Amino acids and proteins Flashcards
Tell me the two types of protein classes? Their properties and some of their uses.
Fibrous
- insoluble
- provides strength
- makes protective layers
- linear
- USES: silk, coatings of secretory granuels/ seeds/ viruses also the intracellular cytoskeleton
Globular
- spherical
- soluble
- USES: enzymes, transport proteins, hormones, toxins
Whats the geneal amino acid strucure?

Draw the zwitterion for amino acids and how the charges change in a positive and negative solution

Amino acids have L and D structures. What form is found within our systems?
L form as it is most stable
What amino acid is found at the start of the chain where every protein is made?
Methionine (AUG) but sometimes Valine might be found (GUG)
What is tryptophan a precursor to?
Melanin and serotonin
What is proline an unusual amino acid
its a cyclic, aromatic amino acid
Do uncharged R groups tend to be hydrophilic or hydrophobic ?
Hydrophilic
Give examples for what the following amino acids are used for?
- Glutamate/ aspartate/ glycine
- tryptophan
- tyrosine
- cysteine/ glycine/ glutamate
- neurotransmitters
- precursor for melatonin and serotonin
- precursor for adrenaline and noradrenaline
- these make glutathione
What are the two types of amino acids?
polar and nonpolar
What charge is the side chain in polar amino acids?
negative
poisitive
uncharged polar
What charge is the side chain in nonpolar amino acids?
nonpolar
Name the two polar amino acids that have a negative side chain, their 3 letter code and 1 letter code.
Polar amino acids with negative side chain
- Aspartic acid, Asp, D
- Glutamic acid, Glu, E
Name the 3 polar amino acids that have a positive side chains, their 3 letter code and 1 letter code
Polar amino acids with positive side chain
- Arginine, Arg, R
- Lysine, Lys, K
- Histidine, His, H
Name the 5 polar amino acids with an uncharged polar side chain, their 3 letter code and 1 letter code
Polar amino acids with an uncharged polar side chain
- Asparagine, Asn, N
- Glutamine, Gln, Q
- Serine, Ser, S
- Threonine, Thr, T
- Tyrosine, Tyr, Y
Name all 10 Nonpolar amino acids with nonpolar side chians, their 3 letter code and 1 letter code
Nonpolar amino acids with nonpolar side chains
- Alanine, Ala, A
- Glycine, Gly, G
- Valine, Val, V
- Leucine, Leu, L
- Isoleucine, Ile, I
- Proline, Pro, P
- Phenylalanine, Phe, F
- Methionine, Met, M
- Trytophan, Trp, W
- Cysteins, Cys, C
Identify these amino acids…


Why is cysteine sometime classed as hydrophilic (polar)?
Because it is a weak acid
What reaction joins amino acids together?
A condensation reaction
During translation of mRNA, what become the site for the condensation reacitons?
ribosomes
Whats required to break a peptide bond?
Protease enzyme or an extreme condition
Polypeptide have a sequence of residues. What is the sequence decribed as ?
N to C
What calculation is done to estimate the molar mass of a protein?
Multiply the number of residues by 100
Whats the only amino acid that isn’t in L form?
Glycine
What are the 4 steps involved with translation?
- Initiation
- elongation
- termination
- post-translational processing of the protein
Tell me what occurs in the initiation process of translation?
- small subunit of the ribosome binds at the 5’ end of the mRNA molecules and moves in a 3; direction until it meets a start codon (AUG)
- it then forms a complex with the large unit of the ribosomes complex and an initiation tRNA molecule
What happens in the elongation process of translation?
- codons on the mRNA molecule determine which tRNA moelcule linked to an amino acid bind to the mRNA
- an enzyme- peptidyl transferase- links the amino acids together using peptide bonds
- the process continues producing a chain of amino acids as the ribosome moves along the mRNA moleucle
What happens in the termination process of translation?
- translation is terminated when the ribosomal complex reached one or more stop codons (UAA, UAG, UGA)
- the ribosomal complex in eukaryotes is larger and more complicated than in prokaryotes
- in addition, the processes of transcription and translation are divided in eukaryotes between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, which provides more opportunities for the regulation of gene expression
Where are ribosomes assembles and where do they then mature?
Ribosomes are assembled in the nucleolus and then mature in the cytoplasm
What type of ribosomes are present in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes: 80s
Prokaryotes: 70s
The 80s and 70s ribosomes are composed of two subunits, what are they for each?
80s is composed of 60s and 40s subunits
70s is composed of 50s and 30s subunits
What does the ‘s’ on the end of ribosome names stand for?
e.g. 80s
S: Svedberg (denotes sedimentation)
Whats ribozyme and its function?
It is an enzyme that catalyses a chemical reaction
They are found in ribosomes where they join amino acids together to make protein chains
Name the 3 types of ribosome’s used in translation? And they roles in translation?
- mRNA: codes for proteins
- rRNA: subunit of the ribosomes
- tRNA: brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome
What type of moleucle is tRNA?
An adaptor molecule
Label this ribosome with its general structure…
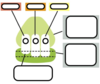

In the ribosome tell me what happens at each site…
P site
E site
A site
P site: where proteins are made
E site: Where tRNA exit’s
A site: This is the acceptor site for charged tRNA molecules
Why do the small and large subunits of the ribosome have to be joined together?
Otherwise no translation will occur
When mRNA is translated, which part of the ribosome does it slide through?
through a channel on the small subunit
in 1961, what did the two scientists Brenner and crick suggest?
That each codon must contain 3 bases, from an analysis of a large number of genetic crosses which resulted in the addition or subtraction of 1, 2 or 3 bases
With the addition of one, two or three bases within the RNA, which addition resulted in the active proteins?
The addtion of three bases resulted in active proteins
Whilst the addition of one or two bases resulted in inactive proteins
How many combinations do the following give?
singlet code
doublet code
triplet code
quartet code
singlet code: 4
doublet code: 16 (42)
triplet code: 64 (43)
quartet code: 256 (44)
What else did brenner and cricks experiment suggest about the properties of the genetic code?
There is a non-overlapping reading frame which is a triplet code
Tell me the 5 properties of the genetic code?
- triplet code
- degenerate
- non-overlapping
- no punctuation
- universal
The genetic doe is said to be universal, but what are the two exceptions to this?
- Mitochondria
- chloroplasts
In the mitochondria and chloroplasts, why is the genetic code not universal?
- translation is more like a prokaryotic system
- it uses mitochondria-specific ribosomes (55s)
- uses a different set of tRNA genes
In eukaryotes what the first amino acid that always is found at the start of peptide synthesis that initiates the process?
What might happen to this amino acid after synthesis?
Methionine (AUG)
After synthesis, this amino acid might be cleaved off
In bacteria, what is added to the start of the chain during peptide synthesis?
Formylmethionine
How do the bacteria know where to start protein synthesis in bacteria and eukaryotes, whats present?
In bacteria: it contains a Shine-Dalgarno sequence(which is complementary to 3’ end of 16s rRNA). the ribosomes slows down when it passes this sequence then just starts from the first AUG after that
In eukaryotes: translation starts at the first AUG from the 5’ end
Whats the equation for the activation if the amino acid?
ATP + Amino acid –> Aminoacyl adenylate + PPi
(intermediate)
Whats the equation for the formation of aminoacyl-tRNA?
Aminoacyl adenylate + tRNA –> aminoacyl-tRNA + AMP
Ribosomes cannot proofread, whats their general error rate?
1 in 10,000
Whats a polysome?
A cluster of ribosomes held together by a strand of mRNA which each is translating
What are the types of DNA/mRNA mutations and what they cause?
1. Point mutations: Where a base is changed for another in a gene
- Silent: changes base code but doesnt effect 1˚. codes for the same amino acid due to DNA’s degenerative nature
- missense: new triplet code for different amino acid. change in 1˚
- non-sense: introduces a stop code part way through the gene. change in 1˚
2. Indel mutations: individual base pairs are added or removed from the gene sequence which leads to frame shift
- insertion: addition of bp
- deletion: deletion of bp
3. Expanding triple nucleotides: whole triplet codes are added to the gene sequence. DOES NOT lead to frame shift. does change the 1˚
What can distrupt protein synthesis and what is it selective for?
Antibiotics can act on protein synthesis and are selective for the bacterial 70s ribosomes (not the 80s)
Name some antibiotics and their affect on protein synthesis
- Streptomycin: freezes the initiation complex and causes misreading of the mRNA
- Tetracycline: prevents binding of incoming aminoacyl-tRNA
- Chloramphenicol: inhibits peptidyl transferase
- Erythromycin: binds to 50s and inhibits translocation
- Puromycin (not selective): mimics the terminus of aminoacyl-tRNA so is added on the growing chain, causing premature termination
What is the name of the reaction that joins amino acids together? and what parts of the amino acid is the bond between?
Whats then produced by this?
A condensation reaction joins the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino acid group of the next
This produces the primary structure (N-C terminus)
What does N terminus to C terminus mean?
The chain has two ends- an amine group, the N terminus and an unbound carboyxl group, the C terminus. when a protein is translated from mRNA, it is created from the N-terminus to C-terminus
What are the levels of a protein’s structure?
Primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure
What does the secondary structure define?
The relationship between amino acids close to each other in the sequence
The scientists Pauline and Corey, tried to work out the structure of the fibrous protein alpha-ketain following X-ray diffraction. What were the 3 rules they had to follow?
- There can be no rotation around the planar peptide bonds
- Other parts of the chain must be rhythmically flexible
- the strucutre must have the maximum number of stabilising forces between residues
For rule 2 of Pauline and Corey’s experiment, What were the available bonds for folding to allow flexibility?
- The bond between the amino group and the alpha carbon (Phi)
- The bond between the alpha carbon and the carboxyl group (Psi)
- R-groups define the phi and psi bonds

Why does the amino acid have to rotate around the phi and psi bonds?
Because peptide bonds are rigid
For rule 3 for Pauline and corey’s experiment what were the rules for the stabilising forces?
- the forces must be independant of the primary structure
- The only bonds permitted are the hydrogen bonds, which have to be made between the NH of one residue and the C=O of another
What are the two types of secondary structures?
Why are these structures accepted?
- Alpha helix
- Beta sheet
Each of these strucutres are very stable and have the maximum number of hydrogen bonds between peptide bonds
What view of the alpha helix is this?

The side view
In the alpha helix…
- how many Å per complete turn?
- How many amino acids per turn?
- Whats the length per residue?
- 54Å per complete turn (0.54 nm)
- 3.6 amino acids per turn
- 1.5 Å length per residue
What view of the alpha helix is this?

Top view
What directions does the N-C terminus go in the alpha helix?
Clockwise (right-handed)
in the alpha helix, what do the side chains project?
what is this opposite to?
The side chains project outwards
This is opposite to DNA where the nucleotide bases are on the interior of the double helix
in the alpha helix, there are 3.6 residues per turn. What therefore, is the angle between each side of the chain in the primary structure?
100˚
Why is proline and glycine not in alpha helix form?
Glycine: no chrial centre so is more flexible which would be unstable and wouldn’t form the desired shape
Proline: circularise ‘imino’ acid. it cannot donate an amide hydrogen bond
What does the perfect alpha helix require the psi and phi bonds to be?
Psi = -60˚
Phi = -60˚
Consider a peptide section of 8 residues…
You can label the residues R1-R8. What residues are hydrophobic and what ones are polar.

Hydrophobic: R1, R4, R7, R8
Polar: R2, R3, R5, R6
In an alpha helix, are the hydrophobic and polar side chains on the same side or the opposite.
They are on opposite sides

What can amphiphatic helices assemble to generate?
proteins which are soluble in water
Are beta sheets found within one or more peptide chains?
within one peptide chain
What orientation can beta sheets be to one another?
Parallel or anti-parallel
In beta sheets, do more hydrogen bonds form between parallel or anti-parallel chains?
more hydrogen bonds form between anti-parallel chains
What does the Ramachandran plot represent?
A plot of the bond angles between each of the residues following x-ray crystallography to show what the secondary structure is (whether it be anti-paraelle beta, parallel beta of alpha helix)
What types of bonds can be present in a proteins tertiary structure and give examples for each?
1. Non-covalent forces/bonds
- Hydrophobic interactions
- Hydrogen bonds
- Van der waals interactions
- electrostatic bonds (ionic)
2. Covalent links
- disulphide bonds
What are the 4 ways to distrupt a proteins structure?
- Heat (20-40˚c)
- PH (normal intracellular PH 7.2 +/- 0.4)
- Ionic strength (0.1 M KCl)
- Denaturing agents
Name some examples for denaturing agents for proteins?
- organic solvents
- chaotropic agents (urea, guanidinium hydrochloride)
- Proteolytic enzymes (protease)
- UV/ Oxidative/ radiation damage
Name 2 types of hydrophbic interactions?
- Hydrophobic clusters
- Pi-bond interactions
What are hydrophobic clusters generally broken by?
organic solvents or denaturing agents
What type of amino acids are Pi bond interactions generally found in?
aromatic amino acids only?
What are Pi-bond interactions and what are they disrupted by?
A mixing of clouds of π electrons and they are disrupted by heat
What do hydrogen bonds involve and what are disrupted and broken by?
Hydrogen bonds involve polar non-charged R groups
They are broken by heat and denaturing agents
exposed hydrogen bonds are also disrupted by water
Are van der waals forces work in short or large range?
very short range effects
What are Van der walls forces broken by?
Heat and denaturing agents
What type of interactions are electrostatic bonds and what do they form?
They are ionic interactions and they form salt bridges
What do electrostatic bonds have to be surrounded by in order to be effective?
they have to be surrounded by hydrophobic interactions
In electrostatic bonds, when can the protonation of the R-groups of amino acids change?
Also, when the side chain has no net charge, what is this known as?
The protonation of the R-groups of amino acids can also change according to PH
The PH where the side chain has no net charge is called the isoelectric point (pI)
Whats the dissociation formula of a weak acid?
HA <–> A- + H+
Whats the formula for PH involving PKa and weak acid dissociation?
PH= PKa + log([A-] / [HA])
What is the charge on a protein determined by?
- PH
- number/type of each amino acid residues with ionisable side chains
What process is an important molecular switch from changing proteins from a neurtal to negative state?
Phosphorylation
In phosphorylation, a molecule can be changed from being neutral to negative.
What amino acid mimics this switch permanently and what can create an unswitchable version?
Can mimic this switch permanently using Aspartate
Can create unswitchable version with alanine
Why are disulphide bonds important for extracellular proteins?
to make the proteins robust
Whats needed to form a disulphide bond and what needed to break it?
Made: + O2
Broken: + beta-mercaptoethanol
What did the Anfinsen experiment on ribonuclease show?
- the folded, active form of a protein has the lowest free energy
- all of the information needed by a protein to fold to this strucutre is encoded in the primary structure
- not all proteins fold as easily
- some require protein disulphide isomerases (PDIs)
Give some examples of of post-translational modifications that can alter amino acids to alter protein properties?
- phosphorylation of serine, threonine and tyrosine
- formation of disulpide bonds between cysteines
- glycosylation of asparagine
- additions of sugars/ lipids to help target/secrete protein
Give an example of when DNA bases are modified?
methylation of epigenetics
interactions in quaternary structures can be what?
transient (variable/ short-lived) or stable
What type of networks and larger complexes do protein form?
- monomer, dimer, trimer… oligomer (a smaller protein chain), polymer (A large protein chain)
- Homomeric (all same subunit) or heteromeric (differing subunits)
What are the 2 ways that proteins can interact and are these short/long and a 1˚/2˚/3˚ or 4˚ strucutre?
1. Motifs
- short
- usually primary sequence
2. Domains
- larger
- usually strucutural
- secondary or tertiary structures
What are microtubules made out of?
alpha and beta tubulin heterodimers all lined up and stacked around the lumen.
When beta subunit is at the end its a positive end
when the alpha subunit is at the ends its a negative end
When an actin filament is formed, a globular protein is turned into what?
A fibrous protein
How to proteins act as a scaffold?
- The compartmentalise organelles
- sometimes make organelles bind to membrane
- then the protein holds the enzymes in the right order/ position so substrates/ intermediates can find them quicker and reactions dont take as long
What happens in unwanted protein-protein interactions and what can this lead to, give examples?
- motif/ domain recognition is
- ‘blind’ to the rest of the protein
- only recognises the part its targeting
- antibodies are programmed to recognise foregin antigens but can instead targer own cells leading to autoimmune diseases e.g. MS, Crohn’s, Lupus, type 1 diabetes
Proteins can have prosthetic groups, name the prosthetic group, an emample and a function for the following class of proteins
- Glycoprotein
- Haemoprotein
- Lipoprotein
- Metalloprotein
- Nucleoprotein
1. Glycoprotein
Prosthetic group: Saccharide
Example: Immunoglobulin, Interferon
Function: Antibody, antiviral agent
2. Haemoprotein
Prosthetic group: Haem
Example: Haemoglobin, Myoglobin
Function: O2 carrier in blood, O2 carrier in muscle
3. Lipoprotein
Prosthetic group: Lipid
Example: Low and high density lipoprotein (LDL, HDL)
Function: lipid carriers
4. Metalloprotein
Prosthetic group: Metal ion
Example: Calmodulin, Ferritin, carboxypeptidase
Function: Ca2+ carrier, Fe2+ storage, Zn2+ used in digestion
5. Nucleoprotein
Prosthetic group: Nucleic acid
Example: small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP)
Function: RNA splicing
How can peptide bonds be broken?
in hydrolysis by boiling 6M acid (or alklai)


