Fructose 1,6-biphosphate into Glyceraldehyde 3-P (3C) and Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (3C)

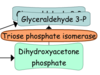
Describe the 5th step of Glycolysis
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate can be converted to glyceraldehyde 3-P by Triose Phosphate Isomerase.
Describe the 6th step of Glycolysis
2 x Glyceraldehyde 3-P is oxidised to 2 x 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate by Glyceraldehyde 3-P Dehydrogenase.
2 x NAD+ is reduced to 2 x NADH

Describe the 7th step of Glycolysis
2 x 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate is dephosphorylated by Phosphoglycerate Kinase to form 2 x 3-Phosphoglycerate and 2 x ATP (substrate-level phosphorylation)

Describe the 8th step of Glycolysis
2 x 3-phosphoglycerate is converted to
2 x 2-phosphoglycerate by Phosphoglycerate mutase

Describe the 9th step of Glycolysis
2 x 2-phosphoglycerate is converted into 2 x Phosphoenolpyruvate by Enolase

Describe the 10th step of Glycolysis
2 x Phosphoenolpyruvate is dephosphorylated by Pyruvate Kinase to form 2 x Enolpyruvate and 2 x ATP
The 2 x Enolpyruvate is rapidly and non-enzymatically converted to form 2 x Pyruvate
This causes the former reaction to be irreversible.

Give an overview of the process of Glycolysis and the net products per molecule of Glucose.
2 x Pyruvate
2 x ATP (2 ATP loss, 4 ATP gained)
2 x NADH
Name the 3 enzymes in glycolysis that are regulated.
- Hexokinase
- Phosphofructokinase
- Pyruvate Kinase



