An Introduction to the Structure of Cells Flashcards
What do all cells have in common?
DNA
Cytoplasm
Plasma membrane surrounding the cell
Where is DNA stored in prokaryotic cells
Nucleoid
Where is DNA stored in eukaryotic cells
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Semi-fluid matrix
Contains sugars, amino acids, proteins etc In a cytosol
How big are prokaryotes
1-10µm
How big are eukaryotes
10-100µm
Why aren’t cells bigger?
Would make diffusion less efficient
Surface area : volume ratio would be worse
Why is the surface area : volume ratio important in cells
Communication and interaction with internal environment happens through the surface of the cell
If the volume in the ratio was too large it wouldn’t be able to keep up
2 types of cell
Prokaryotes
Eurkaryotes
Types of prokaryotes
Bacteria
Archaea
Archaea
Ancient prokaryotes
Often adapted to extreme conditions
Extreme conditions arachaea
Methanogens
Extreme halophiles
Extreme thermophiles
Methanogens
Archaea
Metabolic activities produce methane
Poisoned by oxygen
Extreme halophiles
Archaea
Salt lovers
Extreme thermophiles
Archaea
Heat lovers
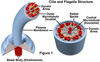
Structure of a prokaryotic cell
Nucleoid
Ribosomes
Cytoplasm
Pili
Plasma membrane
Cell wall
Flagellum (sometimes)
Prokaryote cell wall
Outside plasma membrane
Quite porous
Function of prokaryote cell wall
Protection
Maintains shape
Helps prevent excessive water uptake
Gram positive bacteria
Thick, single layered cell wall
Retains dye
Gram negative bacteria
More complex then gram positive
Many layers
Doesn’t retain dye
How do antibiotics often work
By disrupting cell walls
Bacteria
What is the cell wall often covered by What does it do
Capsule Is slimy, prevents it drying out and helps attachment
Ways prokaryotic cells move about
Flagellum
Pili
Interior organisation of prokaryotes
Simple
No internal compartmentalisation
No membrane bound organelles
No nucleus Cytoplasm with internal support structure
Types of Eukaryotes
Protists
Fungi
Plants
Animals
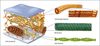
Structure of eukaryote cell
Compartmentalised
Plasma membrane
Cytoplasm
Organelles
Nuclear envelope
Nucleus
Which eukaryote cells have a cell wall
Plants
Fungi
What does the cell wall do
Provides mechanical support
Protects against infection
Eukaryote meaning
True nucleus
Prokaryote meaning
Before nucleus
Plant cell wall
Composed of fibres of cellulose embedded in polysaccharides and proteins
Interconnected by plasmadesmata
Plasmadesmata
Physical passageway in cell wall
Allows communication and movement of molecules between cells that the cell wall would stop
Central vacuole
Large membrane bound sac in plant cells
Stores proteins, pigments and waste
Presses against cell wall giving tugor pressure
How much of the cell does the central vacuole take up
Up to 80%
Contractile vacuole
Found in some protist cells
Stores water coming in by osmosis then expels the water
Stops the cell bursting from excess water
Types of vacuoles
Central (plant)
Contractile (protists)
Phagocytic
Food
Cytosol
Region of eukaryotic cells that is inside the plasma membrane and outside the organeles
Cytoplasm =
Cytosol + Organelles
Cytoplasm is the site of…
Metabolism
Catabalism
Metabolism
Utilisation of energy for synthesis of materials
Catabalism
Breakdown of materials to utilize energy and generate building blocks for construction macromolecules
Each step catalysed by an enzyme
Nucleus
Contains DNA
Spherical
Surrounded by nuclear envelope
What amount of cell volume is the nucleus
10-20%
Nucleolus
Inside nucleus
Site of intense ribosomal RNA synthesis
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane
Has nuclear pores to allow passage of substance
Interior filled with fluid containing chromosomes
What is eukaryotic DNA divided into?
Chromosomes
Chromosomal territory
Distinct
Non-overlapping
Where each chromosome is located within the cell nucleus of eurkaryotic cells
Chromosome
Unit of genetic material
Composed of DNA and proteins
Types of histone proteins
Central histone
Spacer histone
Nucleosomes
Formed by DNA coiled around clusters of histones
Looks like beads on a string
Chromotins around surrounded by…
Nucleoplasm
Nuclear lamina
Made of intermediate filaments
Lines the inner nuclear membrane
Attaches to chromatins which helps maintain nuclear shape and keep chromosomes in their territories
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis
Structure of ribosomes
Ribosomal Ribonuceic acid (rRNA) bound with several dozen types of protein 2 subunits, 1 large and 1 small
When are ribosomes functional and why
Only when attached to messenger RNA (mRNA)
mRNA contains the code required to make the protein
Free ribosomes
Make proteins that function in the cytoplasm
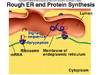
Proteins that function in membranes or for transport are made by…
Ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum
RER stands for
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Why do cells in the same organism, with the same DNA, look and function differently
They share the same genome
But the proteome is different