Amino acid metabolism Flashcards
What can’t happen when there is excess amino acids?
- They can’t be stores
- They aren’t secreted
What happens when there are excess amino acids in the body?
Tell me the amount in g/day that are used?

Whats the final destination for the AA in pool?
- protein synthesis
- direct use/ minor modification
- Breakdown and redeployment
AA can be used as neurotransmitters. Name some neurotransmitters
- glutamate
- aspartate
- glycine
What neurotransmitters are the following AA turned into?
- Glutamate
- Tyrosine
- Tryptophan
- Arginine
- glutamate –> GABA
- Tyrosine –> Dopamine, noradrenaline, adrenaline
- Tryptophan –> Serotonin
- Arginine –> NO
What hormones do the following AA produce
- Tyrosine
- Tryptophan
Tyrosine –> Thyroxine
Tryptophan –> melatonin
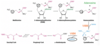
Draw the process of how a carbon skeleton is formed from an amino acid?
What can the carbon skeleton be used for?

Draw the reaction, including intermediates, of how most AA form urea?
What is the name of the processes?
- Transferring amino group from the AA onto something else like alpha-ketoglutarate to then form glutamate
- Kidney then converts ammonia –> urea
- Can reuse alpha ketoglutarate

Draw the overall process of transamination and the enzyme used?

Is there energy use in the process of transamination?
No
What does it mean if the enzyme AST is present in the blood?
Then it indicates liver damage
What does aminotransferase use to do the amino group transfer
Aminotransferases use a Vit B6-derived prosthetic group called Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) to do the amino group transfer
- ping-pong mechanism where the substrates don’t meet
- Reaction can go in either direction

How are amino groups funnelled into Glu removed?
deamination
Whats the process of deamination?

Whats the process of urea synthesis ?