All cardiovasc Flashcards
What three factors determine CO?
CO = SV x HR
where SV is a function of preload and contractility
What kind of drug is clopidrogel? Use?
antiplatelet - adjunctive in pts w/ CAD, ischemic neuro syndromes, or stenting. PO.
Discuss pathology of the following stages of cardiac ischemia
- 20 - 30 mins
- 24 h
- 1-3 d
- 3-7 (10) days
- 20 - 30 mins: reversible ischemia (angina)
- 24 h: cut surface pallor
- 1-3 d: mottling w/ yellow-tan infarct ctr
- 3-7 (10) days: sharply outlined w/ central pale, yellowish necrotic region
Pattern of a Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block?
Same PR int. for each cycle w/ blocked P waves.
Calcific aortic stenosis
- one of most common valvular probs
- congenital biscuspid valve –> aging degeneration of valve w/ calcification
Major complications (3) of infective endocarditis?
- valve dest
- abscesses
- purulent pericarditis
histologic findings of giant cell myocarditis
myocyte necrosis and numerous giant cells
How do PDEi’s work (give rep. drug)
PDEs (milrinone) also increase contractility (similar to B1 agonists) but by inhibiting PDE thus keeping cAMP levels hi within myocytes.
What hemydynamic finding correlates best w/ RH failure?
Prominent RA v waves
Complete AV canal defect
- Describe (give 3 morphological features)
- Assoc. w/ what genotype
- Generally has complete mixing of ventricular contents due to defects in septation (endocardial cushions) – It is characterized by a primum atrial septal defect (ASD) that is contiguous with a posterior (or inlet) ventricular septal defect (VSD), and a common AV valve
- Assoc. w/ T-21.
What is a major problem w/ Eisenmenger’s syndrome? What is the goal of corrective surg for shunts?
- Once Eisenmenger’s sets in, surg is contraindicated and outcomes much worse
- Corrective surg: goal is to avoid dev’t of Eisenmenger’s
Temporal (Giant Cell) arteritis
- How common
- Symptoms
- Biopsy consideration
- Common complications
- Rx
- Most common vasculitis
- Headaches, scalp tender, jaw pain, visual loss
- A segmental dz so at least 2-3 cm of artery needed
- rapid response cort’s
What are the ANCA+ dz’s we learned?
- pANCA+
- cANCA+
- pANCA = hypersens. vasculitis (in 70% of pts)
- cANCA = granulomatosis w/ polyangiitis
What are 2 diff’s b/t PAN and hypersens. vasculitis?
- Hypersens = smaller vessels than PAN
- Lesions in hypersens at same stage of dev’t (as opposed 2 PAN)
Primary use of Type II CCB’s? HOw does this differ from Type I?
These are vasodilators used more for HTN control, and generally don’t have electrophysiological (cardiac) effect. Type I used more for cardiac, and cause electrophys. changes.
Infarction zones based on LAD, RCA or left circumflex?
- LAD: anterior wall LV
- RCA: post. wall LV + post septum
- Left Circ: lateral wall LV
Typical pathology of bacterial myocarditis?
Infectious foci w/ PMNs and bacteria
What are some causes of impaired DIA filling (leading to DIA heart failure)?
As these advance to HF, comment on the EF you might see.
Impaired DIA filling
- LV hypertrophy (Ao stenosis, HTN)
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy (amyloid, sarcoid, hemochromatosis, etc.)
- Pericardial constriction (constrictive pericarditis, cx, etc.) / tamponade
Hallmark dz of restrictive cardiomyopathy? Other big players in this condition?
amyloid; hemocrhomatosis/siderosis, sarcoidosis
Primary medical Rx of aortic regurg? Surg?
afterload reduction (nifedipine - CCB, ACEi)
surg: AVR
What are some of the key S/S of HF?
Decreased CO leading to:
- fatigue
- increased pulmonary venous pressure (exertional dyspnea, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea)
- increased systemic venous pressure (lower extremity edema)
Dichrotic notch
Brief uptick in aortic pressure after the AV valve closes (after S2) due to recoil pressure following vent. contraction.
What are hallmark EKG signs in RBBB?
- wide QRS (>120ms)
- rSR’ in V1 (a tall “rabbit ear” secondary R wave in V1)

Claudication
limb angina: Pain in calf, thigh or buttock after some excercise; generaly resolves w/ rest.
Findings in acute chagas
- physical exam
- gross path
- micro path
- chagoma (bump) + lymphadenopathy
- organ involvement (parasitemia)
- often myocardial involvement w/ parasite-filled pseudocysts, INF
Polyaerterisis nodosa (PAN)
- Arteries affected
- Lesion
- Popn most often affected
- IF
- Common co-infection
- Musc. a.s
- Nodular
- Young males
- pANCA+
- 30% have HepB
What is the significance of an AV block above, at, or below the AV node?
Very important - at level or above AV node = reliable escape rhythm.
Below = unreliable escaple rhythm. This is especially important b/c if pt. goes into complete AV block (3o), they won’t have a reliable escape rhythm.
Histopath of temporal (giant cell) arteritis (3)
- Lc infiltration
- Intimal fibrosis
- Granuloma formation
Transposition of the Great A.s
Parallel circ. where RV outflows to Ao –> systemic –> back to RA
and
LV –> pulm. a. –> lungs –> LA
rupture of fibrous cap =
progressive narrowing of vessel lumens (cor. a.s) =
weakening of vessel wall w/ dilatation =
- acute cor. syndrome
- chronic CAD
- aneurysm
What is the most common type of infarction in actue MI?
transmural… usually LV.
Granulomatosis w/ polyangiitis
- Key IF marker
- Vessels affected
- Lesions
- Other organ involvement
- Rx
- cANCA
- mostly small vessels (caps)
- Granulomas
- Kidney, lung
- Cyclophosphamide
Rx for variant angina?
nitro, CCB’s (1st line)
top 3 RF’s for CAD?
- dyslipidemia
- HTN
- smoking
Etiology of renovascular HTN
Stenosis of one or both renal a.s –> HTN.
What are two anti-arrhythmics to avoid in pts w/ renal dysfunction?
sotalol & dofetilide
Hallmark of cardiac sarcoidosis?
Micro path?
non-necrotizing granulomas w/ dilated & restrictive cardiomyopathy
- granulomas, giant cells
What are the major clinical manifestations (symptoms) of CAD?
- chest pain (angina pect.)
- SOB
Heart Dev’t
- Origin tissue
- What key structure formed by day 22? How does it move to create chambers?
- What type of cells necessary for normal dev’t?
- What structures contribue to normal septation?
- Mesoderm
- heart tube; rightward looping
- neural crest
- endocardial cushions
Effects of aortic stenosis / incompetence?
- Decreased output –> angina, syncope
- Effects on LV –> hypertrophy, failure
Explain how mital stenosis can lead to venous congestion of liver? What is a typical gross anatomical description of this condition?
Venous cong. of liver via advanced mitral stenosis that causes backup of pressure all the way to R side of heart and into the portal system thus congesting liver. Described as nutmeg liver
What is the standard way to quantify vasc. resistance? Give EQ.
MAP = Dia + 1/3 (Sys - Dia)
What does mitral regurg lead to?
LV overload –> eccentric LV hypertrophy –> symptoms/complications
Describe hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (PRIMARY/IDIOPATHIC)
- etiology of most cases
- clinical features & pop’n most often afflicted
- Hallmark gross path
- Hallmark micro path
- Uncommon condition w/ genetic links, familial patterns (B-myosin heavy chain)
- Affects young males; commonly present w/ sudden cardiac death, syncope, a fib, chest pain, etc.
- Gross: hypertrophic LV, in particular a very hypertrophic septum
- Micro: myofiber disarray, esp. in septum
def Heart Failure
when heart is unable to pump blood florward at sufficient rate to meet metabolic demands of body (forward failure).
What drugs used in acute Rx of HF (types, not drug names)?
- diuretics
- O2
- nitrates
- inotropes
- vent. assist. devices
c wave
increase in atrial pressure as AV valves bulge out during ventricular SYS
S3
Normal until ~40 y/o. During filling (DIA) it’s the sound of the mitral valve opening.
What does a wide QRS represent in AV block? Why signficiant?
Indicates block below level of AV node (generally a bundle branch block). Important b/c pt. may not have reliable escape rhythm.
- What types of drugs are Type II antiarrhythmics?
- What type preferred for cards pts?
- What is contraindicated in pts w/ CAD?
- What is the prototype drug?
- B blockers
- B1 selective preferred
- Contra: CAD pts should NOT use B blockers w/ ISA (acebutolol)
- Metolprolol, atenolol = B1 selective w/o ISA
Match the following genetic states to congenital heart defects
- Trisomy 21
- DiGeorge
- complete AV canal, VSD, ASD.
- Teratology of FAllot
Most common cause of dilated cardiomyopathy in UW/Europe?
- Etiology
Alcoholic DCM
etiology: direct tissue dmg from alcohol, metabolites
Although Pouseuille’s law is nice, what is the important derivation in terms of pathophys/clinical medicine? Hint: resistance!
Q = dP x r4/8(Pi)(mu)L
Q = dP/R
therefore
R = 8(pi)mu(L)/r4
This last derivation shows the very important fact that resistance increases by a factor of 4 for every decrease in the radius (r) of the vessel.
What are three most common vessels in CAD, in order? What % obstruction do most pts have?
LAD > RCA > L circumflex
most have ~75%
- Receptor targets of class III antiarrhythmics
- Drug names
- K channels
- dofetilide, sotalol, amiodarone
What characterizes RHF? What usually precedes it?
Generally preceded by LHF but not always (depends on etiology). If related to LHF, it shows advanced dz. Non-LH etiologies of RHF include Cor Pulmonale.
Characterized by:
- SIgns of venous congestion: Increased JVP, lower ext. edema due to increased afterload on RV.
- Could have RUQ pain if hepatomegaly.
An “anterolateral” infarct is due to occlusion of which cor. a.?
LAD
Draw out the pressure-vol. loop w/ proper lettering from a-d.
- What does the slope reflect?
- Discuss what’s happening all along the loop, starting at d (lower left).
see notes
- Etiologies of RHF?
- Common manifestations?
- Etiologies: LHF, cardiomyop., valvular, lung dz, PE
- Manif: periph edema, ascites, lo card. output
Tetralogy of Fallot
- Genetic assoc.
- the 4 malformations
- 22q11 deletion
- VSD, sub-pulm. obstruction, overriding Ao, RV hypertrophy
Most common sympts of pericarditis
possible sign?
symptoms
- chest pain, sharp, well localized, relieved by leaning forward
- may get worse with inspiration (pleuritic component)
sign
- friction rub on auscultation.
What are the most common non-infx couses of myocarditis?
- Immune-related: Rheumatic, SLE, etc.
- Radiation
- Misc: Sarcoid
What is the major limitation to long-term success of cardiac transplantations?
Graft arteriopathy
what shown?

rhabdomyoma
Important secondary causes of hyperlipidemia (3)?
- Hypothyroidism
- DM
- Obstructive liver disease
SYS heart failure is primarily a problem of ______, whereas DIA heart failure is a problem of _______.
SYS: problem of contractility due to dilatation, remodeling, etc.
DIA: problem of filling due to stiffness or impaired relaxation.
What is the most common drug class that can lead to drug-induced (dilated) cardiomyopathy?
Anthracyclines (chemo agents) – in some cases, S/E is that it leads to necrosis that results in dilated cardiomyopathy (non-reversible)
- What is the best diagnostic tool for assessing peripheral (including carotid) atherscler?
- How do you reduce risk of stroke in cases of confirmed carotid atherscler?
- Duplex US
- endarterectomy
What is the preferred class of AAA w/o the presence of structural heart dz?
1C (these are generally used for Rx of supraventricular arrythmias in pts w/o heart dz; in pts with heart dz [eg post MI], they are thought to increase mortality).
What is the hallmark EKG morphology of RBBB and LBBB? What is different clinically re: RBBBs vs LBBBs?
Wide QRS (>120ms)
RBBB = probably normal heart
LBBB = probably CVD (HTN and/or CAD)
Key short - term and long-term cosequences of MI?
- short: cardiac arrest (v fib)
- long: CHF, sudden card. death (v tach/fib)
what does this show?

hemorrhagic pericarditis
- Most common type of cardiomyopathy?
- Etiology?
- Clinical progression
- Dilated (also called congestive cardiomyopathy)
- Viral (cocksackie B), alcoholic, pregnancy
- often asymptomatic then presenting w/ exercise intol., CHF, arrythmia, death
What is a way to quanitatively describe contractility?
Ejection fraction or left vent. ejection fraction (LVEF):
LVEF = SV/EDV
Where do the coronary arteries originate?
aortic valve
Pathology (micro) of viral myocarditits?
presence of chronic Lc’s + myocyte necrosis.
A-fib: what is the common (and less common) way to return normal sinus rhythm?
- common: DC cardioversion (synchronized shock)
- less common: anti-arrhythmic agents
By definition in EKG, the left side is _____ and right side ______. A vector going toward the positive pole produces a ______ spike in the EKG reading.
Positive, negative, positive (up).
Buerger dz
- Etiology
- Leads to ?
- Histopath
- 1st line Rx
- Smoking-related
- dry gangrene ext’s
- granulomatous actue & chronic INF
- smoking cess.
Describe the lesion in atherscler
Thickened intima w/ fibrous cap, necrotic core w/ chol clefts and calcification (intimal lesion = hi yield)
Rx for reversible DVT?
Anticoag 6 mos (if can’t anticoag then Greenfield IVC filter)
What are some key signs that might point toward PVD?
- dec. periph. pulses
- bruits
- skin changes
- musc. atrophy
- ulceration/gangrene
What is key contraindication of nitrate therapy? How to Rx if taken together?
Sildenafil. Can lead to hypotensive shock/ hypotension. Rx w/ pressors, fluids, monitor.
What are type I (dihydropirine) CCBs used for? Type II? Give examples of each.
Major S/E of Type I CCB? Type II?
Type I (dihydropyridines): Rx HTN (amlodipine)
Type II: Cardiac drugs used an antiarrhythmics, and to reduce CO (verapamil, diltiazem)
S/Es:
type I: edema, headacne
type II: bradycardia, AV block
ECG sign of pericarditis
- diffuse ST elev (all leads)
Discuss the heart sounds S1 and S2; how do they correspond to SYS?
S1: vibration created when Pvent > Patria, forcing the AV valve to close. So this is the start of SYS.
S2: This occurs when the Paorta > PLV, at the end of SYS, forcing the aortic valve shut and producing a vibration.
What is a procedural cure for a-fib?
catheter ablation in LA (if fails to respond to 1st line Rx’s)
- What type of drugs are class IV antiarrhythmics?
- Prototype drugs to know
- Rx what condition?
- Non-dihidropyridine CCB’s (Fleckenstein Type I)
- Diltiazem, verapamil
- Rx superaventricular tachys
PSVT has a _____ QRS whereas ________ have widened QRS and usually occur in the setting of structural heart disease.
PSVT: narrow QRS (
Ventricular tachyarhythmias: widened QRS (>120ms)
Differentiate b/t monomorphic & polymorphic ventricular tachyarhythmias
Monomorph: remote MI (scar formation)
Poly: ischemic/ACS
V-fib def & Rx
Vent. fibrillation not compatible w/ life. Rx w/ immediate defibrillation.
most common malignant neoplasm of heart?
Sarcoma
What characterizes hypersensitivity vasculitis? Mention what size vessels affected.
acute necrotizing inflammation of small vessels, especially postcapillary venules of the skin.
v wave
gradual increase in Patria as they villed with “returning” venous blood (the AV valve is closed during v wave)
Def. pericarditis
INF of visc or parietal pericardium w/ formation of effusions
What are the 2 types of ASD? Which most common ASD?
- Primum and secundum ASDs
- Secundum most common, usually around fossa ovalis
Serious pericarditis
- Def
- Commonly caused by
- Gross appearance
- INF reaction w/ scant INF cells, slow accum. of fluid
- non-INFx (rheum fever)
- Yellowish (see below)

What is the mechanism by which ASA helps in angina?
Prevents platelet aggregation by inhibiting COX, reducing formation of TxA2.
Which classes of AAA’s have elevated risk of TDP?
1a, 1c, 3
on EKG what does S wave represent?
Depol of ventricular bases/epicardium
P wave
atrial depolarization producing measured dipole. this is atrial systole
Rx 4 granulomatosis w/ polyangiitis?
cyclophosphamide
Major cardiac outcomes in chronic chagas
The infection causes tissue dmg leading to Dilatation w/ fibrosis (LV) + effacement –>risk of aneurysm (LV/apex)
What is an acute indication for b blocker?
acute MI: reduces mortality, recurrence, etc.
Hallmark sign of acute STEMI? Weeks later what might you see?
elevated ST; weeks later = persistent Q.

Claudication may progress to rest pain.
- Describe
- Relieving factors
- Urgent?
- Complications/ sequellae
Rest pain:
- Dull, aching pain of foot or toes at rest.
- Releived by dependency (gravity, due to increased Q to area)
- Needs prompt attention
- can lead to tissue loss (ulcer, dry gangrene)
Sawtooth pattern on EKG indicates ?
Atrial flutter (atrial rate is between 250 and 350 bpm)
Eventual symptoms of aortic regurg?
- dyspnea on exertion
- fatigue
(Caused by decrease in SV and increased LV pressure)
What is most widely employed index of LV systolic function ? Normal range?
LVEF (normally 55-65%)
Statins
- Target
- Action
- Risk reduction
- S/E
- HMG CoA reductse (INH)
- Lowers LDL (66%), Lowers TG’s
- Risk reduction in pts w/ CAD
- Myalgias most common, rare: rhabdo
How do you clinically diagnose an acute MI?
- typical rise/fall of cardiac enzymes (CK-MB/troponin)
and
one of of the following four:
- ischemic symptoms
- ST changes
- persistent Q waves (old MI)
- Imaging/echo showing new loss or wall abnormality.
Most common infectious cause of myocarditis?
Coxsackie A/B viruses then range of viral, bact, fungal infxs (don’t have to memorize those)
Clinical pres of rheum fever on heart?
pancarditis: pericarditis, myocarditis (aschoff), endocarditis (vegetations on mitral,aortic valves) –> mitral (70%), mitral/aortic (25%) stenosis
How is atrial septum formed?
- septum primum forms first
- Cell death of upper septum primum
- septum secundum appears, growing sup–>inf
- for. ovale remains b/t them

What is most common cong. heart dz in infants?
If large & persistent, what is one of the primary risks/complications?
VSDs
Eisenmenger’s syndrome
SA node
dominant rate-setting pacemaker of the heart
Churg-Strauss Syndrome
- Common PMH
- Histo hallmark
- Rx
- asthma
- eosinophlic
- cort’s
Common etiologies of LHF?
Clinical manifestations?
Etiologies
- MI (ischemic)
- valvular
- cardiomyopathy
- HTN
Manifestations
- pulm. congestion
- low CO
Primary sign of Eisenmenger’s?
- cyanosis
Sick sinus syndrome (EKG, symptoms)
Rx:
- acute, symptomatic
- long-term
A type of bradyarrhythmia where P waves are absent.
- Often symptomatic (lightheadedness, presyncope, syncope, dyspnea on exertion, angina, and/or palpitations).
Rx:
- acute, symptomatic: B agonist (atropine)
- long-term: withdraw offending agent (eg diltiazem) +/or permanent pacemaker.
Key physical finding in mitral regurg? Rx? Which Rx preferred?
holoSYS murmur
Rx: repair/replacement (repair preferred if possible)
How to Rx transposition of the great a.s (TGA)?
- Historical: atrial setpostomy
- Current: aterial switch
what does this show?

caseous pericarditis
What is 1st line for most pts in treating stable angina?
ASA (aspirin)
Most shunts are L–>R in the beginning - why?
Why is it that the flow in shunts can become reversed in late dz? What is this called?
B/c left pressure > R pressure so flow goes in that direction.
Can reverse to a R–>L shunt as pulm pressures rise
(for example, a L–>R shunt from ASD will eventually increase pulm. blood flow - and pressure - to such an extent that will result in eventual R–>L shunting)
This reversal is called Eisenmenger Syndrome
Framingham Risk Score
- DEF
- Factors
- 10 yr risk of developing CAD
- Factpors: o LDL (or total cholesterol)
o HDL
o HTN
o Smoking
o Gender
o Age
Cardiac myxoma
- How common
- Common gross path
- most common primary tumor in heart
- tumor on stalk = “wrecking ball”
Def. of cardiomyopathy
heart dz resulting from primary abnormality of myocardium excluding secondary causes (MI/ischemic, HTN, valvular, etc.)
Etiology of mitral stenosis in adults?
“always rheumatic”
SInus venosus ADS
ASD that causes inflow from pulm. v.s to be directed to RA (instead of LA) leading to vol. overload of RH
Histopath in dilated cardiomyopathy?
Same as other forms of hypertrophy w/ fibrosis; abnormal, enlarged myocytes w/ interstitial fibrosis.
Tricuspid regurg
- Etiology
- Popn often affected
- Signs
- EKG finding
- Rx
- Secondary to RV dilatation (or IVDA)
- IV drug users w/ endocarditis but also rheumatic pts.
- Pulsatile liver; SYS murmur LL sternal border.
- Large V waves in jugular veins.
- Repair (in severe cases)
Q = AV = CO= ~ Pi(r2)aorta x Vaorta
where V = velocity, CO = cardiac output
Given the above, how does doppler US measure CO?
Doppler approximates CO by measuring the area of the aorta and the velocity of flow.
Remember that CO = vol x HR. So if we can approximate CO, then we can calculate the volume which in this case would be the ejection fraction (the blood that is actively pumped out of LV during SYS).
How can the following help to diagnose/specify a PVD?
- Segmental pressures
- Duplex US
- Segmental P: shows diff’s between diff’t body parts, esp used in lower limb to assess stenosis.
- Duplex US: to asses Q in periph. arteries.
Define ejection fraction. Why is it important?
What factors determine EF?
EF = SV/EDV
Key indicator of SYStolic performance
Determined by:
- Myocardial mass & architecture
- Contractility
- Preload
- Afterload
3 common etiologies of mitral regurg?
- prolapse (congenital)
- endocarditis
- rheumatic
Describe diff b/t primary and secondary dextrocardia.
- Primary dextrocardia: Heart is in right chest with rightward-pointing apex.
- Secondary dextrocardia: heart in right chest with leftward-pointing apex, due to starting out in the normal leftward-apex position but displaced into the right chest by extrinsic forces.
Common infectious cause of valvular dz? What is the common infectious agent?
Rheumatic fever (s/p Group A beta hemolytic strep. pharyngitis)
What is preferred drug for preventing VT/VF in pt w/ Class I-II heart failure? Class III-IV?
Sotalol; amiodarone.
Rx for pericarditis?
- Rx underlying condition
- NSAIDS
In terms of ion flux, discuss phases 0, 2 and 3 of the myocyte AP
- Phase 0: Na influx (depol)
- Phase 2: Slow Ca influx and K efflux (plateau phase)
- Phase 3: K efflux (rapid depol)
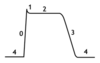
SE’s/interactions of amiodarone?
amiodarone rarely causes life threatening arrhythmias (TDP), it has serious pulmonary, thyroid and hepatic toxicities that limit its long term use
Anion XC resins
- Use
- MOA
- Examples
- S/E
- To lower LDL/chol
- Binds bile acids to drive increased chol–>bile acid (liver)
- GI S/E’s can be appreciable, limiting use to 3rd line
Fibrates
- use
- examples
- Effective TG-lowering drugs (for hyperTG >200 mg/dL)
- Gemfibrozil, fenofibrate
What is the most common congenital heart defect found in adults?
What does it predispose pt. to?
Bicuspid Ao valve.
Predisposes pt. to aortic stenosis.
LV hypertrophy
- Symptoms
- Complication
- Rx’s
- Can be asymptomatic for many years but then dyspnea, angina, syncope
- CHF
- If HTN-related, reduce afterload; Rx underlying condition.
Two primary causes of renovascular stenosis
atherslerosis & fibromusc. dysplasia
Abd. Ao. Aneurysm
- 2 RF’s
- Complications
- Most common region
- Smoking, genetic (Fam Hx very important!)
- Rupture: related to diameter of affected site
- most common: infrarenal Ao
Constrictive pericarditis
- Def
- Etiology
- Most common causes
- Due to chronic pericarditis
- Cuased by repeated/chronic insults
- Post viral (50%), TB (15%), Rad Ther, PostSurg
Casesous pericarditis
- Assoc w/ what infx
TB
Major complication of a fib and a flutter? How to prevent?
STROKE: intra-atrial clots that can dislodge leading to devastating strokes.
- Anticoagulation is one of the cornerstones of managing both of these arrhythmias
What is the basic pathology of chronic ischemic heart dz?
myocard. atrophy & fibrosis
Discuss Ankle Brachial Index: how used, and values that show pathology?
- used to asses arterial obst. (stenosis) - quantifies it.
- Gives ratio of arm:leg BP’s (leg at various segments); normal is >0.92. The lower the ratio below normal, the higher the degree of stenosis.
Hallmark micro path of rheum fever?
aschoff nodule: fibrinoid necrosis and INF cells (LC’s, histiocytes)

Describe pathophys of mitral stenosis
Primary increase in PLA –> pulm. venous pressure –> pulmonary congestion (and shortness of breath) –> increased PA pressure –> RV hypertrophy –(late stage)–> liver congestion, etc. (signs of RH failure)
Renovasc. HTN
- Clinical picture
- What med should be avoided in pts w/ bilat dz?
- Hard to control HTN (often on >2-3 antihypertensives)
- HI Diastolic BP > 120 mmHg
- Flash pulmonary edema
- ACEi’s should be avoided in pts with bilateral renal stenosis.
Constrictive pericarditis
- Sympts
- Exam
- CXR
- Hemodynamics
- Fatigue, dyspnea and leg swelling (edema)
- Exam: JVD, jugular venous pressure rises or fails to drop with inspiration (Kussmau), hepatomegaly, ascites, lower extremity edema
- CXR: pericardial calcification
- Hemodynamics: elevated JVP, prominent y descent, ventricular “square root sign, low cardiac output.
Chronic pericarditis, though rare, can lead to ______.
constrictive pericarditis
Rx for claudication?
- Cilastozol: PDEi - vasodilation.
- Endovasc. Rx: stents, for shorter stenoses
- Bypass grafts: for longer stenoses
Polyarteritis Nodosa (PAN) Rx
Corts or cyclophosphamide –> 90% remission or cure
Metoprolol, atenolol (drug type and class)
B-1 selective blockers w/o ISA (B blockers are Type II anti-arrhtymics as well)
Fish Oil
- action
reduces VLDL & TG’s
Why is a Mobitz II 2o block more ominous than a Mobitz I? What do these patients need?
Mobitz I is often asymptomatic whereas Mobitz II is usually at level below AV node and can progres to compolete heart block associated w/ slow/unreliable escape.
Pts need permanent pacemaker irrespective of symptoms.
Fibrinous pericarditis
- Def
- How common?
- Possible sign
- Causes
- INF rxn w/ exudate
- Most freq cause of pericarditis
- Friction rub
- MI, post MI, uremia…. (most of the general causes of any pericarditis!!)
What is the process by which restrictive cardiomyopathy results in decreased CO?
the restriction limits diastolic filling (due to dec. ventricular compliance) –> dec. CO
What does PWCP approximate? Why important?
PCWP = filling pressure of LA; important b/c it characterizes preload and tells you the pulm. venous pressure
What would you see on a Wigger’s in aortic stenosis?
gradient between LV pressure and aorta pressure - the LV has to generate additional pressure to overcome the increased resistance in the aorta.
What dz’s put pt automatically in hi-risk category for developing CAD?
DM & vasc. dz
What 2 things needed to diagnose MI?
- Rise/fall card. enzymes
- EKG changes
What is the lipid goal for Framingham hi risk?
LDL < 100 mg./dL
What are the 3 general etiologies of myocarditis?
- idiopathic
- infectious
- non-infx
What are the “5 P’s” of limb threatening ischemia? Rx?
- Pain, Pallor, Pulseless, Parasthesias, Paralysis.
- An emergency that requires immediate surgical intervention to relieve irreversible limb ischemia that would likely lead to limb loss.
What is the normal PR interval?
What is the pattern in 1o AV block?
Where is the delay generally?
Normal PR = 200 ms = 1 large square = 0.2 s
1o AV block: represented by prolonged (> 200 ms) PR, and each P wave is followed by a QRS complex.
- generally a delay at level of AV node.
What is the most important direct consequence of aortic stenosis? What does this lead to?
LV pressure overload –> concentric LV hypertrophy
Sinus bradycardia
- Def
- Etiologies
- Rx
- HR > 60bpm due to decreased SA node firing
- Drugs: B blockers, certain CCB’s, Medical: hypoThyr, aging, isch heart dz, cardiomyopathy.
- Generally, Rx underyling condition or remove offending agent.
What does this show?

purulent pericarditis
What is the difference between valvular vegetations in rheumatic vs. infective endocarditis?
Rheumatic: adherent lesions on valves
Infective: friable
Discuss SNS and PNS stimulation to heart, including where this happens.
SNS: E/NE stimulate B1 receptor –> activation of adenylate cyclase –> inc. cAMP –> increased Ca influx –> inhibition of Ca-sensitive K channels —> more rapid spontaneous depol = increased HR.
PNS: mAChR stimulated via vagus n. –> increase in K+ –> hyperpol. –> slower HR
What is the most common etiology of arrhythmias?
reentry (90%)
2 most common organisms contributing to infective endocarditis?
- alpha hemolytic strep (60%)
- S. aureus (20%)
Discuss epidem. of chagas dz
- Endemic Colombia, Brazil, Central Am, Mex
- T. Cruzi is transmitted by reduviid bug via feces
Drug classes/types used in long-term therapy for HF?
- ACEi or AT receptor blocker
- B blocker
- Aldo blocker
- Diuretic
Ezetemibe
- MOA
- Action
- Common co-drug
- Reduces intestinal abs. of chol (binds a receptor)
- Lowers LDL-chol
- Often w/ statins
ST segment depression - what does this signify?
unstable angia or acute cor. syndrome
Beck’s Triad
- Def
- Sign of what condition?
- Hypotens, elev. JVP, muffled heart sounds
- Signs of pericard. tamponade
explain diff b/t a junctional esape rhythm and ventricular escape. where doe these come from? How do these differ on EKG?
- Junctional: 40-60 bpm, from AV node or proximal His bundle.
- Ventricular:
- EKG: Junctional = narrow QRS, ventricular = widened QRS (>200ms).
What does this EKG show?

ST depression - NSTEMI.
Amaurosis fugax
- def
- what causes it?
complication of carotid atheroscler.: fleeting blindness from emboli.
tricuspid stenosis
- Etiology
- Signs on exam
- EKG changes
- Rx
- Generally rheumatic.
- JVD due to pressure overload/backup
- EKG: will see large a wave pushing against increased resistance.
- Surgical valve replacement or valvuloplasty.
Major effects of mitral incompetence
Mitral regurg (incompetence) leads to chronic vol overload of LV (normal DIA vol + regurgitant vol). This leads to dilatation + hypertrophy of LV. Can also lead to pulm. venous HTN if there is building up back pressure in system.
Hemochromatosis
- Etiology
- Type of dz?
abnormal Fe deposition in myocytes; leads to a restrictive cardiomyopathy
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Risk factor for ??
Ductus is abnormally open postnatally. A large PDA will cause clubbing, hypoxemia, and continuous murmur throughout card. cycle.
PDA is a L–>R shunt that, if large enough, will increase pulmonary pressures. If the PDA is large enough, Pulm HTN ensues and could result in reversal of shunt (Eisenmenger Syndrome). This could cause LV overload.
Draw the various derangements on a pressure-volume loop, and explain them. Note the hallmark pathologies of each, in parens:
- Decline in inotropy (post-MI)
- Increase in afterload (aortic stenosis)
- Decrease in preload (hemorrage or dehydration)
see notes
Henoch-Schonen Purpura
- Age affected
- Key skin finding
- Other organs affected
- IF findings
- Kids 3-8
- Purpurae (non blanching)
- Renal
- IgA deposition
- What is the action of Beta Blockers on myocardium?
- Key S/E or complication (2)
- reduce HR
- reduce BP (afterload)
- reduce contractility
S/E:
- increases wall tension acutely in pts w/ left vent. dysfunction.
- bradycardia if overshoot
What do the linear portions of the Frank-Starling curve tell us?
That as preload increases, SV increases.
What are two etiologies for complete heart block (aka ??)?
- congenital
- lyme dz
aka 3o AV block
Mitral valve prolapse
- Def
- Etiology
- Gross pathology
- Common cause of mitral regurgitation
- Congenital, often assoc. w/ Marfans, Ehler-Danlos, etc.
- Floppy, enlarged leaflest –> prolapse
What is the primary goal of anginal therapy? Via what mechanisms?
reduce the O2 demand of myocardium by decreasing:
- preload
- contractility
- afterload
- HR
Most common cause of periph. vasc dz? Most common sites for this form?
- Atheroscler.
- birfucation, branch points (eg carotid bifurc, aortoiliac, superficial fem., tibial)
Paroxysmal supreventricular tachycardia (PSVT)
- EKG signs
- Clinical picture
- EKG: narrow (QRS < 120 ms) complex tachycardia w/ rapid rate.
- Clinical: sudden onset (paroxysmal) and sudden offset
What are the 2 causes of renovasc. HTN?
- Atherscler.
- Fibromusc. dysplasia
Physical findings (Exam findings!) of progressed mitral stenosis (2)?
- elevated JVP (if pulmonary HTN),
- decrescendo diastolic murmur (“rumble”) from tubulent flow across valve during DIA.
- Opening snap following S2.
How would mitral stenosis appear on wigger’s?
increase PLA due to impaired QLA–>LV.
What is classic triad of advanced, symptomatic calcific stenosis?
- chest pain
- heart failure
- syncope
What is the primary systemic effect of nitrates?
Venodilation - decreases preload by increasing venous capacitance… but also dilates arterioles & arteries. Will decrease BP.
Hallmark restrictive HF cause?
chronic pericarditis (viral, TB, other)
By what mechanism does B1 stimulation affect myocytes, and how?
Agonist –> B1R –> +adenylate cyclase –> +cAMP –> +CaIC –> increased contractility + HR
What does this show?

serous pericarditis
a wave
small increase in Patria as atrial pressure rises due to atrial SYS
Gross appearance of heart in dilated cardiomyopathy?
4-chamber dilatation –> enlarged globoid shape
What class of AAA best if structural heart dz present?
Class III
Hallmarks of a-fib on EKG (2 criteria)?
- irregularly irregular, rapid QRS complex
- No P waves
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
pts have an accessory bypass tract causing arrhythmias (mostly a-fib via reentry but can progress to Vfib)
Digoxin
- Uses (2) - first line?
- S/E’s
- inotropic (HF), antiarrhytmic (SVT) - generally a 2nd line Rx to B-Blockers
- Narrow TM, small doses, arrhythmias + LOTS of others
Purulent pericarditis
- Etiology
- Signs
- Bact. infx
- fever, friction rub
3o AV block pattern; discuss high vs. low blocks
- All P waves blocked
- No visible relationship b/t P waves and QRS
- High block: OK escape w/ BPM = 40-60; Low block = unreliable
Rhabdomyoma
- Def
- Popn affected most
- Important assoc. w/ what condition
- Benign primary tumor of heart
- Kids (most common primary tumor in kids)
- 50% assoc. w/ tuberous sclerosis (possibly same genotype leads to both tumors & tub. sclerosis)
Virchow’s Triad (for what condition?)
- Stasis, hypercoag., epith. injury
- relates to DVT
Rx of hemodynamically stable v-tach? Unstable VT?
- Stable: IV procainamide or IV amiodarone (antiarrhytmics)
- Unstable: Immediate cardioversion
Aortic Dissection
- Diff b/t Type A & B
- How to Rx Type A vs B
- Major RF’s
- Type A: asc. Ao, needs immed. surg.; Type B: desc. Ao could treat medically
- HTN, Ao stenosis, or connective tissue dz (Marfan’s, Ehler-Danlos, etc.)
DEF vasculitis
leukocytes in vessel wall w/ reactive damage to tissues
Possible sign of Fallot on CXR
“boot-shaped heart” due to enlarged RV
Hypoplastic left heart synd
Often secondary to mitral or aortic stenosis/atresia causing lo Q to LV. Inadequate Q = poor growth.
What are symptoms and signs of Ao coarctation?
- Symptom: leg fatigue
- Signs: HTN, lower ext BP>upper ext. BP
What is the char histopath of acute cardiac rejection?
Interstitial lymphocytic infiltrate with focal myocyte degeneration.
x descent
following c wave, relaxed venous pressure/ low return.
Pericard. tamponade
- Def
- Common causes
- Symptoms
- Exam
- Fluid accumulation pericardial space —> poor diastolic filling
- idiopathic, malignancy, hemorrhage and uremia
- Fatigue, shortness of breath
- Exam; hypotension*, tachycardia, pulsus paradoxus (> 10 mmHg drop in systolic BP with inspiration) jugular venous distension (with blunted y descent)*, clear lungs, muffled heart sounds*
What are the major causes of SYS dysfunction (impaired contractility)?
What might you see on gross inspection of heart?
Causes
- CAD –> MI
- Chronic vol overload (mitral or Ao regurg)
- Dilated cardiomyopathies (familial/genetic, viral, EtOH, secondary, pregnancy)
Gross dissection
- Large globoid heart.
- Which vessels most affected in diabetic vasc. dz?
- distal > proximal
what are 2 factors that can increase ejection fraction?
- increase preload (the reason this happens is indirect; due to the Frank-Starling “law”, when ventricular stretch increases, so does the ability of the ventricle to strongly contract; so as preload increases, stretch increases, and EF increases).
EDV and preload are more directly related; in physiolgical terms they are equivalent except in dz states.
- increase inotropy (contractility): could be done vis SNS stim, reduced PNS tone, inotropic drugs.
What is characteristic of “systolic dysfunction”(3) ?
Some dz processes leading to it?
- chronic volume overload
- dilated & hypertropic LV
- Reduced EF at rest (reduced contractility)
- Vol overload in LV: think aortic stenosis, aortic regurg, mitral regurg.
dP = QR. Why is this important? What is the actual physiological dP?
Just says that the diff in pressure is the driving force for the flow.
Derivation of Q = dP/R (Ohm’s law)
dP = Paorta - Pvena cava/central venous pressure
For entire system:
Paorta - Pvena cava/central venous pressure = CO x R
Hemorrhagic pericarditis
- Def
- Usual etiology
- Bloody, fibriounus exudate
- secondary to malignancy
What are the most common etiologies for aortic stenosis for the following age groups?
- 50-60
- 60-70
- >70
- Bicuspid (congenital)
- Rheumatic
- Senile degenerative
By what mechanism do nitrates reduce myocardial O2 demand? What is best way to avoid tolerance?
By decreasing preload through venodilation. At least 8 hours free of dosage / 24h period.
What does chronic LV vol. overload lead to? What is a possible complication?
eccentric hypertrophy; as wall stress increases, leads to CHF
General effects of mitral stenosis?
Buildup of “back pressure” into LA –> Pulmonary system, resulging in pulmonary edema (assoc. w/ dypsnea, caough, exertional dyspnea, etc.)
Define preload; what is relationship b/t preload and CO? How would you clinically approximate preload (technique & theory)?
def: amount of blood the heart receives to distribute to body.
increasing preload –> increase in CO; this has a limit - when vent. wall compliance exceeded, CO decreases dramatically (CHF)
Preload = pressure in LA = PCWP (via Swan-Ganz cath)
Class I Anti-arrhythmic agents
- Channel action
- 1A prototype, used for what?
- 1B used for ? What are the 2 types and how administered?
- Indications & contraindications of 1C? What are the prototype drugs?
- act on Na and K channels
- 1A: Quinidine, used for a-fib.
- 1B: used for vent. tachyarrhythmias; lidocaine (IV), mexiletine (PO)
- 1C: For prevention of a-fib only in pts w/o structural heart dz; contra: BBB w/o pacemaker, structural heart dz. prototypes: propafenone and flecainide
Junctional rhythm
Rhythm coming from atria or AV node, producing a reliable rhythm. Infranodal rhythms (below AV node) = unreliable escape rhythm.
EKG time:
large square =
small square =
large = 5 mm = 0.2 s (200 ms)
small = 1mm = 0.04s (40 ms)
When do the coronary a.s receive most of their flow?
DIA
Rx for pericardial tamp?
Pericardiocentesis
Microscopic changes in ischemic heart dz
- 1st 24 hrs
- 1-2 days
- 5-10 days
- wavy fibers, eosinophilic w/ contraction band necrosis (banding across width of myocytes)
- Polymorphonuclear monocytes (PMNs = neutrophils) attracted to necrosis; edema, hmg, obviously necrotic myocytes.
- Few PMNs; granulation tissue: fibroblasts, LCs + pigment-laden MP’s, w/ abundant neocaps.
Most common etiologies of pericarditis?
- Infectious (viral)
- Immuno (eg rheum fever)
- Misc (rad, uremia, trauma etc)
What does this picture show?

myocard. hypertrophy
General approach to dyslipidemia Rx
- exclude secondary causes
- lifestyle mod (diet, exc)
- adherence (meds, etc)
What are the two types of inotropic drugs most often used? Give prototype of each.
- B-agonist (dolbutamine)
- PDEi: milrinone
Small VSD’s have a ____ murmur; large ones have a _____ murmur
large; small
Torsade de Pointes
Wide complex Vtach w/ hi risk mortality; caused by some AAA’s including Class Ia (quinidine, procainamide), Ic (flecainide, propafenone), III (amiodarone, dofetilide, sotalol)
What are two types of non-infective valvular vegetations?
- Non-bacterial thrombotic endocarditis (NBTE)
- Libman-Sacks endocard (SLE)
EKG signs of a LBBB?
- Lead I: widened R (quite prominent)
- V6: often a notched R

Primary effect of Type I CCBs?
myocardial vasodilation w/ electrophysiological effect of slowing HR
What is area affected in secundum ASD?
fossa ovalis
What two primary factors determine BP? Break those down into their respective contributions.
- Now, explain how hypovol. shock affects those.
- Cardiogenic shock takes place often post-MI. How does this derange above? Why do you see cold, clammy skin?
- Hypotension 2ndary to anaphylaxis or sepsis
BP = CO x PVR
CO = HR x SV
SV is a function of preload, contractility, and afterload.
- Hypovol. shock: decrease in preload –> decreased in SV –> decreased CO –> decreased BP.
- cardiogenic shock results in reduced contractility which in turn reduces SV –> CO –> BP. See cold, clammy skin b/c the body’s compensatory mechanism is to vasoconstrict (to raise BP/perfusion). This has skin effects.
- anaphylaxis or sepsis: these are somewhat unique in that they lead to systemic vasoDILATION resulting in decreased in PVR –> dec. in BP.
What is characterized by valvular dz w/ bulky friable vegetations anywhere on valve?

infective endocarditis
What is the more common location of a cardiac fibroma?
LV > RV
NB: fibromas are 2nd most common pediatric card. tumor (primary).
What is the hallmark EKG sign of an acute MI? Do all acute MI’s have it?
How to Rx STEMI?
ST segment elevation (STEMI). NO - there are also non-ST elevation MI’s (non-STEMI).
Rx: angioplasty if avail. otherwise lytic (latter is not standard of care but more like best option if cath lab not avail.)
Useful/common lab tests/diag. tests for vasculites?
- cANCA
- pANCA
- SED rate (INF marker)
- ANA (SLE)
Ostium primum ASD
- Malformation
- Association w/ what genotype
- An ASD due to endocard. cushion defect, one variation is a large, malformed AV valve.
- assoc. w/ T-21
What kind of murmur is heard w/ VSD?
holoSYS
QRS complex
vent. depolarization dipole
What is the most common heart defect in children? What is the most common subtype?
ASD; secundum most common.
What is the most common combination therapy for Rx’ing angina?
ASA, nitro, b blocker.
def. Ductus arteriosus
fetal circ. shunt (R–>L) from Pulm a. –> Ao, thus shunting flow from the hi resistance pulm. circulation of the fetus.
What is the primary mechanism by which aortic regurg causes dz? Discuss early and late stages of regurgitant dz.
regurg –> chronic LV vol. overload; this causes dilatation of the LV w/ some hypertrophy.
As remodeling continues, the heart progresses to SYS dysfunction. Back pressure also builds up, creating high pressures in the LA and pulmonary vasculature. All of these can lead to LHF.
End dias vol. (EDV)
This is also termed the preload; this is the volume of the ‘comletely filled’ ventricle at the end of DIA. Remember that the ejection fraction = EDV - ESV.
Subclavian Steal Synd
- Which side more common?
- Symptoms
- Signs
- What is the “steal” part about?
- L > R
- Usually asympt.
- Higher BP in unaffected vs. affected arm
- activity of affected side arm –> “stealing” (shunting) of arterial Q from verterbral a.
What is considered a high risk Framigham score and what should you do?
** > 20%** = aggressive risk modification
Possible consequences (2) of carotid athersclerosis?
TIA (from carotid emboli) or stroke
What are the three most important determinants of myocard. O2 consumption in order of importance?
How does this affect Rx of CAD?
HR > load > contractility
This is also the Rx priority - first line is beta blockers whose primary action is to reduce HR.
Def. afterload; what is the hallmark pathology assoc. w/ increased afterload?
Afterload: pressure the LV needs to overcome during SYS = SYS BP; this is essentially the impedance or R.
Hallmark pathology of increased afterload = aortic stenosis
What is the pattern of a Mobitz I 2o AV block (Wenckenbach)?
Normal PR –> prolonged PR –> blocked P wave
NB: a ‘blocked P wave’ means P wave that is not followed by QRS.
What EKG anomaly found in acute chagas dz?
LBBB
Niacin
- aka
- Action
- Evidence
- Vit B3
- Inc. HDL, lower LDL
- Lack of clinical evidence that it works
Supraventricular Tachy
- Def
- Rx’s
- A narrow complex (
- Rx: Type I CCB’s (Type IV AAA) - diltiazem, verapamil.
What does this show?

Fibrinous pericarditis
When reading EKG, remember that the first negative deflection = ?, the first positive = ? and the 2nd neg = ?
Q, R, S
“Diastolic HF” characterized by ?
Chronic pressure overload: results in hypertrophy w/o dilatation. Association w/ normal or “preserved” EF w/ poor relaxation & compliance.
Def’n of a 2o AV block. What is an advanced AV block?
Non-consecutive blocked P waves. advanced AV block is similar but w/ consecutive blocked P waves.
What are some common clinical manif’s of vasculitis?
- Multisys dz
- Skin lesions
- Ischemic vasc. changes
- Weight loss
What combo of drugs (classes, not names) has statistically led to greatest decrease on HF mortality?
ACEi/ARB + B blocker + Aldo blocker


